TLR9 Mediated Tumor-Stroma Interactions in Human Papilloma Virus (HPV)-Positive Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Up-Regulate PD-L1 and PD-L2
- PMID: 31379843
- PMCID: PMC6648892
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01644
TLR9 Mediated Tumor-Stroma Interactions in Human Papilloma Virus (HPV)-Positive Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Up-Regulate PD-L1 and PD-L2
Abstract
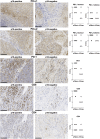
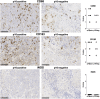
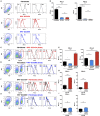
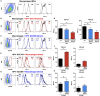
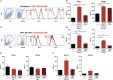
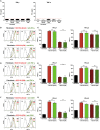
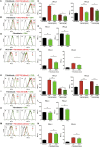
Background: The co-inhibitory receptor PD-1 is expressed in many tumors including head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) and is an important immunotherapy target. However, the role of PD-1 ligands, PD-L1, and particularly PD-L2, in the tumor-stromal cell interactions that cause a tumor-permissive environment in HNSCC is not completely understood and is the focus of our study. Methods: Expression of PD-L1 and PD-L2 was analyzed by immunohistochemistry in situ in HNSCC tumor tissue. Co-cultures were established between stromal cells (fibroblasts and macrophages) and human papilloma virus (HPV)-positive and HPV-negative HNSCC cell lines (HNSCCs) and PD-1 ligands expression was analyzed using flow cytometry. Results: PD-L1 and PD-L2 were expressed both in tumor cells and stroma in HNSCC tissue in situ. In vitro, basal expression of PD-L1 and PD-L2 was low in HNSCCs and high on fibroblasts and macrophages. Interestingly, HPV-positive but not HPV-negative HNSCCs increased the expression of both PD-1 ligands on fibroblasts upon co-culture. This effect was not observed with macrophages. Conversely, both fibroblasts and macrophages increased PD-1 ligands on HPV-positive HNSCCs, whilst this was not observed in HPV-negative HNSCCs. Crucially, we demonstrate that up-regulation of PD-L1 and PD-L2 on fibroblasts by HPV-positive HNSCCs is mediated via TLR9. Conclusions: This work demonstrates in an in vitro model that HPV-positive HNSCCs regulate PD-L1/2 expression on fibroblasts via TLR9. This may open novel avenues to modulate immune checkpoint regulator PD-1 and its ligands by targeting TLR9.
Keywords: HNSCC; HPV; PD-1; PD-L1; PD-L2; TLR9; fibroblasts.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Characterization of the tumor immune microenvironment in human papillomavirus-positive and -negative head and neck squamous cell carcinomas.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2021 May;70(5):1227-1237. doi: 10.1007/s00262-020-02747-w. Epub 2020 Oct 30. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2021. PMID: 33125511 Free PMC article.
-
High-Grade Neuroendocrine Carcinoma of the Head and Neck: Human Papillomavirus Status and PD-L1 Expression.ORL J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec. 2019;81(5-6):309-316. doi: 10.1159/000502325. Epub 2019 Sep 24. ORL J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec. 2019. PMID: 31550725
-
PD-L1 expression correlates with tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and better prognosis in patients with HPV-negative head and neck squamous cell carcinomas.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2020 Oct;69(10):2089-2100. doi: 10.1007/s00262-020-02604-w. Epub 2020 May 24. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2020. PMID: 32448984 Free PMC article.
-
Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: Genomics and emerging biomarkers for immunomodulatory cancer treatments.Semin Cancer Biol. 2018 Oct;52(Pt 2):228-240. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2018.01.008. Epub 2018 Jan 31. Semin Cancer Biol. 2018. PMID: 29355614 Review.
-
The Role of the Programmed Death Receptor-1/Programmed Death Ligand-1: Immunologic Checkpoint in Human Papillomavirus-Associated Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2018 Jun;142(6):719-720. doi: 10.5858/arpa.2017-0561-RA. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2018. PMID: 29848031 Review.
Cited by
-
Randomized phase II trial of avelumab alone or in combination with cetuximab for patients with previously treated, locally advanced, or metastatic squamous cell anal carcinoma: the CARACAS study.J Immunother Cancer. 2021 Nov;9(11):e002996. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2021-002996. J Immunother Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34815354 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
HPV Involvement in the Tumor Microenvironment and Immune Treatment in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinomas.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Apr 25;12(5):1060. doi: 10.3390/cancers12051060. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32344813 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evolving landscape of PD-L2: bring new light to checkpoint immunotherapy.Br J Cancer. 2023 Mar;128(7):1196-1207. doi: 10.1038/s41416-022-02084-y. Epub 2022 Dec 15. Br J Cancer. 2023. PMID: 36522474 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prognostic value of PD-1, PD-L1 and PD-L2 deserves attention in head and neck cancer.Front Immunol. 2022 Sep 2;13:988416. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.988416. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36119046 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Common Microbial Genital Infections and Their Impact on the Innate Immune Response to HPV in Cervical Cells.Pathogens. 2022 Nov 16;11(11):1361. doi: 10.3390/pathogens11111361. Pathogens. 2022. PMID: 36422611 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Venuti A, Badaracco G, Rizzo C, Mafera B, Rahimi S, Vigili M. Presence of HPV in head and neck tumors: high prevalence in tonsillar localization. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. (2004) 23:561–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

