Clotrimazole-Loaded Mediterranean Essential Oils NLC: A Synergic Treatment of Candida Skin Infections
- PMID: 31085997
- PMCID: PMC6572383
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics11050231
Clotrimazole-Loaded Mediterranean Essential Oils NLC: A Synergic Treatment of Candida Skin Infections
Abstract
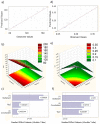
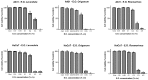
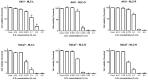
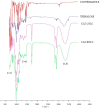
The increasing development of resistance of Candida species to traditional drugs represents a great challenge to the medical field for the treatment of skin infections. Essential oils were recently proposed to increase drug effectiveness. Herein, we developed and optimized (23 full factorial design) Mediterranean essential oil (Rosmarinus officinalis, Lavandula x intermedia "Sumian", Origanum vulgare subsp. hirtum) lipid nanoparticles for clotrimazole delivery, exploring the potential synergistic effects against Candida spp. Small sized nanoparticles (<100 nm) with a very broad size distribution (PDI < 0.15) and long-term stability were successfully prepared. Results of the in vitro biosafety on HaCaT (normal cell line) and A431 (tumoral cell line), allowed us to select Lavandula and Rosmarinus as anti-proliferative agents with the potential to be used as co-adjuvants in the treatment of non-tumoral proliferative dermal diseases. Results of calorimetric studies on biomembrane models, confirmed the potential antimicrobial activity of the selected oils due to their interaction with membrane permeabilization. Nanoparticles provided a prolonged in vitro release of clotrimazole. In vitro studies against Candida albicans, Candida krusei and Candida parapsilosis, showed an increase of the antifungal activity of clotrimazole-loaded nanoparticles prepared with Lavandula or Rosmarinus, thus confirming nanostructured lipid carriers (NLC) containing Mediterranean essential oils represent a promising strategy to improve drug effectiveness against topical candidiasis.
Keywords: DSC; Lavandula x intermedia “Sumian”; Lumisizer; MIC; Origanum vulgare subsp. hirtum; Rosmarinus officinalis L.; Turbiscan; cytotoxicity; factorial design; stability.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Essential Oil-Loaded NLC for Potential Intranasal Administration.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Jul 28;13(8):1166. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13081166. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 34452126 Free PMC article.
-
Mediterranean essential oils as precious matrix components and active ingredients of lipid nanoparticles.Int J Pharm. 2018 Sep 5;548(1):217-226. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2018.06.064. Epub 2018 Jun 30. Int J Pharm. 2018. PMID: 29966744
-
Anti-Candida and Antibiofilm Activity of Selected Lamiaceae Essential Oils.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2023 Feb 16;28(2):28. doi: 10.31083/j.fbl2802028. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2023. PMID: 36866556
-
Candida and candidaemia. Susceptibility and epidemiology.Dan Med J. 2013 Nov;60(11):B4698. Dan Med J. 2013. PMID: 24192246 Review.
-
Anti-Candida Activity of Essential Oils from Lamiaceae Plants from the Mediterranean Area and the Middle East.Antibiotics (Basel). 2020 Jul 9;9(7):395. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics9070395. Antibiotics (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32660009 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Lecithin and Chitosan as Building Blocks in Anti-Candida Clotrimazole Nanoparticles.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 May 25;16(6):790. doi: 10.3390/ph16060790. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37375738 Free PMC article.
-
Solid Lipid Nanoparticles as Carriers of Natural Phenolic Compounds.Antioxidants (Basel). 2020 Oct 15;9(10):998. doi: 10.3390/antiox9100998. Antioxidants (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33076501 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Applications and Prospects of Nanotechnology in Food and Cosmetics Preservation.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022 Apr 3;12(7):1196. doi: 10.3390/nano12071196. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35407315 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Essential Oil-Loaded NLC for Potential Intranasal Administration.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Jul 28;13(8):1166. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13081166. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 34452126 Free PMC article.
-
Antifungal Properties of Essential Oils and Their Compounds for Application in Skin Fungal Infections: Conventional and Nonconventional Approaches.Molecules. 2021 Feb 19;26(4):1093. doi: 10.3390/molecules26041093. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 33669627 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Costa C., Ribeiro J., Miranda I.M., Silva-Dias A., Cavalheiro M., Costa-de-Oliveira S., Rodrigues A.G., Teixeira M.C. Clotrimazole Drug Resistance in Candida glabrata Clinical Isolates Correlates with Increased Expression of the Drug:H(+) Antiporters Cgaqr1, Cgtpo1_1, Cgtpo3, and Cgqdr2. Front. Microbiol. 2016;7:526. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.00526. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

