Protein tyrosine kinase 2: a novel therapeutic target to overcome acquired EGFR-TKI resistance in non-small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 31791326
- PMCID: PMC6889213
- DOI: 10.1186/s12931-019-1244-2
Protein tyrosine kinase 2: a novel therapeutic target to overcome acquired EGFR-TKI resistance in non-small cell lung cancer
Abstract
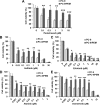
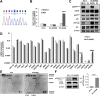
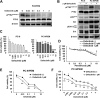
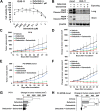
Background: Protein tyrosine kinase 2 (PTK2) expression has been reported in various types of human epithelial cancers including lung cancer; however, the role of PTK2 in epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-mutant non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) has not been elucidated. We previously reported that pemetrexed-resistant NSCLC cell line PC-9/PEM also acquired EGFR-TKI resistance with constitutive Akt activation, but we could not find a therapeutic target.
Methods: Cell viability in EGFR-mutant NSCLC cell lines was measured by the WST-8 assay. Phosphorylation antibody array assay for receptor tyrosine kinases was performed in PC-9 and PC-9/PEM cell lines. We evaluated the efficacy of EGFR and PTK2 co-inhibition in EGFR-TKI-resistant NSCLC in vitro. Oral defactinib and osimertinib were administered in mice bearing subcutaneous xenografts to evaluate the efficacy of the treatment combination in vivo. Both the PTK2 phosphorylation and the treatment combination efficacy were evaluated in erlotinib-resistant EGFR-mutant NSCLC cell lines.
Results: PTK2 was hyperphosphorylated in PC-9/PEM. Defactinib (PTK2 inhibitor) and PD173074 (FGFR inhibitor) inhibited PTK2 phosphorylation. Combination of PTK2 inhibitor and EGFR-TKI inhibited Akt and induced apoptosis in PC-9/PEM. The combination treatment showed improved in vivo therapeutic efficacy compared to the single-agent treatments. Furthermore, erlotinib-resistant NSCLC cell lines showed PTK2 hyperphosphorylation. PTK2 inhibition in the PTK2 hyperphosphorylated erlotinib-resistant cell lines also recovered EGFR-TKI sensitivity.
Conclusion: PTK2 hyperphosphorylation occurs in various EGFR-TKI-resistant NSCLCs. Combination of PTK2 inhibitor and EGFR-TKI (defactinib and osimertinib) recovered EGFR-TKI sensitivity in the EGFR-TKI-resistant NSCLC. Our study result suggests that this combination therapy may be a viable option to overcome EGFR-TKI resistance in NSCLC.
Keywords: Combined inhibition; Drug resistance; EGFR; PTK2; Tyrosine kinase inhibitor.
Conflict of interest statement
Takeshi Isobe reports personal fees from AstraZeneca, personal fees from Pfizer, personal fees from Boehringer Ingelheim, outside the submitted work. Yukari Tsubata reports personal fees from AstraZeneca, personal fees from Daiichi Sankyo, outside the submitted work. Ryosuke Tanino reports grants from Nippon Boehringer Ingelheim, outside the submitted work. The remaining authors declare no competing interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Chloroquine in combination with aptamer-modified nanocomplexes for tumor vessel normalization and efficient erlotinib/Survivin shRNA co-delivery to overcome drug resistance in EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer.Acta Biomater. 2018 Aug;76:257-274. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2018.06.034. Epub 2018 Jun 28. Acta Biomater. 2018. PMID: 29960010
-
Inhibition of histone deacetylases sensitizes EGF receptor-TK inhibitor-resistant non-small-cell lung cancer cells to erlotinib in vitro and in vivo.Br J Pharmacol. 2017 Oct;174(20):3608-3622. doi: 10.1111/bph.13961. Epub 2017 Aug 24. Br J Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28749535 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of JAK1/2 can overcome EGFR-TKI resistance in human NSCLC.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020 Jun 18;527(1):305-310. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.04.095. Epub 2020 May 11. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020. PMID: 32446385
-
Strategies to overcome acquired resistance to EGFR TKI in the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer.Clin Transl Oncol. 2019 Oct;21(10):1287-1301. doi: 10.1007/s12094-019-02075-1. Epub 2019 Mar 12. Clin Transl Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30864018 Review.
-
Nanomodified strategies to overcome EGFR-tyrosine kinase inhibitors resistance in non-small cell lung cancer.J Control Release. 2020 Aug 10;324:482-492. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.05.043. Epub 2020 Jun 1. J Control Release. 2020. PMID: 32497570 Review.
Cited by
-
Phosphoproteomic Analysis Identified Mutual Phosphorylation of FAK and Src as a Mechanism of Osimertinib Resistance in EGFR-Mutant Lung Cancer.JTO Clin Res Rep. 2024 Mar 21;5(4):100668. doi: 10.1016/j.jtocrr.2024.100668. eCollection 2024 Apr. JTO Clin Res Rep. 2024. PMID: 38646155 Free PMC article.
-
DLX1 acts as a novel prognostic biomarker involved in immune cell infiltration and tumor progression in lung adenocarcinoma.PeerJ. 2024 Feb 2;12:e16823. doi: 10.7717/peerj.16823. eCollection 2024. PeerJ. 2024. PMID: 38317839 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Resistance Mechanisms to Osimertinib Analysed by Whole-Exome Sequencing in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.Cancer Manag Res. 2021 Feb 25;13:2025-2032. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S292342. eCollection 2021. Cancer Manag Res. 2021. PMID: 33658860 Free PMC article.
-
ptk2 and mt2a Genes Expression in Gastritis and Gastric Cancer Patients with Helicobacter pylori Infection.Can J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022 Aug 25;2022:8699408. doi: 10.1155/2022/8699408. eCollection 2022. Can J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022. PMID: 36060520 Free PMC article.
-
Gene selection using pyramid gravitational search algorithm.PLoS One. 2022 Mar 15;17(3):e0265351. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0265351. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35290401 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wu Y-L, Zhou C, Hu C-P, Feng J, Lu S, Huang Y, et al. Afatinib versus cisplatin plus gemcitabine for first-line treatment of Asian patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer harbouring EGFR mutations (LUX-Lung 6): an open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2014;15:213–222. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(13)70604-1. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Inoue A, Suzuki T, Fukuhara T, Maemondo M, Kimura Y, Morikawa N, et al. Prospective phase II study of gefitinib for chemotherapy-naïve patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer with epidermal growth factor receptor gene mutations. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24:3340–3346. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2005.05.4692. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

