The P-selectin and PSGL-1 axis accelerates atherosclerosis via activation of dendritic cells by the TLR4 signaling pathway
- PMID: 31263109
- PMCID: PMC6602970
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-019-1736-5
The P-selectin and PSGL-1 axis accelerates atherosclerosis via activation of dendritic cells by the TLR4 signaling pathway
Abstract
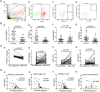
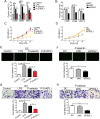
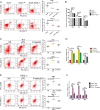
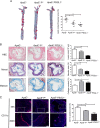
P-selectin and dendritic cells (DCs) are associated with atherosclerosis. However, their interactions in this setting are undefined. Herein, we investigated the role of P-selectin and its receptor P-selectin glycoprotein ligand (PSGL)-1 on atherosclerosis via activation of DCs. In the current study, a total of 34 patients with ST elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) and 34 healthy control subjects were enrolled. Serum concentration of P-selectin was higher and the myeloid DC/plasmacytoid DC (mDC/pDC) ratio was lower in STEMI patients than in normal individuals. Interestingly, in STEMI patients, P-selectin was decreased and the mDC/pDC ratio was increased at 5-7 days after successful percutaneous coronary intervention, as compared with values on admission. Serum P-selectin was inversely correlated with the mDC/pDC ratio. Moreover, ApoE-/-P-/- and ApoE-/-PSGL-1-/- mice developed small atherosclerotic plaques after feeding of a western diet for 12 weeks and DC infiltration was significantly reduced. P-selectin stimulation markedly induced phenotypic maturation, enhanced secretion of inflammatory cytokines, communication with T cells, and the adhesion and migration of DCs. In vivo, DC maturation was significantly attenuated in P-selectin and PSGL1 knockout mice under hypercholesterolemic and inflammatory conditions. These effects were associated with the activation of myeloid differentiation primary response 88 (MYD88)-dependent and MyD88-independent Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) signaling pathways. Taken together, binding of P-selectin to PSGL-1 on DCs contributes to atherosclerosis progression via DC activation via the TLR4 signaling pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
P-selectin glycoprotein ligand-1 is highly expressed on Ly-6Chi monocytes and a major determinant for Ly-6Chi monocyte recruitment to sites of atherosclerosis in mice.Circulation. 2008 Jun 24;117(25):3227-37. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.108.771048. Epub 2008 Jun 2. Circulation. 2008. PMID: 18519846 Free PMC article.
-
TLR/MyD88 and liver X receptor alpha signaling pathways reciprocally control Chlamydia pneumoniae-induced acceleration of atherosclerosis.J Immunol. 2008 Nov 15;181(10):7176-85. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.181.10.7176. J Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18981139 Free PMC article.
-
P-selectin glycoprotein ligand-1 deficiency leads to cytokine resistance and protection against atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E deficient mice.Atherosclerosis. 2012 Jan;220(1):110-7. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2011.10.012. Epub 2011 Oct 17. Atherosclerosis. 2012. PMID: 22041028 Free PMC article.
-
Treg-mediated suppression of atherosclerosis requires MYD88 signaling in DCs.J Clin Invest. 2013 Jan;123(1):179-88. doi: 10.1172/JCI64617. Epub 2012 Dec 21. J Clin Invest. 2013. PMID: 23257360 Free PMC article.
-
Toll-like receptors in atherosclerosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2013 Jul 4;14(7):14008-23. doi: 10.3390/ijms140714008. Int J Mol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23880853 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Inflammatory and Prothrombotic Biomarkers Contribute to the Persistence of Sequelae in Recovered COVID-19 Patients.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 14;24(24):17468. doi: 10.3390/ijms242417468. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38139298 Free PMC article.
-
Genistein promotes M1 macrophage apoptosis and reduces inflammatory response by disrupting miR-21/TIPE2 pathway.Saudi Pharm J. 2022 Jul;30(7):934-945. doi: 10.1016/j.jsps.2022.05.009. Epub 2022 May 23. Saudi Pharm J. 2022. PMID: 35903524 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Platelet in Atherosclerosis Plaque Formation: Current Knowledge and Future Perspectives.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Dec 21;21(24):9760. doi: 10.3390/ijms21249760. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33371312 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multiple exposures to low-dose ionizing radiation induced the initiation and progression of pro-atherosclerotic phenotypes in mice and vascular endothelial cell damage.Sci Prog. 2024 Jan-Mar;107(1):368504241228668. doi: 10.1177/00368504241228668. Sci Prog. 2024. PMID: 38385346 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging Trends and Innovations in the Treatment and Diagnosis of Atherosclerosis and Cardiovascular Disease: A Comprehensive Review towards Healthier Aging.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Aug 3;16(8):1037. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16081037. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 39204382 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

