T Regulatory Cells and Priming the Suppressive Tumor Microenvironment
- PMID: 31681327
- PMCID: PMC6803384
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02453
T Regulatory Cells and Priming the Suppressive Tumor Microenvironment
Abstract
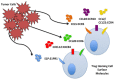
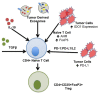
Treg play a central role in maintenance of self tolerance and homeostasis through suppression of self-reactive T cell populations. In addition to that role, Treg also survey cancers and suppress anti-tumor immune responses. Thus, understanding the unique attributes of Treg-tumor interactions may permit control of this pathologic suppression without interfering with homeostatic self-tolerance. This review will define the unique role of Treg in cancer growth, and the ways by which Treg inhibit a robust anti-tumor immune response. There will be specific focus placed on Treg homing to the tumor microenvironment (TME), TME formation of induced Treg (iTreg), mechanisms of suppression that underpin cancer immune escape, and trophic nonimmunologic effects of Treg on tumor cells.
Keywords: Treg; anti-tumor immunity; immunosuppression; metastasis; tumor microenvironment.
Copyright © 2019 Paluskievicz, Cao, Abdi, Zheng, Liu and Bromberg.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Tumor microenvironment dictates regulatory T cell phenotype: Upregulated immune checkpoints reinforce suppressive function.J Immunother Cancer. 2019 Dec 4;7(1):339. doi: 10.1186/s40425-019-0785-8. J Immunother Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31801611 Free PMC article.
-
Remodeling of the tumor microenvironment via disrupting Blimp1+ effector Treg activity augments response to anti-PD-1 blockade.Mol Cancer. 2021 Nov 20;20(1):150. doi: 10.1186/s12943-021-01450-3. Mol Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34798898 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic profiles of regulatory T cells in the tumour microenvironment.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2021 Sep;70(9):2417-2427. doi: 10.1007/s00262-021-02881-z. Epub 2021 Feb 12. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2021. PMID: 33576875 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unlocking the Complexities of Tumor-Associated Regulatory T Cells.J Immunol. 2018 Jan 15;200(2):415-421. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1701188. J Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29311383 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The PD-1 expression balance between effector and regulatory T cells predicts the clinical efficacy of PD-1 blockade therapies.Nat Immunol. 2020 Nov;21(11):1346-1358. doi: 10.1038/s41590-020-0769-3. Epub 2020 Aug 31. Nat Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32868929
Cited by
-
Impact of histamine H4 receptor deficiency on the modulation of T cells in a murine breast cancer model.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2021 Jan;70(1):233-244. doi: 10.1007/s00262-020-02672-y. Epub 2020 Jul 22. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2021. PMID: 32700092 Free PMC article.
-
cAMP-PKA/EPAC signaling and cancer: the interplay in tumor microenvironment.J Hematol Oncol. 2024 Jan 17;17(1):5. doi: 10.1186/s13045-024-01524-x. J Hematol Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38233872 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunotherapy in Ovarian Cancer: Thinking Beyond PD-1/PD-L1.Front Oncol. 2021 Dec 13;11:795547. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.795547. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34966689 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lrig1-expression confers suppressive function to CD4+ cells and is essential for averting autoimmunity via the Smad2/3/Foxp3 axis.Nat Commun. 2023 Sep 4;14(1):5382. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-40986-4. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37666819 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor Microenvironment Mediators CD8+- and FOXP3+-Labeled T Lymphocytes Are Prospective Prognosticators in Curatively Treated Rectal Cancer Patients.J Gastrointest Cancer. 2021 Mar;52(1):177-186. doi: 10.1007/s12029-020-00376-1. J Gastrointest Cancer. 2021. PMID: 32112202
References
-
- Thornton AM, Korty PE, Tran DQ, Wohlfert EA, Murray PE, Belkaid Y, et al. . Expression of Helios, an Ikaros transcription factor family member, differentiates thymic-derived from peripherally induced Foxp3 + T regulatory cells. J Immunol. (2010) 184:3433–41. 10.4049/jimmunol.0904028 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

