Depalmitoylation by Palmitoyl-Protein Thioesterase 1 in Neuronal Health and Degeneration
- PMID: 31555119
- PMCID: PMC6727029
- DOI: 10.3389/fnsyn.2019.00025
Depalmitoylation by Palmitoyl-Protein Thioesterase 1 in Neuronal Health and Degeneration
Abstract
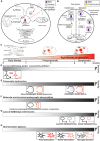
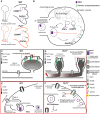
Protein palmitoylation is the post-translational, reversible addition of a 16-carbon fatty acid, palmitate, to proteins. Protein palmitoylation has recently garnered much attention, as it robustly modifies the localization and function of canonical signaling molecules and receptors. Protein depalmitoylation, on the other hand, is the process by which palmitic acid is removed from modified proteins and contributes, therefore, comparably to palmitoylated-protein dynamics. Palmitoylated proteins also require depalmitoylation prior to lysosomal degradation, demonstrating the significance of this process in protein sorting and turnover. Palmitoylation and depalmitoylation serve as particularly crucial regulators of protein function in neurons, where a specialized molecular architecture and cholesterol-rich membrane microdomains contribute to synaptic transmission. Three classes of depalmitoylating enzymes are currently recognized, the acyl protein thioesterases, α/β hydrolase domain-containing 17 proteins (ABHD17s), and the palmitoyl-protein thioesterases (PPTs). However, a clear picture of depalmitoylation has not yet emerged, in part because the enzyme-substrate relationships and specific functions of depalmitoylation are only beginning to be uncovered. Further, despite the finding that loss-of-function mutations affecting palmitoyl-protein thioesterase 1 (PPT1) function cause a severe pediatric neurodegenerative disease, the role of PPT1 as a depalmitoylase has attracted relatively little attention. Understanding the role of depalmitoylation by PPT1 in neuronal function is a fertile area for ongoing basic science and translational research that may have broader therapeutic implications for neurodegeneration. Here, we will briefly introduce the rapidly growing field surrounding protein palmitoylation and depalmitoylation, then will focus on the role of PPT1 in development, health, and neurological disease.
Keywords: NMDA; PPT1; depalmitoylation; lipofuscinosis; neurodegeneration; palmitoylation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Loss of Depalmitoylation Disrupts Homeostatic Plasticity of AMPARs in a Mouse Model of Infantile Neuronal Ceroid Lipofuscinosis.J Neurosci. 2023 Dec 6;43(49):8317-8335. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1113-23.2023. J Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37884348 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of substrates of palmitoyl protein thioesterase 1 highlights roles of depalmitoylation in disulfide bond formation and synaptic function.PLoS Biol. 2022 Mar 31;20(3):e3001590. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3001590. eCollection 2022 Mar. PLoS Biol. 2022. PMID: 35358180 Free PMC article.
-
Reversible Cysteine Acylation Regulates the Activity of Human Palmitoyl-Protein Thioesterase 1 (PPT1).PLoS One. 2016 Jan 5;11(1):e0146466. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0146466. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26731412 Free PMC article.
-
Protein palmitoylation in cancer: molecular functions and therapeutic potential.Mol Oncol. 2023 Jan;17(1):3-26. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.13308. Epub 2022 Sep 10. Mol Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36018061 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protein Palmitoylation by DHHC Protein Family.In: Kittler JT, Moss SJ, editors. The Dynamic Synapse: Molecular Methods in Ionotropic Receptor Biology. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press/Taylor & Francis; 2006. Chapter 5. In: Kittler JT, Moss SJ, editors. The Dynamic Synapse: Molecular Methods in Ionotropic Receptor Biology. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press/Taylor & Francis; 2006. Chapter 5. PMID: 21204476 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
Editorial: Role of protein palmitoylation in synaptic plasticity and neuronal differentiation, volume II.Front Synaptic Neurosci. 2024 Sep 10;16:1473989. doi: 10.3389/fnsyn.2024.1473989. eCollection 2024. Front Synaptic Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39319198 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Electrophysiological Profile Remodeling via Selective Suppression of Voltage-Gated Currents by CLN1/PPT1 Overexpression in Human Neuronal-Like Cells.Front Cell Neurosci. 2020 Dec 16;14:569598. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2020.569598. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 33390903 Free PMC article.
-
The converging roles of Batten disease proteins in neurodegeneration and cancer.iScience. 2021 Mar 19;24(4):102337. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2021.102337. eCollection 2021 Apr 23. iScience. 2021. PMID: 33889828 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of s-palmitoylation in neurological diseases: implication for zDHHC family.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jan 16;14:1342830. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1342830. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38293675 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of New Modulators and Inhibitors of Palmitoyl-Protein Thioesterase 1 for CLN1 Batten Disease and Cancer.ACS Omega. 2024 Feb 28;9(10):11870-11882. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c09607. eCollection 2024 Mar 12. ACS Omega. 2024. PMID: 38496939 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

