HawkDock: a web server to predict and analyze the protein-protein complex based on computational docking and MM/GBSA
- PMID: 31106357
- PMCID: PMC6602443
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkz397
HawkDock: a web server to predict and analyze the protein-protein complex based on computational docking and MM/GBSA
Abstract
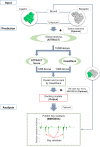
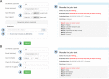
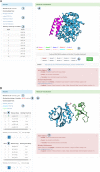
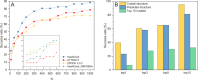
Protein-protein interactions (PPIs) play an important role in the different functions of cells, but accurate prediction of the three-dimensional structures for PPIs is still a notoriously difficult task. In this study, HawkDock, a free and open accessed web server, was developed to predict and analyze the structures of PPIs. In the HawkDock server, the ATTRACT docking algorithm, the HawkRank scoring function developed in our group and the MM/GBSA free energy decomposition analysis were seamlessly integrated into a multi-functional platform. The structures of PPIs were predicted by combining the ATTRACT docking and the HawkRank re-scoring, and the key residues for PPIs were highlighted by the MM/GBSA free energy decomposition. The molecular visualization was supported by 3Dmol.js. For the structural modeling of PPIs, HawkDock could achieve a better performance than ZDOCK 3.0.2 in the benchmark testing. For the prediction of key residues, the important residues that play an essential role in PPIs could be identified in the top 10 residues for ∼81.4% predicted models and ∼95.4% crystal structures in the benchmark dataset. To sum up, the HawkDock server is a powerful tool to predict the binding structures and identify the key residues of PPIs. The HawkDock server is accessible free of charge at http://cadd.zju.edu.cn/hawkdock/.
© The Author(s) 2019. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Protein Interaction Z Score Assessment (PIZSA): an empirical scoring scheme for evaluation of protein-protein interactions.Nucleic Acids Res. 2019 Jul 2;47(W1):W331-W337. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz368. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019. PMID: 31114890 Free PMC article.
-
HPEPDOCK: a web server for blind peptide-protein docking based on a hierarchical algorithm.Nucleic Acids Res. 2018 Jul 2;46(W1):W443-W450. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky357. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018. PMID: 29746661 Free PMC article.
-
InterEvDock2: an expanded server for protein docking using evolutionary and biological information from homology models and multimeric inputs.Nucleic Acids Res. 2018 Jul 2;46(W1):W408-W416. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky377. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018. PMID: 29741647 Free PMC article.
-
The trRosetta server for fast and accurate protein structure prediction.Nat Protoc. 2021 Dec;16(12):5634-5651. doi: 10.1038/s41596-021-00628-9. Epub 2021 Nov 10. Nat Protoc. 2021. PMID: 34759384 Review.
-
Recent Advances in Protein-Protein Docking.Curr Drug Targets. 2016;17(14):1586-1594. doi: 10.2174/1389450117666160112112640. Curr Drug Targets. 2016. PMID: 26758670 Review.
Cited by
-
Insights into structural vaccinology harnessed for universal coronavirus vaccine development.Clin Exp Vaccine Res. 2024 Jul;13(3):202-217. doi: 10.7774/cevr.2024.13.3.202. Epub 2024 Jul 31. Clin Exp Vaccine Res. 2024. PMID: 39144127 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Design of multi-epitope vaccine candidate based on OmpA, CarO and ZnuD proteins against multi-drug resistant Acinetobacter baumannii.Heliyon. 2024 Jul 16;10(14):e34690. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e34690. eCollection 2024 Jul 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39149030 Free PMC article.
-
An mRNA vaccine for pancreatic cancer designed by applying in silico immunoinformatics and reverse vaccinology approaches.PLoS One. 2024 Jul 8;19(7):e0305413. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0305413. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38976715 Free PMC article.
-
Structural modelling of human complement FHR1 and two of its synthetic derivatives provides insight into their in-vivo functions.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2023 Feb 3;21:1473-1486. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2023.02.002. eCollection 2023. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2023. PMID: 36851916 Free PMC article.
-
A comparative study of the arazyme-based fusion proteins with various ligands for more effective targeting cancer therapy: an in-silico analysis.Res Pharm Sci. 2023 Jan 19;18(2):159-176. doi: 10.4103/1735-5362.367795. eCollection 2023 Apr. Res Pharm Sci. 2023. PMID: 36873271 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aloy P., Ceulemans H., Stark A., Russell R.B.. The relationship between sequence and interaction divergence in proteins. J. Mol. Biol. 2003; 332:989–998. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

