Improved metagenomic analysis with Kraken 2
- PMID: 31779668
- PMCID: PMC6883579
- DOI: 10.1186/s13059-019-1891-0
Improved metagenomic analysis with Kraken 2
Abstract
Although Kraken's k-mer-based approach provides a fast taxonomic classification of metagenomic sequence data, its large memory requirements can be limiting for some applications. Kraken 2 improves upon Kraken 1 by reducing memory usage by 85%, allowing greater amounts of reference genomic data to be used, while maintaining high accuracy and increasing speed fivefold. Kraken 2 also introduces a translated search mode, providing increased sensitivity in viral metagenomics analysis.
Keywords: Alignment-free methods; Metagenomics; Metagenomics classification; Microbiome; Minimizers; Probabilistic data structures.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
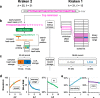
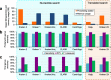
Similar articles
-
Kraken: ultrafast metagenomic sequence classification using exact alignments.Genome Biol. 2014 Mar 3;15(3):R46. doi: 10.1186/gb-2014-15-3-r46. Genome Biol. 2014. PMID: 24580807 Free PMC article.
-
Studying long 16S rDNA sequences with ultrafast-metagenomic sequence classification using exact alignments (Kraken).J Microbiol Methods. 2016 Mar;122:38-42. doi: 10.1016/j.mimet.2016.01.011. Epub 2016 Jan 23. J Microbiol Methods. 2016. PMID: 26812576
-
KrakenUniq: confident and fast metagenomics classification using unique k-mer counts.Genome Biol. 2018 Nov 16;19(1):198. doi: 10.1186/s13059-018-1568-0. Genome Biol. 2018. PMID: 30445993 Free PMC article.
-
Scalable metagenomics alignment research tool (SMART): a scalable, rapid, and complete search heuristic for the classification of metagenomic sequences from complex sequence populations.BMC Bioinformatics. 2016 Jul 28;17:292. doi: 10.1186/s12859-016-1159-6. BMC Bioinformatics. 2016. PMID: 27465705 Free PMC article.
-
When less is more: sketching with minimizers in genomics.Genome Biol. 2024 Oct 14;25(1):270. doi: 10.1186/s13059-024-03414-4. Genome Biol. 2024. PMID: 39402664 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Assessment and Monitoring of the Wound Micro-Environment in Chronic Wounds Using Standardized Wound Swabbing for Individualized Diagnostics and Targeted Interventions.Biomedicines. 2024 Sep 26;12(10):2187. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12102187. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39457500 Free PMC article.
-
The need for high-resolution gut microbiome characterization to design efficient strategies for sustainable aquaculture production.Commun Biol. 2024 Oct 25;7(1):1391. doi: 10.1038/s42003-024-07087-4. Commun Biol. 2024. PMID: 39455736 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Based Targeted Sequencing as a Reproducible Microbial Community Profiling Assay.mSphere. 2021 Apr 7;6(2):e01325-20. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.01325-20. mSphere. 2021. PMID: 33827913 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated characterization of SARS-CoV-2 genome, microbiome, antibiotic resistance and host response from single throat swabs.Cell Discov. 2021 Mar 30;7(1):19. doi: 10.1038/s41421-021-00248-3. Cell Discov. 2021. PMID: 33785729 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Genomic Analysis of Antimicrobial-Resistant Escherichia coli from South American Camelids in Central Germany.Microorganisms. 2022 Aug 24;10(9):1697. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10091697. Microorganisms. 2022. PMID: 36144308 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

