Transcriptional Responses to IFN-γ Require Mediator Kinase-Dependent Pause Release and Mechanistically Distinct CDK8 and CDK19 Functions
- PMID: 31495563
- PMCID: PMC6842433
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2019.07.034
Transcriptional Responses to IFN-γ Require Mediator Kinase-Dependent Pause Release and Mechanistically Distinct CDK8 and CDK19 Functions
Abstract
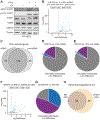
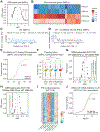
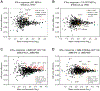
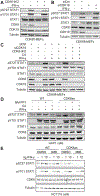
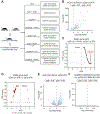
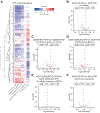
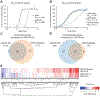
Transcriptional responses to external stimuli remain poorly understood. Using global nuclear run-on followed by sequencing (GRO-seq) and precision nuclear run-on sequencing (PRO-seq), we show that CDK8 kinase activity promotes RNA polymerase II pause release in response to interferon-γ (IFN-γ), a universal cytokine involved in immunity and tumor surveillance. The Mediator kinase module contains CDK8 or CDK19, which are presumed to be functionally redundant. We implemented cortistatin A, chemical genetics, transcriptomics, and other methods to decouple their function while assessing enzymatic versus structural roles. Unexpectedly, CDK8 and CDK19 regulated different gene sets via distinct mechanisms. CDK8-dependent regulation required its kinase activity, whereas CDK19 governed IFN-γ responses through its scaffolding function (i.e., it was kinase independent). Accordingly, CDK8, not CDK19, phosphorylates the STAT1 transcription factor (TF) during IFN-γ stimulation, and CDK8 kinase inhibition blocked activation of JAK-STAT pathway TFs. Cytokines such as IFN-γ rapidly mobilize TFs to "reprogram" cellular transcription; our results implicate CDK8 and CDK19 as essential for this transcriptional reprogramming.
Keywords: CDK19; CDK8; Mediator kinase; RNA polymerase II; STAT1; cortistatin A; eRNA; interferon; promoter-proximal pausing; transcription.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
DECLARATION OF INTERESTS
The authors declare no competing financial interests
Figures
Similar articles
-
Human airway macrophages are metabolically reprogrammed by IFN-γ resulting in glycolysis-dependent functional plasticity.Elife. 2024 Dec 2;13:RP98449. doi: 10.7554/eLife.98449. Elife. 2024. PMID: 39620891 Free PMC article.
-
CDK8 and CDK19: positive regulators of signal-induced transcription and negative regulators of Mediator complex proteins.Nucleic Acids Res. 2023 Aug 11;51(14):7288-7313. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad538. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023. PMID: 37378433 Free PMC article.
-
Depressing time: Waiting, melancholia, and the psychoanalytic practice of care.In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. PMID: 36137063 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Mediator kinase inhibition suppresses hyperactive interferon signaling in Down syndrome.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Nov 20:2023.07.05.547813. doi: 10.1101/2023.07.05.547813. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 37461585 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Interventions for supporting pregnant women's decision-making about mode of birth after a caesarean.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Jul 30;2013(7):CD010041. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010041.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013. PMID: 23897547 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
CDK19 regulates the proliferation of hematopoietic stem cells and acute myeloid leukemia cells by suppressing p53-mediated transcription of p21.Leukemia. 2022 Apr;36(4):956-969. doi: 10.1038/s41375-022-01512-5. Epub 2022 Feb 2. Leukemia. 2022. PMID: 35110726
-
Interferons reshape the 3D conformation and accessibility of macrophage chromatin.iScience. 2022 Feb 1;25(3):103840. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2022.103840. eCollection 2022 Mar 18. iScience. 2022. PMID: 35243225 Free PMC article.
-
Genome Editing As an Approach to the Study of in Vivo Transcription Reprogramming.Dokl Biochem Biophys. 2020 Jan;490(1):43-46. doi: 10.1134/S1607672920010147. Epub 2020 Apr 27. Dokl Biochem Biophys. 2020. PMID: 32342312
-
Restrictor synergizes with Symplekin and PNUTS to terminate extragenic transcription.Genes Dev. 2023 Dec 26;37(21-24):1017-1040. doi: 10.1101/gad.351057.123. Genes Dev. 2023. PMID: 38092518 Free PMC article.
-
Exploitation of the Mediator complex by viruses.PLoS Pathog. 2022 Apr 21;18(4):e1010422. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1010422. eCollection 2022 Apr. PLoS Pathog. 2022. PMID: 35446926 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

