HDL subclass proteomic analysis and functional implication of protein dynamic change during HDL maturation
- PMID: 31153037
- PMCID: PMC6541906
- DOI: 10.1016/j.redox.2019.101222
HDL subclass proteomic analysis and functional implication of protein dynamic change during HDL maturation
Abstract
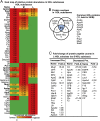
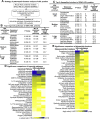
Recent clinical trials reported that increasing high-density lipoprotein-cholesterol (HDL-C) levels does not improve cardiovascular outcomes. We hypothesize that HDL proteome dynamics determine HDL cardioprotective functions. In this study, we characterized proteome profiles in HDL subclasses and established their functional connection. Mouse plasma was fractionized by fast protein liquid chromatography, examined for protein, cholesterial, phospholipid and trigliceride content. Small, medium and large (S/M/L)-HDL subclasseses were collected for proteomic analysis by mass spectrometry. Fifty-one HDL proteins (39 in S-HDL, 27 in M-HDL and 29 in L-HDL) were identified and grouped into 4 functional categories (lipid metabolism, immune response, coagulation, and others). Eleven HDL common proteins were identified in all HDL subclasses. Sixteen, 3 and 7 proteins were found only in S-HDL, M-HDL and L-HDL, respectively. We established HDL protein dynamic distribution in S/M/L-HDL and developed a model of protein composition change during HDL maturation. We found that cholesterol efflux and immune response are essential functions for all HDL particles, and amino acid metabolism is a special function of S-HDL, whereas anti-coagulation is special for M-HDL. Pon1 is recruited into M/L-HDL to provide its antioxidative function. ApoE is incorporated into L-HDL to optimize its cholesterial clearance function. Next, we acquired HDL proteome data from Pubmed and identified 12 replicated proteins in human and mouse HDL particle. Finally, we extracted 3 shared top moleccular pathways (LXR/RXR, FXR/RXR and acute phase response) for all HDL particles and 5 top disease/bio-functions differentially related to S/M/L-HDL subclasses, and presented one top net works for each HDL subclass. We conclude that beside their essencial functions of cholesterol efflux and immune response, HDL aquired antioxidative and cholesterol clearance functions by recruiting Pon1 and ApoE during HDL maturation.
Keywords: Cardiovascular disease; Lipids and cholesterol; Metabolism; Proteomics; Risk factors.
Copyright © 2019 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Proteomic and functional analysis of HDL subclasses in humans and rats: a proof-of-concept study.Lipids Health Dis. 2023 Jun 29;22(1):86. doi: 10.1186/s12944-023-01829-9. Lipids Health Dis. 2023. PMID: 37386457 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding high-density lipoprotein function in disease: recent advances in proteomics unravel the complexity of its composition and biology.Prog Lipid Res. 2014 Oct;56:36-46. doi: 10.1016/j.plipres.2014.07.003. Epub 2014 Aug 6. Prog Lipid Res. 2014. PMID: 25107698 Review.
-
Functional and proteomic alterations of plasma high density lipoproteins in type 1 diabetes mellitus.Metabolism. 2016 Sep;65(9):1421-31. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2016.06.008. Epub 2016 Jun 29. Metabolism. 2016. PMID: 27506748
-
Composition and lipid spatial distribution of HDL particles in subjects with low and high HDL-cholesterol.J Lipid Res. 2010 Aug;51(8):2341-51. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M006494. Epub 2010 Apr 29. J Lipid Res. 2010. PMID: 20431113 Free PMC article.
-
Apolipoprotein A-II is a key regulatory factor of HDL metabolism as appears from studies with transgenic animals and clinical outcomes.Biochimie. 2014 Jan;96:56-66. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2013.08.027. Epub 2013 Sep 5. Biochimie. 2014. PMID: 24012775 Review.
Cited by
-
Lipoprotein proteome profile: novel insight into hyperlipidemia.Clin Transl Med. 2021 Apr;11(4):e361. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.361. Clin Transl Med. 2021. PMID: 33931962 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Proteomic and functional analysis of HDL subclasses in humans and rats: a proof-of-concept study.Lipids Health Dis. 2023 Jun 29;22(1):86. doi: 10.1186/s12944-023-01829-9. Lipids Health Dis. 2023. PMID: 37386457 Free PMC article.
