Senescent cells evade immune clearance via HLA-E-mediated NK and CD8+ T cell inhibition
- PMID: 31160572
- PMCID: PMC6547655
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-019-10335-5
Senescent cells evade immune clearance via HLA-E-mediated NK and CD8+ T cell inhibition
Abstract
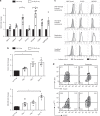
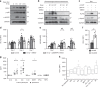
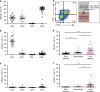
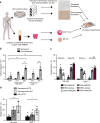
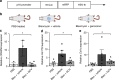
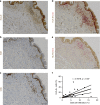
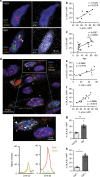
Senescent cells accumulate in human tissues during ageing and contribute to age-related pathologies. The mechanisms responsible for their accumulation are unclear. Here we show that senescent dermal fibroblasts express the non-classical MHC molecule HLA-E, which interacts with the inhibitory receptor NKG2A expressed by NK and highly differentiated CD8+ T cells to inhibit immune responses against senescent cells. HLA-E expression is induced by senescence-associated secretary phenotype-related pro-inflammatory cytokines, and is regulated by p38 MAP kinase signalling in vitro. Consistently, HLA-E expression is increased on senescent cells in human skin sections from old individuals, when compared with those from young, and in human melanocytic nevi relative to normal skin. Lastly, blocking the interaction between HLA-E and NKG2A boosts immune responses against senescent cells in vitro. We thus propose that increased HLA-E expression contributes to persistence of senescent cells in tissues, thereby suggesting a new strategy for eliminating senescent cells during ageing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Unlocking the therapeutic potential of the NKG2A-HLA-E immune checkpoint pathway in T cells and NK cells for cancer immunotherapy.J Immunother Cancer. 2024 Oct 31;12(10):e009934. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2024-009934. J Immunother Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39486805 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Torque teno viruses exhaust and imprint the human immune system via the HLA-E/NKG2A axis.Front Immunol. 2024 Sep 4;15:1447980. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1447980. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39295866 Free PMC article.
-
Balance between activating NKG2D, DNAM-1, NKp44 and NKp46 and inhibitory CD94/NKG2A receptors determine natural killer degranulation towards rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts.Immunology. 2014 Aug;142(4):581-93. doi: 10.1111/imm.12271. Immunology. 2014. PMID: 24673109 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
HLA-E restricted CD8+ T cell subsets are phenotypically altered in multiple sclerosis patients.Mult Scler. 2014 Jun;20(7):790-801. doi: 10.1177/1352458513509703. Epub 2013 Oct 21. Mult Scler. 2014. PMID: 24144875
-
Enhancing Natural Killer and CD8+ T Cell-Mediated Anticancer Cytotoxicity and Proliferation of CD8+ T Cells with HLA-E Monospecific Monoclonal Antibodies.Monoclon Antib Immunodiagn Immunother. 2019 Apr;38(2):38-59. doi: 10.1089/mab.2018.0043. Monoclon Antib Immunodiagn Immunother. 2019. PMID: 31009335 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Therapy-Induced Cellular Senescence: Potentiating Tumor Elimination or Driving Cancer Resistance and Recurrence?Cells. 2024 Jul 30;13(15):1281. doi: 10.3390/cells13151281. Cells. 2024. PMID: 39120312 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Senescence in Wound Repair: Emerging Strategies to Target Chronic Healing Wounds.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Aug 11;8:773. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.00773. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 32850866 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical application and prospect of immune checkpoint inhibitors for CAR-NK cell in tumor immunotherapy.Front Immunol. 2023 Jan 19;13:1081546. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1081546. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36741400 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting senescent cells for a healthier longevity: the roadmap for an era of global aging.Life Med. 2022 Aug 9;1(2):103-119. doi: 10.1093/lifemedi/lnac030. eCollection 2022 Oct. Life Med. 2022. PMID: 36699942 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Age-Related Changes in the Fibroblastic Differon of the Dermis: Role in Skin Aging.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 May 30;23(11):6135. doi: 10.3390/ijms23116135. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35682813 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

