A Design of Experiments (DoE) Approach Accelerates the Optimization of Copper-Mediated 18F-Fluorination Reactions of Arylstannanes
- PMID: 31388076
- PMCID: PMC6684620
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-47846-6
A Design of Experiments (DoE) Approach Accelerates the Optimization of Copper-Mediated 18F-Fluorination Reactions of Arylstannanes
Abstract
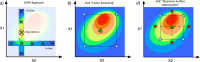
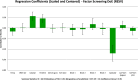
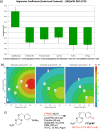
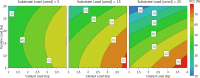
Recent advancements in 18F radiochemistry, such as the advent of copper-mediated radiofluorination (CMRF) chemistry, have provided unprecedented access to novel chemically diverse PET probes; however, these multicomponent reactions have come with a new set of complex optimization problems. Design of experiments (DoE) is a statistical approach to process optimization that is used across a variety of industries. It possesses a number of advantages over the traditionally employed "one variable at a time" (OVAT) approach, such as increased experimental efficiency as well as an ability to resolve factor interactions and provide detailed maps of a process's behavior. Here we demonstrate the utility of DoE to the development and optimization of new radiochemical methodologies and novel PET tracer synthesis. Using DoE to construct experimentally efficient factor screening and optimization studies, we were able to identify critical factors and model their behavior with more than two-fold greater experimental efficiency than the traditional OVAT approach. Additionally, the use of DoE allowed us to glean new insights into the behavior of the CMRF of a number of arylstannane precursors. This information has guided our decision-making efforts while developing efficient reaction conditions that suit the unique process requirements of 18F PET tracer synthesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
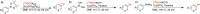
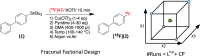
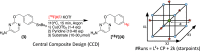
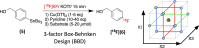
Similar articles
-
Scalable 18F processing conditions for copper-mediated radiofluorination chemistry facilitate DoE optimization studies and afford an improved synthesis of [18F]olaparib.Org Biomol Chem. 2021 Aug 28;19(32):6995-7000. doi: 10.1039/d1ob00903f. Epub 2021 Aug 5. Org Biomol Chem. 2021. PMID: 34351339
-
Fast and efficient copper-mediated 18F-fluorination of arylstannanes, aryl boronic acids, and aryl boronic esters without azeotropic drying.EJNMMI Radiopharm Chem. 2019 Oct 16;4(1):28. doi: 10.1186/s41181-019-0079-y. EJNMMI Radiopharm Chem. 2019. PMID: 31659523 Free PMC article.
-
Statistical Multiobjective Optimization of Thiospinel CoNi2S4 Nanocrystal Synthesis via Design of Experiments.ACS Nano. 2021 Jun 22;15(6):9422-9433. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.1c00502. Epub 2021 Apr 20. ACS Nano. 2021. PMID: 33877801
-
Optimizing drug delivery systems using systematic "design of experiments." Part I: fundamental aspects.Crit Rev Ther Drug Carrier Syst. 2005;22(1):27-105. doi: 10.1615/critrevtherdrugcarriersyst.v22.i1.20. Crit Rev Ther Drug Carrier Syst. 2005. PMID: 15715503 Review.
-
Small Prosthetic Groups in 18F-Radiochemistry: Useful Auxiliaries for the Design of 18F-PET Tracers.Semin Nucl Med. 2017 Sep;47(5):474-492. doi: 10.1053/j.semnuclmed.2017.07.001. Epub 2017 Jul 17. Semin Nucl Med. 2017. PMID: 28826522 Review.
Cited by
-
High-field superconductivity in C-doped MgB2 bulk samples prepared by a rapid synthesis route.Sci Rep. 2020 Oct 19;10(1):17656. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-74300-9. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33077872 Free PMC article.
-
In Situ Synthesis of Keratin and Melanin Chromophoric Submicron Particles.ACS Omega. 2023 Jul 5;8(30):26762-26774. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c00189. eCollection 2023 Aug 1. ACS Omega. 2023. PMID: 37546605 Free PMC article.
-
Scenedesmus rubescens Heterotrophic Production Strategies for Added Value Biomass.Mar Drugs. 2023 Jul 19;21(7):411. doi: 10.3390/md21070411. Mar Drugs. 2023. PMID: 37504942 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a Robust Control Strategy for Fixed-Dose Combination Bilayer Tablets with Integrated Quality by Design, Statistical, and Process Analytical Technology Approach.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Sep 10;13(9):1443. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13091443. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 34575519 Free PMC article.
-
Next Generation Copper Mediators for the Efficient Production of 18 F-Labeled Aromatics.Chemistry. 2023 Jan 9;29(2):e202202965. doi: 10.1002/chem.202202965. Epub 2022 Nov 17. Chemistry. 2023. PMID: 36214204 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

