Epithelial Injury and Dysfunction in the Pathogenesis of Idiopathic PulmonaryFibrosis
- PMID: 31010463
- PMCID: PMC6481315
- DOI: 10.1016/j.amjms.2019.01.010
Epithelial Injury and Dysfunction in the Pathogenesis of Idiopathic PulmonaryFibrosis
Abstract
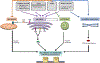
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis is a disease of older adults leading to progressive dyspnea and reduced exercise capacity, typically resulting in death within 3-5years of diagnosis. Underlying genetic susceptibility combined with environmental insults is proposed to trigger a chronic wound repair response, leading to activation of the fibrotic cascade. Perturbations in several molecular pathways mediate vulnerability of the alveolar epithelium to injurious agents, including the unfolded protein response, autophagy, mitophagy, and cellular senescence. These cellular responses are intricately intertwined and link genetic susceptibility to the progressive fibrotic phenotype. Ongoing studies investigating these pathways in type II alveolar epithelial cells show promise for identifying new targeted interventions that could prevent or halt the progression of IPF.
Keywords: Autophagy; Endoplasmic reticulum stress; Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis; Mitophagy; Senescence.
Copyright © 2019 Southern Society for Clinical Investigation. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: TSB and JAK have grant funding from Boehringer Ingelheim and TSB has grant funding from Celgene.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Contributions of alveolar epithelial cell quality control to pulmonary fibrosis.J Clin Invest. 2020 Oct 1;130(10):5088-5099. doi: 10.1172/JCI139519. J Clin Invest. 2020. PMID: 32870817 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mitochondrial Dysfunction as a Pathogenic Mediator of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease and Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis.Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2018 Dec;15(Suppl 4):S266-S272. doi: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.201808-585MG. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2018. PMID: 30759019 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Safety and Tolerability of Alveolar Type II Cell Transplantation in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis.Chest. 2016 Sep;150(3):533-43. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2016.03.021. Epub 2016 Mar 25. Chest. 2016. PMID: 27020420
-
IPF: new insight on pathogenesis and treatment.Allergy. 2010 May;65(5):537-53. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.2009.02305.x. Epub 2010 Feb 1. Allergy. 2010. PMID: 20121758 Review.
-
Cellular senescence and autophagy in the pathogenesis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF).Respir Investig. 2016 Nov;54(6):397-406. doi: 10.1016/j.resinv.2016.03.010. Epub 2016 May 24. Respir Investig. 2016. PMID: 27886850 Review.
Cited by
-
IL-25/IL-33/TSLP contributes to idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Do alveolar epithelial cells and (myo)fibroblasts matter?Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2020 May;245(10):897-901. doi: 10.1177/1535370220915428. Epub 2020 Apr 4. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2020. PMID: 32249602 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Spatial and phenotypic heterogeneity of resident and monocyte-derived macrophages during inflammatory exacerbations leading to pulmonary fibrosis.Front Immunol. 2024 Jul 19;15:1425466. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1425466. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39100672 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting PI3K/AKT signaling for treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2022 Jan;12(1):18-32. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2021.07.023. Epub 2021 Jul 29. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2022. PMID: 35127370 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Loss of IGFBP2 mediates alveolar type 2 cell senescence and promotes lung fibrosis.Cell Rep Med. 2023 Mar 21;4(3):100945. doi: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2023.100945. Epub 2023 Feb 13. Cell Rep Med. 2023. PMID: 36787736 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting GPCR Signaling for Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Therapies.Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2020 Mar;41(3):172-182. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2019.12.008. Epub 2020 Jan 30. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32008852 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cosgrove GP, Brown KK, Schiemann WP, et al. Pigment epithelium-derived factor in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: a role in aberrant angiogenesis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2004;170(3):242–251. - PubMed
-
- Cavazza A, Rossi G, Carbonelli C, et al. The role of histology in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: an update. Respir Med. 2010;104 Suppl 1:S11–22. - PubMed
-
- Myers JL, Katzenstein AL. Beyond a consensus classification for idiopathic interstitial pneumonias: progress and controversies. Histopathology. 2009;54(1):90–103. - PubMed
-
- AL K Pathogenesis of “fibrosis” in interstitial pneumonia: an electron microscopic study. Hum Pathol. 1985;16(10):1015–1024. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

