BAP31 regulates mitochondrial function via interaction with Tom40 within ER-mitochondria contact sites
- PMID: 31206022
- PMCID: PMC6561740
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.aaw1386
BAP31 regulates mitochondrial function via interaction with Tom40 within ER-mitochondria contact sites
Abstract
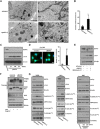
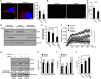
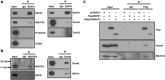
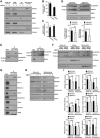
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is composed of large membrane-bound compartments, and its membrane subdomain appears to be in close contact with mitochondria via ER-mitochondria contact sites. Here, I demonstrate that the ER membrane protein, BAP31, acts as a key factor in mitochondrial homeostasis to stimulate the constitution of the mitochondrial complex I by forming an ER-mitochondria bridging protein complex. Within this complex, BAP31 interacts with mitochondria-localized proteins, including Tom40, to stimulate the translocation of NDUFS4, the component of complex I from the cytosol to the mitochondria. Disruption of the BAP31-Tom40 complex inhibits mitochondrial complex I activity and oxygen consumption by the decreased NDUFS4 localization to the mitochondria. Thus, the BAP31-Tom40 ER-mitochondria bridging complex mediates the regulation of mitochondrial function and plays a role as a previously unidentified stress sensor, representing a mechanism for the establishment of ER-mitochondria communication via contact sites between these organelles.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Caspase cleavage product of BAP31 induces mitochondrial fission through endoplasmic reticulum calcium signals, enhancing cytochrome c release to the cytosol.J Cell Biol. 2003 Mar 31;160(7):1115-27. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200212059. J Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 12668660 Free PMC article.
-
Transglutaminase Type 2 Regulates ER-Mitochondria Contact Sites by Interacting with GRP75.Cell Rep. 2018 Dec 26;25(13):3573-3581.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.11.094. Cell Rep. 2018. PMID: 30590033
-
CDIP1-BAP31 complex transduces apoptotic signals from endoplasmic reticulum to mitochondria under endoplasmic reticulum stress.Cell Rep. 2013 Oct 31;5(2):331-9. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2013.09.020. Epub 2013 Oct 17. Cell Rep. 2013. PMID: 24139803 Free PMC article.
-
Endoplasmic Reticulum-Mitochondria Communication Through Ca2+ Signaling: The Importance of Mitochondria-Associated Membranes (MAMs).Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;997:49-67. doi: 10.1007/978-981-10-4567-7_4. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 28815521 Review.
-
Endoplasmic reticulum-mitochondria contacts: function of the junction.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2012 Oct;13(10):607-25. doi: 10.1038/nrm3440. Epub 2012 Sep 20. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22992592 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mitochondrial protein translocation machinery: From TOM structural biogenesis to functional regulation.J Biol Chem. 2022 May;298(5):101870. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2022.101870. Epub 2022 Mar 26. J Biol Chem. 2022. PMID: 35346689 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Construction of an Exudative Age-Related Macular Degeneration Diagnostic and Therapeutic Molecular Network Using Multi-Layer Network Analysis, a Fuzzy Logic Model, and Deep Learning Techniques: Are Retinal and Brain Neurodegenerative Disorders Related?Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Nov 2;16(11):1555. doi: 10.3390/ph16111555. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38004422 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondria-Associated Endoplasmic Reticulum Membranes: Inextricably Linked with Autophagy Process.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022 Aug 23;2022:7086807. doi: 10.1155/2022/7086807. eCollection 2022. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022. PMID: 36052160 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Dysfunctions of Mitochondria-Associated Membranes (MAMs) in Alzheimer's Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Dec 14;21(24):9521. doi: 10.3390/ijms21249521. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33327665 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endoplasmic Reticulum-Mitochondria Contact Sites and Neurodegeneration.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Jun 18;8:428. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.00428. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 32626703 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Suomalainen A., Battersby B. J., Mitochondrial diseases: The contribution of organelle stress responses to pathology. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 19, 77–92 (2018). - PubMed
-
- Walter P., Ron D., The unfolded protein response: From stress pathway to homeostatic regulation. Science 334, 1081–1086 (2011). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

