Serum circular RNAs act as blood-based biomarkers for hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy
- PMID: 31889077
- PMCID: PMC6937321
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-56617-2
Serum circular RNAs act as blood-based biomarkers for hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy
Abstract
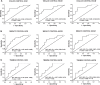
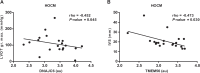
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) is one of the most common hereditary heart diseases and is associated with a high risk of sudden cardiac death. HCM is characterized by pronounced hypertrophy of cardiomyocytes, fiber disarray and development of fibrosis and can be divided into a non-obstructive (HNCM) and obstructive form (HOCM) therefore requiring personalized therapeutic therapies. In the present study, we investigated the expression patterns of several circulating circular RNAs (circRNAs) as potential biomarkers in patients with HCM. We included 64 patients with HCM and 53 healthy controls to the study and quantitatively measured the expression of a set of circRNAs already known to be associated with cardiac diseases (circDNAJC6) and/or being highly abundant in blood (circTMEM56 and circMBOAT2). Abundancy of circRNAs was then correlated to relevant clinical parameters. Serum expression levels of circRNAs DNAJC6, TMEM56 and MBOAT2 were downregulated in patients with HCM. The inverse association between circRNA levels and HCM remained unchanged even after adjusting for confounding factors. All circRNAs, evaluated separately or in combination, showed a robust discrimination capacity when comparing control subjects with HCM, HNCM or HOCM patients (AUC from 0.722 to 0.949). Two circRNAs, circTMEM56 and circDNAJC6, significantly negatively correlated with echocardiographic parameters for HOCM. Collectively, circulating circRNAs DNAJC6, TMEM56 and MBOAT2 can distinguish between healthy and HCM patients. In addition, circTMEM56 and circDNAJC6 could serve as indicators of disease severity in patients with HOCM. Thus, circRNAs emerge as novel biomarkers for HCM facilitating the clinical decision making in a personalized manner.
Conflict of interest statement
T.T. has filed patents in the field of non-coding RNAs and is founder and holds shares of Cardior Pharmaceuticals GmbH. D.d.G.C. have licensed a patent on microRNAs as biomarkers. Other authors have no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Blood-based protein profiling identifies serum protein c-KIT as a novel biomarker for hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.Sci Rep. 2021 Jan 19;11(1):1755. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-80868-z. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33469076 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial long noncoding RNAs as blood based biomarkers for cardiac remodeling in patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2016 Sep 1;311(3):H707-12. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00194.2016. Epub 2016 Jul 15. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27422984
-
Identifying Obstructive Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy from Nonobstructive Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy: Development and Validation of a Model Based on Electrocardiogram Features.Glob Heart. 2023 Aug 4;18(1):40. doi: 10.5334/gh.1250. eCollection 2023. Glob Heart. 2023. PMID: 37547171 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs as Biomarkers in Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy: Current State of the Art.Curr Med Chem. 2021;28(36):7400-7412. doi: 10.2174/0929867328666210405122703. Curr Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 33820510 Review.
-
The diagnosis and treatment of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2011 Apr;108(13):209-15. doi: 10.3238/arztebl.2011.0209. Epub 2011 Apr 1. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2011. PMID: 21505608 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Circulating Cell-Free Nucleic Acids: Main Characteristics and Clinical Application.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Sep 17;21(18):6827. doi: 10.3390/ijms21186827. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32957662 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circular RNAs and glioblastoma multiforme: focus on molecular mechanisms.Cell Commun Signal. 2022 Jan 28;20(1):13. doi: 10.1186/s12964-021-00809-9. Cell Commun Signal. 2022. PMID: 35090496 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Knockdown of circ_0060745 alleviates acute myocardial infarction by suppressing NF-κB activation.J Cell Mol Med. 2020 Nov;24(21):12401-12410. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.15748. Epub 2020 Sep 25. J Cell Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 32977365 Free PMC article.
-
Circular RNAs in Cardiovascular Diseases: Regulation and Therapeutic Applications.Research (Wash D C). 2023;6:0038. doi: 10.34133/research.0038. Epub 2023 Jan 13. Research (Wash D C). 2023. PMID: 37040523 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Blood-based protein profiling identifies serum protein c-KIT as a novel biomarker for hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.Sci Rep. 2021 Jan 19;11(1):1755. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-80868-z. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33469076 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Authors/Task Force members. Elliott PM, et al. ESC Guidelines on diagnosis and management of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: the Task Force for the Diagnosis and Management of Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Eur Heart J. 2014;2014(35):2733–2779. - PubMed

