TRPM7, Magnesium, and Signaling
- PMID: 30995736
- PMCID: PMC6515203
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms20081877
TRPM7, Magnesium, and Signaling
Abstract
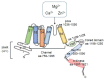
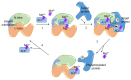
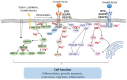
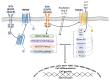
The transient receptor potential melastatin-subfamily member 7 (TRPM7) is a ubiquitously expressed chanzyme that possesses an ion channel permeable to the divalent cations Mg2+, Ca2+, and Zn2+, and an α-kinase that phosphorylates downstream substrates. TRPM7 and its homologue TRPM6 have been implicated in a variety of cellular functions and is critically associated with intracellular signaling, including receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK)-mediated pathways. Emerging evidence indicates that growth factors, such as EGF and VEGF, signal through their RTKs, which regulate activity of TRPM6 and TRPM7. TRPM6 is primarily an epithelial-associated channel, while TRPM7 is more ubiquitous. In this review we focus on TRPM7 and its association with growth factors, RTKs, and downstream kinase signaling. We also highlight how interplay between TRPM7, Mg2+ and signaling kinases influences cell function in physiological and pathological conditions, such as cancer and preeclampsia.
Keywords: EGFR; TRPM7; VEGFR; magnesium transporters; receptor tyrosine kinases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
TRPM6 kinase activity regulates TRPM7 trafficking and inhibits cellular growth under hypomagnesic conditions.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2014 Dec;71(24):4853-67. doi: 10.1007/s00018-014-1647-7. Epub 2014 May 25. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2014. PMID: 24858416 Free PMC article.
-
Transient receptor potential melastatin 6 and 7 channels, magnesium transport, and vascular biology: implications in hypertension.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2008 Mar;294(3):H1103-18. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00903.2007. Epub 2008 Jan 11. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18192217 Review.
-
Epidermal growth factor signaling through transient receptor potential melastatin 7 cation channel regulates vascular smooth muscle cell function.Clin Sci (Lond). 2020 Aug 14;134(15):2019-2035. doi: 10.1042/CS20200827. Clin Sci (Lond). 2020. PMID: 32706027 Free PMC article.
-
TRPM7 and its role in neurodegenerative diseases.Channels (Austin). 2015;9(5):253-61. doi: 10.1080/19336950.2015.1075675. Epub 2015 Jul 28. Channels (Austin). 2015. PMID: 26218331 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The channel-kinase TRPM7, revealing the untold story of Mg(2+) in cellular signaling.Magnes Res. 2014 Jan-Mar;27(1):9-15. doi: 10.1684/mrh.2014.0357. Magnes Res. 2014. PMID: 24752033 Review.
Cited by
-
TRPM7 N-terminal region forms complexes with calcium binding proteins CaM and S100A1.Heliyon. 2021 Nov 27;7(12):e08490. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e08490. eCollection 2021 Dec. Heliyon. 2021. PMID: 34917797 Free PMC article.
-
Role of TRPM7 in cardiac fibrosis: A potential therapeutic target (Review).Exp Ther Med. 2021 Feb;21(2):173. doi: 10.3892/etm.2020.9604. Epub 2020 Dec 27. Exp Ther Med. 2021. PMID: 33456540 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mapping TRPM7 Function by NS8593.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Sep 23;21(19):7017. doi: 10.3390/ijms21197017. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32977698 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptional Control of Trpm6 by the Nuclear Receptor FXR.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Feb 10;23(4):1980. doi: 10.3390/ijms23041980. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35216094 Free PMC article.
-
Ion Channels as Potential Tools for the Diagnosis, Prognosis, and Treatment of HPV-Associated Cancers.Cells. 2023 May 12;12(10):1376. doi: 10.3390/cells12101376. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37408210 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Duan J., Li Z., Li J., Hulse R.E., Santa-Cruz A., Valinsky W.C., Abiria S.A., Krapivinsky G., Zhang J., Clapham D.E. Structure of the mammalian TRPM7, a magnesium channel required during embryonic development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2018;115:E8201–E8210. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1810719115. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

