ACE2 and ADAM17 Interaction Regulates the Activity of Presympathetic Neurons
- PMID: 31564162
- PMCID: PMC6785402
- DOI: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.119.13133
ACE2 and ADAM17 Interaction Regulates the Activity of Presympathetic Neurons
Abstract
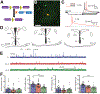
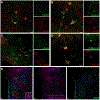
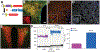
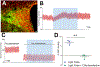
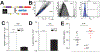
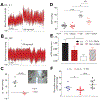
Brain renin angiotensin system within the paraventricular nucleus plays a critical role in balancing excitatory and inhibitory inputs to modulate sympathetic output and blood pressure regulation. We previously identified ACE2 and ADAM17 as a compensatory enzyme and a sheddase, respectively, involved in brain renin angiotensin system regulation. Here, we investigated the opposing contribution of ACE2 and ADAM17 to hypothalamic presympathetic activity and ultimately neurogenic hypertension. New mouse models were generated where ACE2 and ADAM17 were selectively knocked down from all neurons (AC-N) or Sim1 neurons (SAT), respectively. Neuronal ACE2 deletion revealed a reduction of inhibitory inputs to AC-N presympathetic neurons relevant to blood pressure regulation. Primary neuron cultures confirmed ACE2 expression on GABAergic neurons synapsing onto excitatory neurons within the hypothalamus but not on glutamatergic neurons. ADAM17 expression was shown to colocalize with angiotensin-II type 1 receptors on Sim1 neurons, and the pressor relevance of this neuronal population was demonstrated by photoactivation. Selective knockdown of ADAM17 was associated with a reduction of FosB gene expression, increased vagal tone, and prevented the acute pressor response to centrally administered angiotensin-II. Chronically, SAT mice exhibited a blunted blood pressure elevation and preserved ACE2 activity during development of salt-sensitive hypertension. Bicuculline injection in those models confirmed the supporting role of ACE2 on GABAergic tone to the paraventricular nucleus. Together, our study demonstrates the contrasting impact of ACE2 and ADAM17 on neuronal excitability of presympathetic neurons within the paraventricular nucleus and the consequences of this mutual regulation in the context of neurogenic hypertension.
Keywords: autonomic nervous system; hypertension; neurons; optogenetics; renin-angiotensin system.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure
None, the authors declare no potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Activation of ADAM17 (A Disintegrin and Metalloprotease 17) on Glutamatergic Neurons Selectively Promotes Sympathoexcitation.Hypertension. 2019 Jun;73(6):1266-1274. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.119.12832. Hypertension. 2019. PMID: 31006330 Free PMC article.
-
Brain angiotensin-converting enzyme type 2 shedding contributes to the development of neurogenic hypertension.Circ Res. 2013 Oct 12;113(9):1087-1096. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.113.301811. Epub 2013 Sep 6. Circ Res. 2013. PMID: 24014829 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Relevance and Role of Neuronal AT1 Receptors in ADAM17-Mediated ACE2 Shedding in Neurogenic Hypertension.Circ Res. 2017 Jun 23;121(1):43-55. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.310509. Epub 2017 May 16. Circ Res. 2017. PMID: 28512108 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of sympathetic vasomotor activity by the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus in normotensive and hypertensive states.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2018 Nov 1;315(5):H1200-H1214. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00216.2018. Epub 2018 Aug 10. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2018. PMID: 30095973 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The compensatory renin-angiotensin system in the central regulation of arterial pressure: new avenues and new challenges.Ther Adv Cardiovasc Dis. 2015 Aug;9(4):201-8. doi: 10.1177/1753944715578056. Epub 2015 Mar 23. Ther Adv Cardiovasc Dis. 2015. PMID: 25801471 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Comparative ACE2 variation and primate COVID-19 risk.Commun Biol. 2020 Oct 27;3(1):641. doi: 10.1038/s42003-020-01370-w. Commun Biol. 2020. PMID: 33110195 Free PMC article.
-
Hypertension, a Moving Target in COVID-19: Current Views and Perspectives.Circ Res. 2021 Apr 2;128(7):1062-1079. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.121.318054. Epub 2021 Apr 1. Circ Res. 2021. PMID: 33793331 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Changes in the SARS-CoV-2 cellular receptor ACE2 levels in cardiovascular patients: a potential biomarker for the stratification of COVID-19 patients.Geroscience. 2021 Oct;43(5):2289-2304. doi: 10.1007/s11357-021-00467-2. Epub 2021 Oct 21. Geroscience. 2021. PMID: 34674152 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding the Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic, Lockdowns and Social Isolation on Sleep Quality.Nat Sci Sleep. 2021 Nov 11;13:2053-2064. doi: 10.2147/NSS.S266240. eCollection 2021. Nat Sci Sleep. 2021. PMID: 34795545 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Brain angiotensin converting enzyme-2 in central cardiovascular regulation.Clin Sci (Lond). 2020 Oct 16;134(19):2535-2547. doi: 10.1042/CS20200483. Clin Sci (Lond). 2020. PMID: 33016313 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ambrosius WT, Sink KM, Foy CG, Berlowitz DR, Cheung AK, Cushman WC, Fine LJ, Goff DC Jr., Johnson KC, Killeen AA, Lewis CE, Oparil S, Reboussin DM, Rocco MV, Snyder JK, Williamson JD, Wright JT Jr., Whelton PK. The design and rationale of a multicenter clinical trial comparing two strategies for control of systolic blood pressure: The systolic blood pressure intervention trial (SPRINT). Clin Trials. 2014;11:532–546 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Leenen FH. Actions of circulating angiotensin II and aldosterone in the brain contributing to hypertension. Am J Hypertens. 2014;27:1024–1032 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

