TRPC Channels: Dysregulation and Ca2+ Mishandling in Ischemic Heart Disease
- PMID: 31936700
- PMCID: PMC7017417
- DOI: 10.3390/cells9010173
TRPC Channels: Dysregulation and Ca2+ Mishandling in Ischemic Heart Disease
Abstract
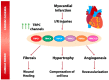
Transient receptor potential canonical (TRPC) channels are ubiquitously expressed in excitable and non-excitable cardiac cells where they sense and respond to a wide variety of physical and chemical stimuli. As other TRP channels, TRPC channels may form homo or heterotetrameric ion channels, and they can associate with other membrane receptors and ion channels to regulate intracellular calcium concentration. Dysfunctions of TRPC channels are involved in many types of cardiovascular diseases. Significant increase in the expression of different TRPC isoforms was observed in different animal models of heart infarcts and in vitro experimental models of ischemia and reperfusion. TRPC channel-mediated increase of the intracellular Ca2+ concentration seems to be required for the activation of the signaling pathway that plays minor roles in the healthy heart, but they are more relevant for cardiac responses to ischemia, such as the activation of different factors of transcription and cardiac hypertrophy, fibrosis, and angiogenesis. In this review, we highlight the current knowledge regarding TRPC implication in different cellular processes related to ischemia and reperfusion and to heart infarction.
Keywords: Ca2+ entry; TRPC channel; cardiac infarction; cardiac repair.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pharmacology of TRPC Channels and Its Potential in Cardiovascular and Metabolic Medicine.Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2022 Jan 6;62:427-446. doi: 10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-030121-122314. Epub 2021 Sep 9. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2022. PMID: 34499525 Review.
-
TRPC Channels in Cardiac Plasticity.Cells. 2020 Feb 17;9(2):454. doi: 10.3390/cells9020454. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32079284 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Muscling in on TRP channels in vascular smooth muscle cells and cardiomyocytes.Cell Calcium. 2017 Sep;66:48-61. doi: 10.1016/j.ceca.2017.06.004. Epub 2017 Jun 15. Cell Calcium. 2017. PMID: 28807149 Review.
-
Transient Receptor Potential Canonical Channel Blockers Improve Ventricular Contractile Functions After Ischemia/Reperfusion in a Langendorff-perfused Mouse Heart Model.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2018 Apr;71(4):248-255. doi: 10.1097/FJC.0000000000000566. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29389740
-
TRP Channels in the Heart.In: Emir TLR, editor. Neurobiology of TRP Channels. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press/Taylor & Francis; 2017. Chapter 9. In: Emir TLR, editor. Neurobiology of TRP Channels. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press/Taylor & Francis; 2017. Chapter 9. PMID: 29356479 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibition of adenylyl cyclase 8 prevents the upregulation of Orai1 channel, which improves cardiac function after myocardial infarction.Mol Ther. 2024 Mar 6;32(3):646-662. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2024.01.026. Epub 2024 Jan 29. Mol Ther. 2024. PMID: 38291755
-
TRPC1 channels underlie stretch-modulated sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium leak in cardiomyocytes.Front Physiol. 2022 Dec 23;13:1056657. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.1056657. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 36620209 Free PMC article.
-
Immunohistochemistry Reveals TRPC Channels in the Human Hearing Organ-A Novel CT-Guided Approach to the Cochlea.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 26;24(11):9290. doi: 10.3390/ijms24119290. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37298241 Free PMC article.
-
The Dysfunction of Ca2+ Channels in Hereditary and Chronic Human Heart Diseases and Experimental Animal Models.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 27;24(21):15682. doi: 10.3390/ijms242115682. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37958665 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Review on the Role of TRP Channels and Their Potential as Drug Targets_An Insight Into the TRP Channel Drug Discovery Methodologies.Front Pharmacol. 2022 May 24;13:914499. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.914499. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35685622 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Rueda A., de Alba-Aguayo D.R., Valdivia H.H. Ryanodine receptor, calcium leak and arrhythmias. Arch. Cardiol. Mex. 2014;84:191–201. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

