NGSEP3: accurate variant calling across species and sequencing protocols
- PMID: 31099384
- PMCID: PMC6853766
- DOI: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btz275
NGSEP3: accurate variant calling across species and sequencing protocols
Abstract
Motivation: Accurate detection, genotyping and downstream analysis of genomic variants from high-throughput sequencing data are fundamental features in modern production pipelines for genetic-based diagnosis in medicine or genomic selection in plant and animal breeding. Our research group maintains the Next-Generation Sequencing Experience Platform (NGSEP) as a precise, efficient and easy-to-use software solution for these features.
Results: Understanding that incorrect alignments around short tandem repeats are an important source of genotyping errors, we implemented in NGSEP new algorithms for realignment and haplotype clustering of reads spanning indels and short tandem repeats. We performed extensive benchmark experiments comparing NGSEP to state-of-the-art software using real data from three sequencing protocols and four species with different distributions of repetitive elements. NGSEP consistently shows comparative accuracy and better efficiency compared to the existing solutions. We expect that this work will contribute to the continuous improvement of quality in variant calling needed for modern applications in medicine and agriculture.
Availability and implementation: NGSEP is available as open source software at http://ngsep.sf.net.
Supplementary information: Supplementary data are available at Bioinformatics online.
© The Author(s) 2019. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures
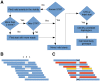
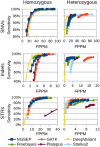

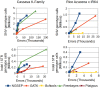
Similar articles
-
Bioinformatic analysis of genotype by sequencing (GBS) data with NGSEP.BMC Genomics. 2016 Aug 31;17 Suppl 5(Suppl 5):498. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-2827-7. BMC Genomics. 2016. PMID: 27585926 Free PMC article.
-
An integrated framework for discovery and genotyping of genomic variants from high-throughput sequencing experiments.Nucleic Acids Res. 2014 Apr;42(6):e44. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt1381. Epub 2014 Jan 11. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014. PMID: 24413664 Free PMC article.
-
Accurate, Efficient and User-Friendly Mutation Calling and Sample Identification for TILLING Experiments.Front Genet. 2021 Feb 3;12:624513. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.624513. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 33613641 Free PMC article.
-
Review of alignment and SNP calling algorithms for next-generation sequencing data.J Appl Genet. 2016 Feb;57(1):71-9. doi: 10.1007/s13353-015-0292-7. Epub 2015 Jun 9. J Appl Genet. 2016. PMID: 26055432 Review.
-
Variant calling: Considerations, practices, and developments.Hum Mutat. 2022 Aug;43(8):976-985. doi: 10.1002/humu.24311. Epub 2021 Dec 16. Hum Mutat. 2022. PMID: 34882898 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Genetic Analyses and Genomic Predictions of Root Rot Resistance in Common Bean Across Trials and Populations.Front Plant Sci. 2021 Mar 12;12:629221. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.629221. eCollection 2021. Front Plant Sci. 2021. PMID: 33777068 Free PMC article.
-
xAtlas: scalable small variant calling across heterogeneous next-generation sequencing experiments.Gigascience. 2022 Dec 28;12:giac125. doi: 10.1093/gigascience/giac125. Epub 2023 Jan 16. Gigascience. 2022. PMID: 36644891 Free PMC article.
-
Large genomic introgression blocks of Phaseolus parvifolius Freytag bean into the common bean enhance the crossability between tepary and common beans.Plant Direct. 2022 Dec 13;6(12):e470. doi: 10.1002/pld3.470. eCollection 2022 Dec. Plant Direct. 2022. PMID: 36523608 Free PMC article.
-
Improving Association Studies and Genomic Predictions for Climbing Beans With Data From Bush Bean Populations.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Apr 25;13:830896. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.830896. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 35557726 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic Prediction of Agronomic Traits in Common Bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) Under Environmental Stress.Front Plant Sci. 2020 Jul 7;11:1001. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2020.01001. eCollection 2020. Front Plant Sci. 2020. PMID: 32774338 Free PMC article.

