Development and characteristics of novel sonosensitive liposomes for vincristine bitartrate
- PMID: 31293182
- PMCID: PMC6691763
- DOI: 10.1080/10717544.2019.1639845
Development and characteristics of novel sonosensitive liposomes for vincristine bitartrate
Abstract
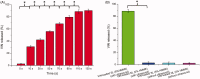
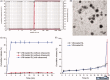
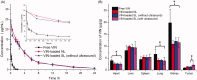
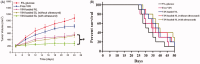
The aim of drug delivery is to increase therapeutic efficacy. Externally triggered drug delivery systems enable site-specific and time-controlled drug release. To achieve this goal, our strategy was based on ultrasound-triggered release of an anticancer agent from sonosensitive liposomes (SL). To realize the ultrasound-triggered drug release, a lipophilic sonosensitizer, hematoporphyrin monomethyl ether (HMME) was incorporated into the lipid bilayer of liposomes. Once irradiated by the ultrasound in tumor tissues, the sonodynamic effect generated by HMME could lead to an efficient disruption of the lipid bilayer in the SL. After encapsulating vincristine bitartrate (VIN) as the model drug, the ultrasound-triggered lipid bilayer breakdown can trigger the instant release of VIN, enabling ultrasound-controlled chemotherapy with great specificity. In the in vitro and in vivo studies, by integrating tumor-specific targeting and stimuli-responsive controlled release into one system, VIN-loaded SL showed excellent antitumor efficacy. The SL could potentially produce viable clinical strategies for improved targeting efficiency of VIN for the treatment of related cancer. More importantly, this report provides an example of controlled release by means of a novel class of ultrasound triggering system.
Keywords: Ultrasound sensitivity; control release; drug delivery system; sonodynamic effect; sonosensitizer.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Novel Class of Ultrasound-Triggerable Drug Delivery Systems for the Improved Treatment of Tumors.Mol Pharm. 2019 Jul 1;16(7):2956-2965. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.9b00194. Epub 2019 May 23. Mol Pharm. 2019. PMID: 31084010
-
Development of a stable single-vial liposomal formulation for vincristine.Int J Nanomedicine. 2019 Jun 21;14:4461-4474. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S205276. eCollection 2019. Int J Nanomedicine. 2019. PMID: 31296986 Free PMC article.
-
A nanoliposome-based photoactivable drug delivery system for enhanced cancer therapy and overcoming treatment resistance.Int J Nanomedicine. 2017 Nov 14;12:8257-8275. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S143776. eCollection 2017. Int J Nanomedicine. 2017. PMID: 29180864 Free PMC article.
-
Review on triggered liposomal drug delivery with a focus on ultrasound.Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2015;15(4):282-313. doi: 10.2174/1568009615666150311100610. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2015. PMID: 25760762 Review.
-
Marqibo® (vincristine sulfate liposome injection) improves the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of vincristine.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2013 Mar;71(3):555-64. doi: 10.1007/s00280-012-2042-4. Epub 2012 Dec 5. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23212117 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Storage Stability of Atheroglitatide, an Echogenic Liposomal Formulation of Pioglitazone Targeted to Advanced Atheroma with a Fibrin-Binding Peptide.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Sep 6;15(9):2288. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15092288. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37765257 Free PMC article.
-
Miniaturized therapeutic systems for ultrasound-modulated drug delivery to the central and peripheral nervous system.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2024 May;208:115275. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2024.115275. Epub 2024 Mar 3. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2024. PMID: 38442747 Review.
-
Liposomes for Tumor Targeted Therapy: A Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 31;24(3):2643. doi: 10.3390/ijms24032643. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36768966 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Advancements in Stimuli Responsive Drug Delivery Platforms for Active and Passive Cancer Targeting.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Feb 7;13(4):670. doi: 10.3390/cancers13040670. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33562376 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Updates on Responsive Drug Delivery Based on Liposome Vehicles for Cancer Treatment.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Oct 15;14(10):2195. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14102195. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 36297630 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Allen TM, Cullis PR (2013). Liposomal drug delivery systems: from concept to clinical applications. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 65:36–48. - PubMed
-
- Barenholz Y. (2012). Doxil®-the first FDA-approved nano-drug: lessons learned. J Control Release 160:117–34. - PubMed
-
- Chiu GNC, Abraham SA, Ickenstein LM, et al. (2005). Encapsulatuon of doxorubicin into thermosensitive liposomes via complexation with transition metal manganese. J Control Release 104:271–88. - PubMed
-
- Costley D, Mc Ewan C, Fowley C, et al. (2015). Treating cancer with sonodynamic therapy: a review. Int J Hyperthermia 31:107–17. - PubMed
-
- Husseini GA, Pitt WG, Martins AM (2014). Ultrasonically triggered drug delivery: breaking the barrier. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 123:364–86. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
