Promoter Methylation Status of the Retinoic Acid Receptor-Beta 2 Gene in Breast Cancer Patients: A Case Control Study and Systematic Review
- PMID: 31798384
- PMCID: PMC6886150
- DOI: 10.1159/000489874
Promoter Methylation Status of the Retinoic Acid Receptor-Beta 2 Gene in Breast Cancer Patients: A Case Control Study and Systematic Review
Abstract
Background: We aimed to determine the promoter methylation status of the retinoic acid receptor-beta 2 (RARβ2) gene among breast cancer patients and to review relevant studies in this field in various populations.
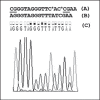
Methods: We analyzed 400 samples which comprised blood specimens from 102 breast cancer patients, 102 first-degree female relatives of patients, 100 cancer-free females, 48 breast cancer tissues, and 48 adjacent normal breast tissues from the same patients. The RARβ2 methylation status was determined using methylation-specific polymerase chain reaction (MSP) and DNA sequencing methods.
Results: The presence of combined partially methylated (MU) and fully methylated (MM) forms of the RARβ2 gene (MU+MM) in the blood of patients was associated with susceptibility to breast cancer (odds ratio = 4.7, p = 0.05). A significantly higher frequency of the MM genotype was observed in cancer tissue (10.4%) compared to matched adjacent normal breast tissue (0%) (p = 0.02).
Conclusion: We found a higher frequency of RARβ2 gene methylation in the blood and cancer tissues of patients compared to the blood of controls and adjacent normal breast tissues. The survey of studies on various populations demonstrated a higher RARβ2 methylation frequency in breast cancer patients compared to normal individuals, and many reports suggest a significant association between hypermethylation of the gene and susceptibility to breast cancer.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Epigenetic; Hypermethylation; Iranian population; MSP; RARβ2.
Copyright © 2019 by S. Karger AG, Basel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no potential or actual conflicts of interest in relation to the current article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Promoter Methylation of the Retinoic Acid Receptor Beta2 (RARβ2) Is Associated with Increased Risk of Breast Cancer: A PRISMA Compliant Meta-Analysis.PLoS One. 2015 Oct 9;10(10):e0140329. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0140329. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26451736 Free PMC article.
-
[DNA methylation status of RARβ2 and p16(INK4α) in peripheral blood and tumor tissue in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma].Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2012 Jun;34(6):441-5. doi: 10. 3760/cma.j.issn.0253-3766.2012.06.009. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2012. PMID: 22967446 Chinese.
-
Quantitative promoter hypermethylation analysis of cancer-related genes in salivary gland carcinomas: comparison with methylation-specific PCR technique and clinical significance.Clin Cancer Res. 2008 May 1;14(9):2664-72. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-1232. Clin Cancer Res. 2008. PMID: 18451230
-
Promoter hypermethylation of RARβ2, DAPK, hMLH1, p14, and p15 is associated with progression of breast cancer: A PRISMA-compliant meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2018 Dec;97(51):e13666. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000013666. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018. PMID: 30572486 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The association of retinoic acid receptor beta2(RARβ2) methylation status and prostate cancer risk: a systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2013 May 13;8(5):e62950. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0062950. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23675444 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
High-Resolution Melting (HRM) analysis of DNA methylation using semiconductor chip-based digital PCR.Genes Genomics. 2024 Aug;46(8):909-915. doi: 10.1007/s13258-024-01527-5. Epub 2024 Jun 8. Genes Genomics. 2024. PMID: 38849705
-
Impact of DNA methylation of the human mesoderm-specific transcript (MEST) on male infertility.Heliyon. 2023 Oct 16;9(10):e21099. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e21099. eCollection 2023 Oct. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37928396 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic Regulation in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Microenvironment: A Comprehensive Review.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Nov 27;15(23):5600. doi: 10.3390/cancers15235600. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38067304 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HOPX Is an Epigenetically Inactivated Tumor Suppressor and Overexpression of HOPX Induce Apoptosis and Cell Cycle Arrest in Breast Cancer.Onco Targets Ther. 2020 Jun 23;13:5955-5965. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S250404. eCollection 2020. Onco Targets Ther. 2020. PMID: 32606804 Free PMC article.
-
Methylation Status of cAMP-responsive Element Modulator (CREM) Gene in Infertile Men and Its Association with Sperm Parameters.Reprod Sci. 2024 Jul;31(7):2001-2008. doi: 10.1007/s43032-024-01510-1. Epub 2024 Mar 18. Reprod Sci. 2024. PMID: 38499948
References
-
- Rahimi Z, Yari K, Rahimi Z. Matrix metalloproteinase-9-1562T allele and its combination with MMP-2-735 C allele are risk factors for breast cancer. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2014;16:1175–1179. - PubMed
-
- Pirouzpanah S, Taleban F-A, Mehdipour P, Atri M. Association of folate and other one-carbon related nutrients with hypermethylation status and expression of RARB, BRCA1, and RASSF1A genes in breast cancer patients. J Mol Med (Berl) 2015;93:917–934. - PubMed
-
- Yari K, Payandeh M, Rahimi Z. Association of the hypermethylation status of PTEN tumor suppressor gene with the risk of breast cancer among Kurdish population from Western Iran. Tumour Biol. 2016;37:8145–8152. - PubMed
-
- Marzese DM, Hoon DS, Chong KK, et al. DNA methylation index and methylation profile of invasive ductal breast tumors. J Mol Diagn. 2012;14:613–622. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

