Dasatinib Inhibits Procoagulant and Clot Retracting Activities of Human Platelets
- PMID: 31683623
- PMCID: PMC6862041
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms20215430
Dasatinib Inhibits Procoagulant and Clot Retracting Activities of Human Platelets
Abstract
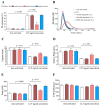
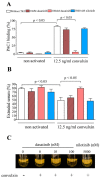
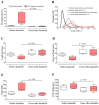
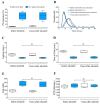
Tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKI) such as the BCR-ABL inhibitor dasatinib and nilotinib are highly effective therapies for chronic myeloid leukemia (CML). However, several lines of evidence suggest that dasatinib can induce bleeding which may be due to impaired collagen-induced platelet adhesion, aggregation, and secretion. Sarcoma family kinases (SFK) play central role in the GPVI-induced signaling pathway. We aimed to investigate whether and how dasatinib can modulate SFK-mediated platelet procoagulant activity in a purified system and in dasatinib/nilotinib treated CML patients. In platelet rich plasmas of healthy volunteers, dasatinib dose-dependently reduced convulxin-induced phosphatidylserine exposure and attenuated thrombin formation. Similarly to these changes, integrin activation and clot retraction were also significantly inhibited by 100 nM dasatinib. Platelets isolated from dasatinib treated patients showed a significantly lower phosphatidylserine expression upon convulxin activation compared to premedication levels. In these samples, thrombin generation was significantly slower, and the quantity of formed thrombin was less compared to the trough sample. Western blot analyses showed decreased phosphorylation levels of the C-terminal tail and the activation loop of SFKs upon dasatinib administration. Taken together, these results suggest that dasatinib inhibits the formation of procoagulant platelets via the GPVI receptor by inhibiting phosphorylation of SFKs.
Keywords: bleeding; dasatinib therapy; glycoprotein VI; platelet activation; thrombin formation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors state that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Varying effects of tyrosine kinase inhibitors on platelet function-A need for individualized CML treatment to minimize the risk for hemostatic and thrombotic complications?Cancer Med. 2020 Jan;9(1):313-323. doi: 10.1002/cam4.2687. Epub 2019 Nov 12. Cancer Med. 2020. PMID: 31714021 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of dasatinib on SRC kinase activity and downstream intracellular signaling in primitive chronic myelogenous leukemia hematopoietic cells.Cancer Res. 2008 Dec 1;68(23):9624-33. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-1131. Cancer Res. 2008. PMID: 19047139 Free PMC article.
-
Platelet activation via the collagen receptor GPVI is not altered in platelets from chronic myeloid leukaemia patients despite the presence of the constitutively phosphorylated adapter protein CrkL.Br J Haematol. 2001 Mar;112(3):609-15. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2141.2001.02624.x. Br J Haematol. 2001. PMID: 11260061
-
Dasatinib: a tyrosine kinase inhibitor for the treatment of chronic myelogenous leukemia and philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia.Clin Ther. 2007 Nov;29(11):2289-308. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2007.11.005. Clin Ther. 2007. PMID: 18158072 Review.
-
Important therapeutic targets in chronic myelogenous leukemia.Clin Cancer Res. 2007 Feb 15;13(4):1089-97. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-2147. Clin Cancer Res. 2007. PMID: 17317816 Review.
Cited by
-
Functional roles of SRC signaling in pancreatic cancer: Recent insights provide novel therapeutic opportunities.Oncogene. 2023 Jun;42(22):1786-1801. doi: 10.1038/s41388-023-02701-x. Epub 2023 Apr 29. Oncogene. 2023. PMID: 37120696 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clot Retraction: Cellular Mechanisms and Inhibitors, Measuring Methods, and Clinical Implications.Biomedicines. 2021 Aug 21;9(8):1064. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9081064. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 34440268 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exosomal microRNAs from Mesenchymal Stem Cells: Novel Therapeutic Effect in Wound Healing.Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2023 Aug;20(5):647-660. doi: 10.1007/s13770-023-00542-z. Epub 2023 May 2. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2023. PMID: 37131016 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Systemic Review of Clot Retraction Modulators.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 25;24(13):10602. doi: 10.3390/ijms241310602. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37445780 Free PMC article.
-
Bioengineered mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes: emerging strategies for diabetic wound healing.Burns Trauma. 2024 Jul 16;12:tkae030. doi: 10.1093/burnst/tkae030. eCollection 2024. Burns Trauma. 2024. PMID: 39015252 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

