Regulation of Brain Cholesterol: What Role Do Liver X Receptors Play in Neurodegenerative Diseases?
- PMID: 31398791
- PMCID: PMC6720493
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms20163858
Regulation of Brain Cholesterol: What Role Do Liver X Receptors Play in Neurodegenerative Diseases?
Abstract
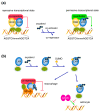
Liver X Receptors (LXR) alpha and beta are two members of nuclear receptor superfamily documented as endogenous cholesterol sensors. Following conversion of cholesterol in oxysterol, both LXR isoforms detect intracellular concentrations and act as transcription factors to promote expression of target genes. Among their numerous physiological roles, they act as central cholesterol-lowering factors. In the central nervous system (CNS), cholesterol has been shown to be an essential determinant of brain function, particularly as a major constituent of myelin and membranes. In the brain, LXRs act as cholesterol central regulators, and, beyond this metabolic function, LXRs have additional roles such as providing neuroprotective effects and lowering neuroinflammation. In many neurodegenerative disorders, including amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), Alzheimer's disease (AD), and multiple sclerosis (MS), dysregulations of cholesterol and oxysterol have been reported. In this paper, we propose to focus on recent advances in the knowledge of the LXRs roles on brain cholesterol and oxysterol homeostasis, neuroinflammation, neuroprotection, and their putative involvement in neurodegenerative disorders. We will discuss their potential use as candidates for both molecular diagnosis and as promising pharmacological targets in the treatment of ALS, AD, or MS patients.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Liver X receptors; amyotrophic lateral sclerosis; cholesterol; multiple sclerosis; neuroinflammation; oxysterols.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Liver X receptors: from cholesterol regulation to neuroprotection-a new barrier against neurodegeneration in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis?Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016 Oct;73(20):3801-8. doi: 10.1007/s00018-016-2330-y. Epub 2016 Aug 10. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016. PMID: 27510420 Free PMC article. Review.
-
LXR Regulation of Brain Cholesterol: From Development to Disease.Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2016 Jun;27(6):404-414. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2016.03.018. Epub 2016 Apr 21. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2016. PMID: 27113081 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oxysterols, cholesterol homeostasis, and Alzheimer disease.J Neurochem. 2007 Sep;102(6):1727-1737. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2007.04689.x. Epub 2007 Jun 15. J Neurochem. 2007. PMID: 17573819 Review.
-
Role of Brain Liver X Receptor in Parkinson's Disease: Hidden Treasure and Emerging Opportunities.Mol Neurobiol. 2024 Jan;61(1):341-357. doi: 10.1007/s12035-023-03561-y. Epub 2023 Aug 22. Mol Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 37606719 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Disrupted Lipid Metabolism in Multiple Sclerosis: A Role for Liver X Receptors?Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Apr 13;12:639757. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.639757. eCollection 2021. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 33927692 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The State of The Art on Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors in the Treatment of Alzheimer's Disease.J Cent Nerv Syst Dis. 2021 Jul 7;13:11795735211029113. doi: 10.1177/11795735211029113. eCollection 2021. J Cent Nerv Syst Dis. 2021. PMID: 34285627 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Liver X Receptor Regulation of Glial Cell Functions in the CNS.Biomedicines. 2022 Sep 2;10(9):2165. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10092165. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36140266 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Meta-Analysis of APP Expression Modulated by SARS-CoV-2 Infection via the ACE2 Receptor.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 21;23(3):1182. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031182. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35163117 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Side Chain Oxidized Sterols as Novel Liver X Receptor Agonists with Therapeutic Potential in the Treatment of Cardiovascular and Neurodegenerative Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 9;24(2):1290. doi: 10.3390/ijms24021290. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36674804 Free PMC article.
-
Roles, molecular mechanisms, and signaling pathways of TMEMs in neurological diseases.Am J Transl Res. 2021 Dec 15;13(12):13273-13297. eCollection 2021. Am J Transl Res. 2021. PMID: 35035675 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

