Rac-GTPase promotes fibrotic TGF-β1 signaling and chronic kidney disease via EGFR, p53, and Hippo/YAP/TAZ pathways
- PMID: 31095421
- PMCID: PMC6704447
- DOI: 10.1096/fj.201802489RR
Rac-GTPase promotes fibrotic TGF-β1 signaling and chronic kidney disease via EGFR, p53, and Hippo/YAP/TAZ pathways
Abstract
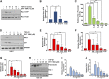
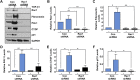
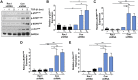
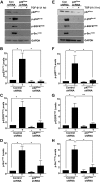
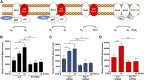
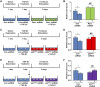
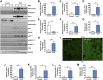
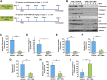
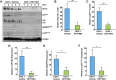
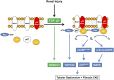
Rac-GTPases are major regulators of cytoskeletal remodeling and their deregulation contributes to numerous pathologies. Whether or how Rac promotes tubulointerstitial fibrosis and chronic kidney disease (CKD) is currently unknown. We showed that the major profibrotic cytokine, TGF-β1 promoted rapid Rac1-GTP loading in human kidney 2 (HK-2) human renal epithelial cells. A Rac-specific chemical inhibitor, EHT 1864, blocked TGF-β1-induced fibrotic reprogramming in kidney epithelial cells and fibroblasts. Stable Rac1 depletion in HK-2 cells, moreover, eliminated TGF-β1-mediated non-SMAD pathway activation [e.g., Src, epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), p53] and subsequent plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1), connective tissue growth factor, fibronectin, and p21 induction. Rac1 and p22phox knockdown abrogated free radical generation by TGF-β1 in HK-2 cells, consistent with the role of Rac1 in NAPD(H). TGF-β1-induced renal epithelial cytostasis was also completely bypassed by Rac1, p22phox, p47phox, and PAI-1 silencing. Rac1b isoform expression was robustly induced in the fibrotic kidneys of mice and humans. Intraperitoneal administration of EHT 1864 in mice dramatically attenuated ureteral unilateral obstruction-driven EGFR, p53, Rac1b, yes-associated protein/transcriptional coactivator with PDZ-binding motif activation/expression, dedifferentiation, cell cycle arrest, and renal fibrogenesis evident in vehicle-treated obstructed kidneys. Thus, the Rac1-directed redox response is critical for TGF-β1-driven epithelial dysfunction orchestrated, in part, via PAI-1 up-regulation. Rac pathway inhibition suppressed renal oxidative stress and maladaptive repair, identifying Rac as a novel therapeutic target against progressive CKD.-Patel, S., Tang, J., Overstreet, J. M., Anorga, S., Lian, F., Arnouk, A., Goldschmeding, R., Higgins, P. J., Samarakoon, R. Rac-GTPase promotes fibrotic TGF-β1 signaling and chronic kidney disease via EGFR, p53, and Hippo/YAP/TAZ pathways.
Keywords: CTGF; NADPH oxidases; PAI-1; Rac1; renal fibrosis.
Conflict of interest statement
R.G. was previously employed (2008–2009) by, performs contract research for, and receives reagents for CTGF-related research from FibroGen, a company involved in the development of anti-CTGF therapies. This study was supported by U.S. National Institutes of Health (NIH), National Institute of General Medical Sciences Grant GM057242 (to P.J.H.), a Capital Region Medical Research Institute grant (to R.S.), the Graver Family Endowment, and the Friedman Family Fund (to P.J.H.). The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Deregulation of Hippo-TAZ pathway during renal injury confers a fibrotic maladaptive phenotype.FASEB J. 2018 May;32(5):2644-2657. doi: 10.1096/fj.201700722R. Epub 2018 Jan 3. FASEB J. 2018. PMID: 29298862 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor suppressor ataxia telangiectasia mutated functions downstream of TGF-β1 in orchestrating profibrotic responses.FASEB J. 2015 Apr;29(4):1258-68. doi: 10.1096/fj.14-262527. Epub 2014 Dec 5. FASEB J. 2015. PMID: 25480384 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of renal fibrotic genes by TGF-β1 requires EGFR activation, p53 and reactive oxygen species.Cell Signal. 2013 Nov;25(11):2198-209. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.07.007. Epub 2013 Jul 18. Cell Signal. 2013. PMID: 23872073
-
TGF-β1-p53 cooperativity regulates a profibrotic genomic program in the kidney: molecular mechanisms and clinical implications.FASEB J. 2019 Oct;33(10):10596-10606. doi: 10.1096/fj.201900943R. Epub 2019 Jul 6. FASEB J. 2019. PMID: 31284746 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TGF-β1 → SMAD/p53/USF2 → PAI-1 transcriptional axis in ureteral obstruction-induced renal fibrosis.Cell Tissue Res. 2012 Jan;347(1):117-28. doi: 10.1007/s00441-011-1181-y. Epub 2011 Jun 4. Cell Tissue Res. 2012. PMID: 21638209 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pregnane X receptor activation alleviates renal fibrosis in mice via interacting with p53 and inhibiting the Wnt7a/β-catenin signaling.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2023 Oct;44(10):2075-2090. doi: 10.1038/s41401-023-01113-7. Epub 2023 Jun 21. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2023. PMID: 37344564 Free PMC article.
-
PAI-1 induction during kidney injury promotes fibrotic epithelial dysfunction via deregulation of klotho, p53, and TGF-β1-receptor signaling.FASEB J. 2021 Jul;35(7):e21725. doi: 10.1096/fj.202002652RR. FASEB J. 2021. PMID: 34110636 Free PMC article.
-
Actin Cytoskeleton and Regulation of TGFβ Signaling: Exploring Their Links.Biomolecules. 2021 Feb 23;11(2):336. doi: 10.3390/biom11020336. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 33672325 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Disruption of LTBP4 Inhibition-Induced TGFβ1 Activation Promoted Cell Proliferation and Metastasis in Skin Melanoma by Inhibiting the Activation of the Hippo-YAP1 Signaling Pathway.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Feb 17;9:673904. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.673904. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35252214 Free PMC article.
-
N6-methyladenosine methylation in kidney injury.Clin Epigenetics. 2023 Oct 21;15(1):170. doi: 10.1186/s13148-023-01586-7. Clin Epigenetics. 2023. PMID: 37865763 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Couser W. G., Remuzzi G., Mendis S., Tonelli M. (2011) The contribution of chronic kidney disease to the global burden of major noncommunicable diseases. Kidney Int. 80, 1258–1270 - PubMed
-
- Jha V., Garcia-Garcia G., Iseki K., Li Z., Naicker S., Plattner B., Saran R., Wang A. Y., Yang C. W. (2013) Chronic kidney disease: global dimension and perspectives. Lancet 382, 260–272 - PubMed
-
- Perico N., Remuzzi G. (2012) Chronic kidney disease: a research and public health priority. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 27(Suppl 3), iii19–iii26 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

