Distinct roles of PIK3CA in the enrichment and maintenance of cancer stem cells in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 31600013
- PMCID: PMC6944113
- DOI: 10.1002/1878-0261.12584
Distinct roles of PIK3CA in the enrichment and maintenance of cancer stem cells in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
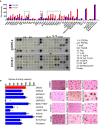
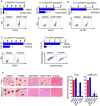
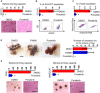
Recurrence and metastasis are the major causes of mortality in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC). It is suggested that cancer stem cells (CSCs) play pivotal roles in recurrence and metastasis. Thus, a greater understanding of the mechanisms of CSC regulation may provide opportunities to develop novel therapies for improving survival by controlling recurrence or metastasis. Here, we report that overexpression of the gene encoding the catalytic subunit of PI3K (PIK3CA), the most frequently amplified oncogene in HNSCC, promotes epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and enriches the CSC population. However, PIK3CA is not required to maintain these traits and inhibition of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) signaling pathway paradoxically promotes CSC population. Molecular analysis revealed that overexpression of PIK3CA activates multiple receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs), in which ephrin receptors (Ephs), tropomyosin receptor kinases (TRK) and mast/stem cell growth factor receptor (c-Kit) contribute to maintain CSC population. Accordingly, simultaneous inhibition of these RTKs using a multi-kinase inhibitor ponatinib has a superior effect at eliminating the CSC population and reduces metastasis of PIK3CA-overexpressing HNSCC cells. Our result suggests that co-targeting of Ephs, TRKs and the c-Kit pathway may be effective at eliminating the PI3K-independent CSC population, thereby providing potential targets for future development of a novel anti-CSC therapeutic approach for HNSCC patients, particularly for patients with PIK3CA amplification.
Keywords: PIK3CA; cancer stem cell; head and neck squamous cell carcinoma; ponatinib; recurrence and metastasis.
© 2019 The Authors. Published by FEBS Press and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
CSC-3436 inhibits TWIST-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition via the suppression of Twist/Bmi1/Akt pathway in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.J Cell Physiol. 2019 Jun;234(6):9118-9129. doi: 10.1002/jcp.27589. Epub 2018 Oct 20. J Cell Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30341909
-
Overexpression of PIK3CA in murine head and neck epithelium drives tumor invasion and metastasis through PDK1 and enhanced TGFβ signaling.Oncogene. 2016 Sep 1;35(35):4641-52. doi: 10.1038/onc.2016.1. Epub 2016 Feb 15. Oncogene. 2016. PMID: 26876212 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of c-Fos in the Promotion of Cancer Stem-like Cell Properties in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Clin Cancer Res. 2017 Jun 15;23(12):3120-3128. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-16-2811. Epub 2016 Dec 13. Clin Cancer Res. 2017. PMID: 27965308 Free PMC article.
-
The PI3K/Akt/mTORC signaling axis in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: Possibilities for therapeutic interventions either as single agents or in combination with conventional therapies.IUBMB Life. 2021 Apr;73(4):618-642. doi: 10.1002/iub.2446. Epub 2021 Feb 4. IUBMB Life. 2021. PMID: 33476088 Review.
-
Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and cancer stem(-like) cells in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Cancer Lett. 2013 Sep 10;338(1):47-56. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2012.06.013. Epub 2012 Jul 4. Cancer Lett. 2013. PMID: 22771535 Review.
Cited by
-
Circ-ZEB1 promotes PIK3CA expression by silencing miR-199a-3p and affects the proliferation and apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma.Mol Cancer. 2022 Mar 11;21(1):72. doi: 10.1186/s12943-022-01529-5. Mol Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35277182 Free PMC article.
-
Combined PIK3CA and SOX2 Gene Amplification Predicts Laryngeal Cancer Risk beyond Histopathological Grading.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Feb 26;25(5):2695. doi: 10.3390/ijms25052695. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38473941 Free PMC article.
-
NTRK Fusions and TRK Inhibitors: Potential Targeted Therapies for Adult Glioblastoma.Front Oncol. 2020 Nov 30;10:593578. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.593578. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 33330081 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Systemic immune responses are associated with molecular characteristics of circulating tumor cells in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Mol Clin Oncol. 2021 Jul;15(1):147. doi: 10.3892/mco.2021.2309. Epub 2021 May 26. Mol Clin Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34094545 Free PMC article.
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor signaling in precancerous keratinocytes promotes neighboring head and neck cancer squamous cell carcinoma cancer stem cell-like properties and phosphoinositide 3-kinase inhibitor insensitivity.Mol Carcinog. 2022 Jul;61(7):664-676. doi: 10.1002/mc.23409. Epub 2022 Apr 13. Mol Carcinog. 2022. PMID: 35417043 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Batlle E and Clevers H (2017) Cancer stem cells revisited. Nat Med 23, 1124–1134. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