-
High-Density Lipoprotein Subclasses and Their Role in the Prevention and Treatment of Cardiovascular Disease: A Narrative Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 18;25(14):7856. doi: 10.3390/ijms25147856. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39063097 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association between human blood metabolome and the risk of pre-eclampsia.Hypertens Res. 2024 Apr;47(4):1063-1072. doi: 10.1038/s41440-024-01586-x. Epub 2024 Feb 8. Hypertens Res. 2024. PMID: 38332312
-
Apolipoprotein A1, the neglected relative of Apolipoprotein E and its potential role in Alzheimer's disease.Neural Regen Res. 2021 Nov;16(11):2141-2148. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.310669. Neural Regen Res. 2021. PMID: 33818485 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Stone N.J., Robinson J.G., Lichtenstein A.H., Bairey Merz C.N., Blum C.B., Eckel R.H., Goldberg A.C., Gordon D., Levy D., Lloyd-Jones D.M., McBride P., Schwartz J.S., Shero S.T., Smith S.C., Jr., Watson K., Wilson P.W., Eddleman K.M., Jarrett N.M., LaBresh K., Nevo L., Wnek J., Anderson J.L., Halperin J.L., Albert N.M., Bozkurt B., Brindis R.G., Curtis L.H., DeMets D., Hochman J.S., Kovacs R.J., Ohman E.M., Pressler S.J., Sellke F.W., Shen W.K., Tomaselli G.F. 2013 ACC/AHA guideline on the treatment of blood cholesterol to reduce atherosclerotic cardiovascular risk in adults: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on practice guidelines. Circulation. 2014;129:S1–S45. - PubMed
- Stone NJ, Robinson JG, Lichtenstein AH, Bairey Merz CN, Blum CB, Eckel RH, Goldberg AC, Gordon D, Levy D, Lloyd-Jones DM, McBride P, Schwartz JS, Shero ST, Smith SC, Jr., Watson K, Wilson PW, Eddleman KM, Jarrett NM, LaBresh K, Nevo L, Wnek J, Anderson JL, Halperin JL, Albert NM, Bozkurt B, Brindis RG, Curtis LH, DeMets D, Hochman JS, Kovacs RJ, Ohman EM, Pressler SJ, Sellke FW, Shen WK and Tomaselli GF. 2013 ACC/AHA guideline on the treatment of blood cholesterol to reduce atherosclerotic cardiovascular risk in adults: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2014;129:S1-S45. - PubMed
-
- Lincoff A.M., Nicholls S.J., Riesmeyer J.S., Barter P.J., Brewer H.B., Fox K.A.A., Gibson C.M., Granger C., Menon V., Montalescot G., Rader D., Tall A.R., McErlean E., Wolski K., Ruotolo G., Vangerow B., Weerakkody G., Goodman S.G., Conde D., McGuire D.K., Nicolau J.C., Leiva-Pons J.L., Pesant Y., Li W., Kandath D., Kouz S., Tahirkheli N., Mason D., Nissen S.E., Investigators A. Evacetrapib and cardiovascular outcomes in high-risk vascular disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017;376:1933–1942. - PubMed
- Lincoff AM, Nicholls SJ, Riesmeyer JS, Barter PJ, Brewer HB, Fox KAA, Gibson CM, Granger C, Menon V, Montalescot G, Rader D, Tall AR, McErlean E, Wolski K, Ruotolo G, Vangerow B, Weerakkody G, Goodman SG, Conde D, McGuire DK, Nicolau JC, Leiva-Pons JL, Pesant Y, Li W, Kandath D, Kouz S, Tahirkheli N, Mason D, Nissen SE and Investigators A. Evacetrapib and Cardiovascular Outcomes in High-Risk Vascular Disease. N Engl J Med. 2017;376:1933-1942. - PubMed
-
- Liao D., Yang X., Wang H. Hyperhomocysteinemia and high-density lipoprotein metabolism in cardiovascular disease. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2007;45:1652–1659. - PubMed
- Liao D, Yang X and Wang H. Hyperhomocysteinemia and high-density lipoprotein metabolism in cardiovascular disease. Clinical chemistry and laboratory medicine. 2007;45:1652-1659. - PubMed
-
- Liao D., Tan H., Hui R., Li Z., Jiang X., Gaubatz J., Yang F., Durante W., Chan L., Schafer A.I., Pownall H.J., Yang X., Wang H. Hyperhomocysteinemia decreases circulating high-density lipoprotein by inhibiting apolipoprotein A-I Protein synthesis and enhancing HDL cholesterol clearance. Circ. Res. 2006;99:598–606. - PMC - PubMed
- Liao D, Tan H, Hui R, Li Z, Jiang X, Gaubatz J, Yang F, Durante W, Chan L, Schafer AI, Pownall HJ, Yang X and Wang H. Hyperhomocysteinemia decreases circulating high-density lipoprotein by inhibiting apolipoprotein A-I Protein synthesis and enhancing HDL cholesterol clearance. Circulation research. 2006;99:598-606. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 HL138749/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL077288/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL117654/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL130233/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL131460/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL082774/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL110764/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK104116/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL135117/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL067033/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL147565/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK113775/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

