LINE-1 hypomethylation in human hepatocellular carcinomas correlates with shorter overall survival and CIMP phenotype
- PMID: 31059558
- PMCID: PMC6502450
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0216374
LINE-1 hypomethylation in human hepatocellular carcinomas correlates with shorter overall survival and CIMP phenotype
Abstract
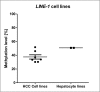
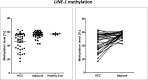
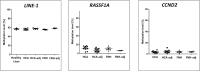
Reactivation of interspersed repetitive sequences due to loss of methylation is associated with genomic instability, one of the hallmarks of cancer cells. LINE-1 hypomethylation is a surrogate marker for global methylation loss and is potentially a new diagnostic and prognostic biomarker in tumors. However, the correlation of LINE-1 hypomethylation with clinicopathological parameters and the CpG island methylator phenotype (CIMP) in patients with liver tumors is not yet well defined, particularly in Caucasians who show quite low rates of HCV/HBV infection and a higher incidence of liver steatosis. Therefore, quantitative DNA methylation analysis of LINE-1, RASSF1A, and CCND2 using pyrosequencing was performed in human hepatocellular carcinomas (HCC, n = 40), hepatocellular adenoma (HCA, n = 10), focal nodular hyperplasia (FNH, n = 5), and corresponding peritumoral liver tissues as well as healthy liver tissues (n = 5) from Caucasian patients. Methylation results were correlated with histopathological findings and clinical data. We found loss of LINE-1 DNA methylation only in HCC. It correlated significantly with poor survival (log rank test, p = 0.007). An inverse correlation was found for LINE-1 and RASSF1A DNA methylation levels (r2 = -0.47, p = 0.002). LINE-1 hypomethylation correlated with concurrent RASSF1/CCND2 hypermethylation (Fisher's exact test, p = 0.02). Both LINE-1 hypomethylation and RASSF1A/CCND2 hypermethylation were not found in benign hepatocellular tumors (HCA and FNH). Our results show that LINE-1 hypomethylation and RASSF1A/CCND2 hypermethylation are epigenetic aberrations specific for the process of malignant liver transformation. In addition, LINE-1 hypomethylation might serve as a future predictive biomarker to identify HCC patients with unfavorable overall survival.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Combination of LINE-1 hypomethylation and RASSF1A promoter hypermethylation in serum DNA is a non-invasion prognostic biomarker for early recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma after curative resection.Neoplasma. 2017;64(5):795-802. doi: 10.4149/neo_2017_519. Neoplasma. 2017. PMID: 28592132
-
LINE-1 methylation level and patient prognosis in a database of 208 hepatocellular carcinomas.Ann Surg Oncol. 2015 Apr;22(4):1280-7. doi: 10.1245/s10434-014-4134-3. Epub 2014 Oct 16. Ann Surg Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25319577 Clinical Trial.
-
hsa-mir-183 is frequently methylated and related to poor survival in human hepatocellular carcinoma.World J Gastroenterol. 2017 Mar 7;23(9):1568-1575. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i9.1568. World J Gastroenterol. 2017. PMID: 28321157 Free PMC article.
-
Association of RASSF1A hypermethylation with risk of HBV/HCV-induced hepatocellular carcinoma: A meta-analysis.Pathol Res Pract. 2020 Oct;216(10):153099. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2020.153099. Epub 2020 Jul 15. Pathol Res Pract. 2020. PMID: 32853942 Review.
-
Review of genetic and epigenetic alterations in hepatocarcinogenesis.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2006 Jan;21(1 Pt 1):15-21. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2005.04043.x. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2006. PMID: 16706806 Review.
Cited by
-
Comprehensive review and updated analysis of DNA methylation in hepatocellular carcinoma: From basic research to clinical application.Clin Transl Med. 2024 Nov;14(11):e70066. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.70066. Clin Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 39462685 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic Regulation in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Microenvironment: A Comprehensive Review.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Nov 27;15(23):5600. doi: 10.3390/cancers15235600. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38067304 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aberrant Methylation of LINE-1 Transposable Elements: A Search for Cancer Biomarkers.Cells. 2020 Sep 2;9(9):2017. doi: 10.3390/cells9092017. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32887319 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hypermethylation of SCAND3 and Myo1g Gene Are Potential Diagnostic Biomarkers for Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Aug 18;12(8):2332. doi: 10.3390/cancers12082332. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32824823 Free PMC article.
-
Global DNA hypomethylation of Alu and LINE-1 transposable elements as an epigenetic biomarker of anti-tuberculosis drug-induced liver injury.Emerg Microbes Infect. 2021 Dec;10(1):1862-1872. doi: 10.1080/22221751.2021.1976079. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2021. PMID: 34467830 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

