Organization of Chromatin by Intrinsic and Regulated Phase Separation
- PMID: 31543265
- PMCID: PMC6778041
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2019.08.037
Organization of Chromatin by Intrinsic and Regulated Phase Separation
Abstract
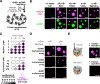
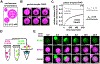
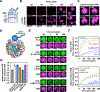
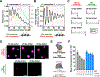
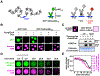
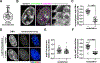
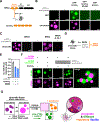
Eukaryotic chromatin is highly condensed but dynamically accessible to regulation and organized into subdomains. We demonstrate that reconstituted chromatin undergoes histone tail-driven liquid-liquid phase separation (LLPS) in physiologic salt and when microinjected into cell nuclei, producing dense and dynamic droplets. Linker histone H1 and internucleosome linker lengths shared across eukaryotes promote phase separation of chromatin, tune droplet properties, and coordinate to form condensates of consistent density in manners that parallel chromatin behavior in cells. Histone acetylation by p300 antagonizes chromatin phase separation, dissolving droplets in vitro and decreasing droplet formation in nuclei. In the presence of multi-bromodomain proteins, such as BRD4, highly acetylated chromatin forms a new phase-separated state with droplets of distinct physical properties, which can be immiscible with unmodified chromatin droplets, mimicking nuclear chromatin subdomains. Our data suggest a framework, based on intrinsic phase separation of the chromatin polymer, for understanding the organization and regulation of eukaryotic genomes.
Keywords: BRD4; acetylation; chromatin organization; epigenetics; genome; histone; histone H1; nucleosome; nucleosome spacing; phase separation.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
DECLARATION OF INTERESTS
M.K.R. is a consultant with Third Rock Ventures.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Nuclear condensates of p300 formed though the structured catalytic core can act as a storage pool of p300 with reduced HAT activity.Nat Commun. 2021 Jul 29;12(1):4618. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-24950-8. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 34326347 Free PMC article.
-
Brd4's Bromodomains Mediate Histone H3 Acetylation and Chromatin Remodeling in Pluripotent Cells through P300 and Brg1.Cell Rep. 2018 Nov 13;25(7):1756-1771. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.10.003. Cell Rep. 2018. PMID: 30428346
-
Liquid-Liquid Phase Separation of Histone Proteins in Cells: Role in Chromatin Organization.Biophys J. 2020 Feb 4;118(3):753-764. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2019.12.022. Epub 2019 Dec 31. Biophys J. 2020. PMID: 31952807 Free PMC article.
-
Liquid-liquid phase separation (LLPS) in DNA and chromatin systems from the perspective of colloid physical chemistry.Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2024 Apr;326:103133. doi: 10.1016/j.cis.2024.103133. Epub 2024 Mar 14. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2024. PMID: 38547652 Review.
-
Nuclear matrix, dynamic histone acetylation and transcriptionally active chromatin.Mol Biol Rep. 1997 Aug;24(3):197-207. doi: 10.1023/a:1006811817247. Mol Biol Rep. 1997. PMID: 9291093 Review.
Cited by
-
Live imaging of chromatin distribution reveals novel principles of nuclear architecture and chromatin compartmentalization.Sci Adv. 2021 Jun 2;7(23):eabf6251. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abf6251. Print 2021 Jun. Sci Adv. 2021. PMID: 34078602 Free PMC article.
-
Context transcription factors establish cooperative environments and mediate enhancer communication.Nat Genet. 2024 Oct;56(10):2199-2212. doi: 10.1038/s41588-024-01892-7. Epub 2024 Oct 3. Nat Genet. 2024. PMID: 39363017 Free PMC article.
-
An RNA-centric view of transcription and genome organization.Mol Cell. 2024 Oct 3;84(19):3627-3643. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2024.08.021. Mol Cell. 2024. PMID: 39366351 Review.
-
Human centromere repositioning activates transcription and opens chromatin fibre structure.Nat Commun. 2022 Sep 24;13(1):5609. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-33426-2. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 36153345 Free PMC article.
-
Phase separation-mediated biomolecular condensates and their relationship to tumor.Cell Commun Signal. 2024 Feb 21;22(1):143. doi: 10.1186/s12964-024-01518-9. Cell Commun Signal. 2024. PMID: 38383403 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

