CYP450s-Activity Relations of Celastrol to Interact with Triptolide Reveal the Reasons of Hepatotoxicity of Tripterygium wilfordii
- PMID: 31181731
- PMCID: PMC6600472
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules24112162
CYP450s-Activity Relations of Celastrol to Interact with Triptolide Reveal the Reasons of Hepatotoxicity of Tripterygium wilfordii
Abstract
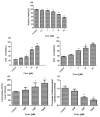
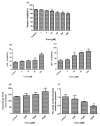
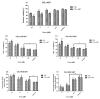
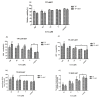
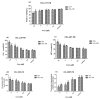
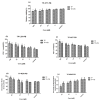
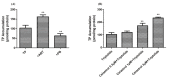
Celastrol and triptolide, as the two main bio-activity ingredients in Tripterygium wilfordii, have wide anticancer pharmacological potency, as well as anti-inflammatory and immunosuppression effects. However, they have potential hepatotoxicity and underlying mechanisms of them-induced toxicity mediated by hepatic CYP450s have not been well delineated. In the present study, we accessed the toxic effects and possible mechanism of celastrol and triptolide on primary rat hepatocytes. Models of subdued/enhanced activity of CYP450 enzymes in primary rat hepatocytes were also constructed to evaluate the relationship between the two ingredients and CYP450s. LC-MS/MS was used to establish a detection method of the amount of triptolide in rat hepatocytes. As the results, cell viability, biochemical index, and mitochondrial membrane potential indicated that celastrol and triptolide had toxic potencies on hepatocytes. Moreover, the toxic effects were enhanced when the compounds combined with 1-aminobenzotriazole (enzyme inhibitor) while they were mitigated when combined with phenobarbital (an enzyme inducer). Meanwhile, celastrol could affect the amount of triptolide in the cell. We therefore put forward that increase of triptolide in the cell might be one of the main causes of hepatotoxicity caused by Tripterygium wilfordii.
Keywords: CYP450 enzymes; celastrol; drug-drug interaction (DDI); hepatotoxicity; triptolide.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Triptolide Induces hepatotoxicity via inhibition of CYP450s in Rat liver microsomes.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2017 Jan 5;17(1):15. doi: 10.1186/s12906-016-1504-3. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2017. PMID: 28056947 Free PMC article.
-
Immunochemical characterization of the functional constituents of Tripterygium wilfordii contributing to its anti-inflammatory property.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2008 Jan;35(1):55-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.2007.04740.x. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18047628
-
Role of CYP3A in regulating hepatic clearance and hepatotoxicity of triptolide in rat liver microsomes and sandwich-cultured hepatocytes.Food Chem Toxicol. 2014 Sep;71:90-6. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2014.05.020. Epub 2014 Jun 6. Food Chem Toxicol. 2014. PMID: 24910460
-
Therapeutic targets of thunder god vine (Tripterygium wilfordii hook) in rheumatoid arthritis (Review).Mol Med Rep. 2020 Jun;21(6):2303-2310. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2020.11052. Epub 2020 Apr 2. Mol Med Rep. 2020. PMID: 32323812 Review.
-
A comprehensive review on celastrol, triptolide and triptonide: Insights on their pharmacological activity, toxicity, combination therapy, new dosage form and novel drug delivery routes.Biomed Pharmacother. 2023 Jun;162:114705. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.114705. Epub 2023 Apr 14. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023. PMID: 37062220 Review.
Cited by
-
The molecular pathogenesis of triptolide-induced hepatotoxicity.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Aug 24;13:979307. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.979307. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36091841 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Celastrol Prevents Oxidative Stress Effects on FSHR, PAPP, and CYP19A1 Gene Expression in Cultured Human Granulosa-Lutein Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 30;22(7):3596. doi: 10.3390/ijms22073596. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33808393 Free PMC article.
-
Advancements in Polymeric Nanocarriers to Mediate Targeted Therapy against Triple-Negative Breast Cancer.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Nov 10;14(11):2432. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14112432. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 36365249 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Celastrol Combats Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus by Targeting Δ1 -Pyrroline-5-Carboxylate Dehydrogenase.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023 Sep;10(25):e2302459. doi: 10.1002/advs.202302459. Epub 2023 Jun 28. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023. PMID: 37381655 Free PMC article.
-
Integrating systematic pharmacology-based strategy and experimental validation to explore mechanism of Tripterygium glycoside on cholangiocyte-related liver injury.Chin Herb Med. 2022 Sep 27;14(4):563-575. doi: 10.1016/j.chmed.2022.02.006. eCollection 2022 Oct. Chin Herb Med. 2022. PMID: 36405068 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tao X.L., Cush J.J., Garret M., Lipsky P.E. A phase I study of ethyl acetate extract of the chinese antirheumatic herb tripterygium wilfordii hook f in rheumatoid arthritis. J. Rheumatol. 2001;28:2160–2167. - PubMed
-
- Chen Y.F., Cai H.D. Investigation of liver damage associated with traditional chinese medicines. Adv. Drug Rea. J. 1999;24:27–32.
-
- Gu S.P., Fan Y.W., Wang L.F., Feng G., Liu S.S., Sheng Y., He X. Analysis on release characteristics of sustained release traditional chinese medicine preparation of leigongteng bilayer tablets based on drug simulating system. Chin. J. Exp. Trad. Med. Formulae. 2015;56:549–567.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

