Evaluation of the acute and sub-acute toxicity of the black caraway seed essential oil in Wistar rats
- PMID: 31497509
- PMCID: PMC6719284
- DOI: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2019.08.010
Evaluation of the acute and sub-acute toxicity of the black caraway seed essential oil in Wistar rats
Abstract
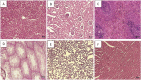
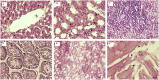
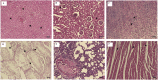
The aim of the present study was to evaluate the acute toxicity as lethal dose 50% (LD50) and sub-acute toxicity of the black caraway Bunium persicum (Bioss) seed essential oil in male Wistar rats. The compounds of B. persicum were identified by GC/MS and amount of each compound was evaluated. 21 different compounds were determined in the essential oil and the main components were: carvone, p-cymene, gamma-terpinene, p-cymene-8-ol, limonene, isoterpinolene, and 2-beta pinene. For acute toxicity evaluation, the animals were randomly divided into nine group (n = 6) and received 500, 1000, 1500, 2000, 2500, 3000, 3500 and 4000 mg/kg seed essential oil, respectively and the LD50 value for black caraway seed essential oil was obtained above 4000 mg/kg body weight. According to data, treatment with the black caraway seed essential oil sub-acute toxicity study attenuated histopathological changes in lung, liver, kidney, testes and spleen tissues and the results of this study show that the black caraway essential oil can not affect the immune and blood system, important enzymes and vital organs of the body..
Keywords: Acute toxicity; Black caraway (Bunium persicum); Essential oil; Rat; Sub-acute toxicity.
Conflict of interest statement
Animals received animal care, and all the experiments were performed in accordance with the Guidelines of the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee and were approved by the Animal Ethics Committee of the Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, University of Tehran, Iran (approval No of 7506023.6.17).
Figures

Similar articles
-
Unraveling the Variability of Essential Oil Composition in Different Accessions of Bunium persicum Collected from Different Temperate Micro-Climates.Molecules. 2023 Mar 6;28(5):2404. doi: 10.3390/molecules28052404. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 36903647 Free PMC article.
-
An investigation of the HMGR gene and IPI gene expression in black caraway (Bunium persicum).3 Biotech. 2018 Sep;8(9):405. doi: 10.1007/s13205-018-1404-y. Epub 2018 Sep 11. 3 Biotech. 2018. PMID: 30221118 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Method for Attaining Caraway Seed Oil Fractions with Different Composition.Chem Biodivers. 2016 Jun;13(6):695-9. doi: 10.1002/cbdv.201500190. Epub 2016 May 27. Chem Biodivers. 2016. PMID: 27119969
-
Laboratory study: Synthesis and optimization of nano nisomes containing Bunium persicum essential oil and investigating its toxicity on Trichomonas vaginalis parasite and HFF cell line.Heliyon. 2024 Aug 8;10(16):e35967. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e35967. eCollection 2024 Aug 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39224365 Free PMC article.
-
Caraway as Important Medicinal Plants in Management of Diseases.Nat Prod Bioprospect. 2019 Jan;9(1):1-11. doi: 10.1007/s13659-018-0190-x. Epub 2018 Oct 29. Nat Prod Bioprospect. 2019. PMID: 30374904 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Assessment of the acute and sub-acute toxicity of the ethanolic extract of the aerial parts of Crassocephalum rabens (Asteraceae) in rats.Toxicol Rep. 2021 Dec 16;9:58-63. doi: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2021.12.005. eCollection 2022. Toxicol Rep. 2021. PMID: 35004182 Free PMC article.
-
Riboflavin recovery of spermatogenic dysfunction via a dual inhibition of oxidative changes and regulation of the PINK1-mediated pathway in arsenic-injured rat model.Physiol Res. 2021 Aug 31;70(4):591-603. doi: 10.33549/physiolres.934658. Epub 2021 Jun 1. Physiol Res. 2021. PMID: 34062077 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Acute and Subchronic Toxicity Induced by the Crude Ethanol Extract of Plukenetia volubilis Linneo Leaves in Swiss Albino Mice.Biomed Res Int. 2021 Oct 19;2021:6524658. doi: 10.1155/2021/6524658. eCollection 2021. Biomed Res Int. 2021. PMID: 34712734 Free PMC article.
-
Acute and repeated-dose toxicity of Echinops kebericho Mesfin essential oil.Toxicol Rep. 2020 Dec 30;8:131-138. doi: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2020.12.027. eCollection 2021. Toxicol Rep. 2020. PMID: 33437654 Free PMC article.
-
Phytochemical analysis and evaluation of skin irritation, acute and sub-acute toxicity of Cymbopogon citratus essential oil in mice and rabbits.Toxicol Rep. 2019 Nov 4;6:1289-1294. doi: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2019.11.002. eCollection 2019. Toxicol Rep. 2019. PMID: 31867219 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gurib-Fakim A. Medicinal plants: traditions of yesterday and drugs of tomorrow. Mol. Aspects Med. 2006;27(1):1–93. - PubMed
-
- Mazaki M., Kataoka K. Inhibitory effects of caraway (Carum carvi L.) and its component on N-methyl-N’-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine-induced mutagenicity. J. Med. Invest. 2006;53(1-2):123–133. - PubMed
-
- Micklefield G., Greving I. Effects of peppermint oil and caraway oil on gastroduodenal motility. Phytother. Res. 2000;14(1):20–23. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

