Mechanisms, Hallmarks, and Implications of Stem Cell Quiescence
- PMID: 31189093
- PMCID: PMC6565921
- DOI: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2019.05.012
Mechanisms, Hallmarks, and Implications of Stem Cell Quiescence
Abstract
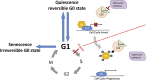
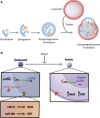
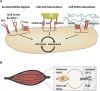
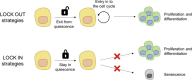
Cellular quiescence is a dormant but reversible cellular state in which cell-cycle entry and proliferation are prevented. Recent studies both in vivo and in vitro demonstrate that quiescence is actively maintained through synergistic interactions between intrinsic and extrinsic signals. Subtypes of adult mammalian stem cells can be maintained in this poised, quiescent state, and subsequently reactivated upon tissue injury to restore homeostasis. However, quiescence can become deregulated in pathological settings. In this review, we discuss the recent advances uncovering intracellular signaling pathways, transcriptional changes, and extracellular cues within the stem cell niche that control induction and exit from quiescence in tissue stem cells. We discuss the implications of quiescence as well as the pharmacological and genetic approaches that are being explored to either induce or prevent quiescence as a therapeutic strategy.
Keywords: autophagy; cancer; cell cycle; cell therapy; niche; quiescence; stem cells.
Copyright © 2019 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Quiescence Entry, Maintenance, and Exit in Adult Stem Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 May 1;20(9):2158. doi: 10.3390/ijms20092158. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31052375 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular regulation of stem cell quiescence.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2013 Jun;14(6):329-40. doi: 10.1038/nrm3591. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23698583 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lysosomes and signaling pathways for maintenance of quiescence in adult neural stem cells.FEBS J. 2021 May;288(10):3082-3093. doi: 10.1111/febs.15555. Epub 2020 Sep 15. FEBS J. 2021. PMID: 32902139 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Regulation of Cellular Quiescence: A Perspective from Adult Stem Cells and Its Niches.Methods Mol Biol. 2018;1686:1-25. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7371-2_1. Methods Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 29030809 Review.
-
Stem cell quiescence: the challenging path to activation.Development. 2021 Feb 8;148(3):dev165084. doi: 10.1242/dev.165084. Development. 2021. PMID: 33558315 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Quiescence and aging of melanocyte stem cells and a novel association with programmed death-ligand 1.iScience. 2024 Sep 12;27(10):110908. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.110908. eCollection 2024 Oct 18. iScience. 2024. PMID: 39351197 Free PMC article.
-
Adult stem cell activity in naked mole rats for long-term tissue maintenance.Nat Commun. 2023 Dec 20;14(1):8484. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-44138-6. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 38123565 Free PMC article.
-
Notch signaling regulates neural stem cell quiescence entry and exit in Drosophila.Development. 2022 Feb 15;149(4):dev200275. doi: 10.1242/dev.200275. Epub 2022 Feb 18. Development. 2022. PMID: 35112131 Free PMC article.
-
Tumour Microenvironment Stress Promotes the Development of Drug Resistance.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Nov 11;10(11):1801. doi: 10.3390/antiox10111801. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34829672 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of metabolism in cellular quiescence.J Cell Sci. 2023 Aug 15;136(16):jcs260787. doi: 10.1242/jcs.260787. Epub 2023 Aug 15. J Cell Sci. 2023. PMID: 37589342 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ali N., Zirak B., Rodriguez R.S., Pauli M.L., Truong H.A., Lai K., Ahn R., Corbin K., Lowe M.M., Scharschmidt T.C. Regulatory T cells in skin facilitate epithelial stem cell differentiation. Cell. 2017;169:1119–1129.e11. - PMC - PubMed
- Ali, N., Zirak, B., Rodriguez, R.S., Pauli, M.L., Truong, H.A., Lai, K., Ahn, R., Corbin, K., Lowe, M.M., Scharschmidt, T.C., et al. (2017). Regulatory T cells in skin facilitate epithelial stem cell differentiation. Cell 169, 1119-1129.e11. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ansó E., Weinberg S.E., Diebold L.P., Thompson B.J., Malinge S., Schumacker P.T., Liu X., Zhang Y., Shao Z., Steadman M. The mitochondrial respiratory chain is essential for haematopoietic stem cell function. Nat. Cell Biol. 2017;19:614–625. - PMC - PubMed
- Anso, E., Weinberg, S.E., Diebold, L.P., Thompson, B.J., Malinge, S., Schumacker, P.T., Liu, X., Zhang, Y., Shao, Z., Steadman, M., et al. (2017). The mitochondrial respiratory chain is essential for haematopoietic stem cell function. Nat. Cell Biol. 19, 614-625. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Arai F., Hirao A., Qhmura M., Sato H., Matsuoka S., Takubo K., Ito K., Koh G.Y., Suda T. Tie2/angiopoietin-1 signaling regulates hematopoietic stem cell quiescence in the bone marrow niche. Cell. 2004;118:149–161. - PubMed
- F. Arai, Hirao, A., Qhmura, M., Sato, H., Matsuoka, S., Takubo, K., Ito, K., and G.Y. Koh, T. Suda. (2004). Tie2/angiopoietin-1 signaling regulates hematopoietic stem cell quiescence in the bone marrow niche. Cell 118, 149-161. - PubMed
-
- Arnold C.P., Tan R., Zhou B., Yue S.-B., Schaffert S., Biggs J.R., Doyonnas R., Lo M.-C., Perry J.M., Renault V.M. MicroRNA programs in normal and aberrant stem and progenitor cells. Genome Res. 2011;21:798–810. - PMC - PubMed
- Arnold, C.P., Tan, R., Zhou, B., Yue, S.-B., Schaffert, S., Biggs, J.R., Doyonnas, R., Lo, M.-C., Perry, J.M., Renault, V.M., et al. (2011). MicroRNA programs in normal and aberrant stem and progenitor cells. Genome Res. 21, 798-810. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

