Galectin-1-driven T cell exclusion in the tumor endothelium promotes immunotherapy resistance
- PMID: 31710313
- PMCID: PMC6877340
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI129025
Galectin-1-driven T cell exclusion in the tumor endothelium promotes immunotherapy resistance
Abstract
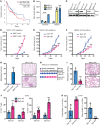
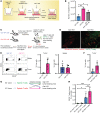
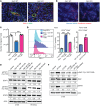
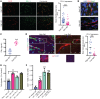
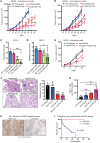
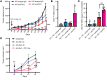
Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs), although promising, have variable benefit in head and neck cancer (HNC). We noted that tumor galectin-1 (Gal1) levels were inversely correlated with treatment response and survival in patients with HNC who were treated with ICIs. Using multiple HNC mouse models, we show that tumor-secreted Gal1 mediates immune evasion by preventing T cell migration into the tumor. Mechanistically, Gal1 reprograms the tumor endothelium to upregulate cell-surface programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1) and galectin-9. Using genetic and pharmacological approaches, we show that Gal1 blockade increases intratumoral T cell infiltration, leading to a better response to anti-PD1 therapy with or without radiotherapy. Our study reveals the function of Gal1 in transforming the tumor endothelium into an immune-suppressive barrier and that its inhibition synergizes with ICIs.
Keywords: Head and neck cancer; Immunotherapy; Oncology; Radiation therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Comment in
-
Cancer immunotherapy needs to learn how to stick to its guns.J Clin Invest. 2019 Dec 2;129(12):5089-5091. doi: 10.1172/JCI133415. J Clin Invest. 2019. PMID: 31710312 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Prognostic role of programmed cell death ligand-1 expression in head and neck cancer treated with programmed cell death protein-1/programmed cell death ligand-1 inhibitors: A meta-analysis based on clinical trials.J Cancer Res Ther. 2021 Jul;17(3):676-687. doi: 10.4103/jcrt.JCRT_1606_20. J Cancer Res Ther. 2021. PMID: 34269299
-
Tumor hypoxia is associated with resistance to PD-1 blockade in squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck.J Immunother Cancer. 2021 May;9(5):e002088. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2020-002088. J Immunother Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33986123 Free PMC article.
-
Immunotherapy and Checkpoint Inhibitors in Recurrent and Metastatic Head and Neck Cancer.Am Soc Clin Oncol Educ Book. 2016;35:e277-82. doi: 10.14694/EDBK_157801. Am Soc Clin Oncol Educ Book. 2016. PMID: 27249733 Review.
-
Combination PD-1 and PD-L1 Blockade Promotes Durable Neoantigen-Specific T Cell-Mediated Immunity in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma.Cell Rep. 2019 Aug 20;28(8):2140-2155.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.07.059. Cell Rep. 2019. PMID: 31433988 Free PMC article.
-
The Evolving Landscape of PD-1/PD-L1 Pathway in Head and Neck Cancer.Front Immunol. 2020 Sep 18;11:1721. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01721. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33072064 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Plasma galectins and metabolites in advanced head and neck carcinomas: evidence of distinct immune characteristics linked to hypopharyngeal tumors.Oncoimmunology. 2022 Dec 17;12(1):2150472. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2022.2150472. eCollection 2023. Oncoimmunology. 2022. PMID: 36545254 Free PMC article.
-
Integrative analysis of non-small cell lung cancer patient-derived xenografts identifies distinct proteotypes associated with patient outcomes.Nat Commun. 2022 Apr 5;13(1):1811. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-29444-9. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 35383171 Free PMC article.
-
Vaccination against galectin-1 promotes cytotoxic T-cell infiltration in melanoma and reduces tumor burden.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2022 Aug;71(8):2029-2040. doi: 10.1007/s00262-021-03139-4. Epub 2022 Jan 11. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2022. PMID: 35018481 Free PMC article.
-
Galectins in Endothelial Cell Biology and Angiogenesis: The Basics.Biomolecules. 2021 Sep 20;11(9):1386. doi: 10.3390/biom11091386. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 34572599 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Blood Vessel-Targeted Therapy in Colorectal Cancer: Current Strategies and Future Perspectives.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Feb 22;16(5):890. doi: 10.3390/cancers16050890. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38473252 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

