Role of prolyl hydroxylation in the molecular interactions of collagens
- PMID: 31350381
- PMCID: PMC6744578
- DOI: 10.1042/EBC20180053
Role of prolyl hydroxylation in the molecular interactions of collagens
Abstract
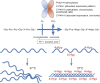
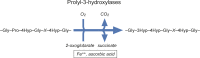
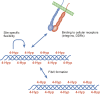
Co- and post-translational hydroxylation of proline residues is critical for the stability of the triple helical collagen structure. In this review, we summarise the biology of collagen prolyl 4-hydroxylases and collagen prolyl 3-hydroxylases, the enzymes responsible for proline hydroxylation. Furthermore, we describe the potential roles of hydroxyproline residues in the complex interplay between collagens and other proteins, especially integrin and discoidin domain receptor type cell adhesion receptors. Qualitative and quantitative regulation of collagen hydroxylation may have remarkable effects on the properties of the extracellular matrix and consequently on the cell behaviour.
Keywords: collagen; extracellular matrix; integrins; molecular interactions; prolyl hydroxylase.
© 2019 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
J.M. owns equity in FibroGen Inc., which develops HIF-P4H inhibitors as potential therapeutics. This company supports HIF-related research in the J.M. group.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Proline hydroxylation in collagen supports integrin binding by two distinct mechanisms.J Biol Chem. 2018 May 18;293(20):7645-7658. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.002200. Epub 2018 Apr 3. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 29615493 Free PMC article.
-
Collagen prolyl 3-hydroxylation: a major role for a minor post-translational modification?Connect Tissue Res. 2013;54(4-5):245-51. doi: 10.3109/03008207.2013.800867. Epub 2013 Jun 21. Connect Tissue Res. 2013. PMID: 23772978 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tunable, post-translational hydroxylation of collagen Domains in Escherichia coli.ACS Chem Biol. 2011 Apr 15;6(4):320-4. doi: 10.1021/cb100298r. Epub 2011 Jan 14. ACS Chem Biol. 2011. PMID: 21210682 Free PMC article.
-
Post-translationally abnormal collagens of prolyl 3-hydroxylase-2 null mice offer a pathobiological mechanism for the high myopia linked to human LEPREL1 mutations.J Biol Chem. 2015 Mar 27;290(13):8613-22. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.634915. Epub 2015 Feb 2. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25645914 Free PMC article.
-
Collagen hydroxylases and the protein disulfide isomerase subunit of prolyl 4-hydroxylases.Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1998;72:325-98. doi: 10.1002/9780470123188.ch9. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1998. PMID: 9559057 Review.
Cited by
-
Profiling of collagen and extracellular matrix deposition from cell culture using in vitro ExtraCellular matrix mass spectrometry imaging (ivECM-MSI).Matrix Biol Plus. 2024 Sep 25;24:100161. doi: 10.1016/j.mbplus.2024.100161. eCollection 2024 Dec. Matrix Biol Plus. 2024. PMID: 39435160 Free PMC article.
-
Beneficial Effects of Zoledronic Acid on Tendons of the Osteogenesis Imperfecta Mouse (Oim).Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Jun 2;16(6):832. doi: 10.3390/ph16060832. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37375779 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic modulation to improve MSC expansion and therapeutic potential for articular cartilage repair.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2024 Sep 16;15(1):308. doi: 10.1186/s13287-024-03923-w. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2024. PMID: 39285485 Free PMC article.
-
Mass Spectrometry Imaging of Fibroblasts: Promise and Challenge.Expert Rev Proteomics. 2021 Jun;18(6):423-436. doi: 10.1080/14789450.2021.1941893. Epub 2021 Jul 24. Expert Rev Proteomics. 2021. PMID: 34129411 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MatrisomeDB: the ECM-protein knowledge database.Nucleic Acids Res. 2020 Jan 8;48(D1):D1136-D1144. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz849. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020. PMID: 31586405 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kivirikko K.I., Myllylä R. and Pihlajaniemi T. (1992) Prolyl hydroxylase, protein disulfide isomerase, and other structurally related proteins. In Post-Translational Modifications of Proteins(Harding J.J. and Crabbe M.J.C., eds), pp. 1–51, CRC Press
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

