Perilipin 5 alleviates HCV NS5A-induced lipotoxic injuries in liver
- PMID: 30954078
- PMCID: PMC6451786
- DOI: 10.1186/s12944-019-1022-7
Perilipin 5 alleviates HCV NS5A-induced lipotoxic injuries in liver
Abstract
Background: The homeostasis of lipid droplets (LDs) plays a crucial role in maintaining the physical metabolic processes in cells, and is regulated by many LD-associated proteins, including perilipin 5 (Plin5) in liver. As the putative sites of hepatitis C virus (HCV) virion assembly, LDs are vital to viral infection. In addition, the hepatic LD metabolism can be disturbed by non-structural HCV proteins, such as NS5A, but the details are still inexplicit.
Methods: HCV NS5A was overexpressed in the livers and hepatocytes of wild-type and Plin5-null mice. BODIPY 493/503 and oil red O staining were used to detect the lipid content in mouse livers and hepatocytes. The levels of lipids, lipid peroxidation and inflammation biomarkers were further determined. Immunofluorescence assay and co-immunoprecipitation assay were performed to investigate the relationship of Plin5 and NS5A.
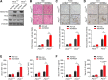
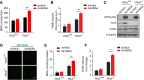
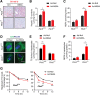
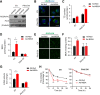
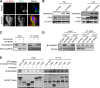
Results: One week after adenovirus injection, livers expressing NS5A showed more inflammatory cell aggregation and more severe hepatic injuries in Plin5-null mice than in control mice, which was consistent with the increased serum levels of IL-2 and TNF-α (P < 0.05) observed in Plin5-null mice. Moreover, Plin5 deficiency in the liver and hepatocytes aggravated the elevation of MDA and 4-HNE levels induced by NS5A expression (P < 0.01). The triglyceride (TG) content was increased approximately 25% by NS5A expression in the wild-type liver and hepatocytes but was unchanged in the Plin5-null liver and hepatocytes. More importantly, Plin5 deficiency in the liver and hepatocytes exacerbated the elevation of non-esterified fatty acids (NEFAs) stimulated by NS5A expression (P < 0.05 and 0.01 respectively). Using triacsin C to block acyl-CoA biosynthesis, we found that Plin5 deficiency aggravated the NS5A-induced lipolysis of TG. In contrast, Plin5 overexpression in HepG2 cells ameliorated the NS5A-induced lipolysis and lipotoxic injuries. Immunofluorescent staining demonstrated that NS5A expression stimulated the targeting of Plin5 to the surface of the LDs in hepatocytes without altering the protein levels of Plin5. By co-IP, we found that the N-terminal domain (aa 32-128) of Plin5 was pivotal for its binding with NS5A.
Conclusions: Our data highlight a protective role of Plin5 against hepatic lipotoxic injuries induced by HCV NS5A, which is helpful for understanding the steatosis and injuries in liver during HCV infection.
Keywords: Hepatitis C virus; Lipid droplet; Lipolysis; Nonstructural protein 5A; Perilipin 5.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All animal experiments were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committees of Fourth Military Medical University.
Consent for publication
All authors read and approve the final manuscript.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Perilipin 5 promotes hepatic steatosis in dairy cows through increasing lipid synthesis and decreasing very low density lipoprotein assembly.J Dairy Sci. 2019 Jan;102(1):833-845. doi: 10.3168/jds.2018-15208. Epub 2018 Nov 8. J Dairy Sci. 2019. PMID: 30415861
-
Perilipin 5 improves hepatic lipotoxicity by inhibiting lipolysis.Hepatology. 2015 Mar;61(3):870-82. doi: 10.1002/hep.27409. Epub 2015 Jan 28. Hepatology. 2015. PMID: 25179419
-
The lipid droplet-associated protein perilipin 3 facilitates hepatitis C virus-driven hepatic steatosis.J Lipid Res. 2017 Feb;58(2):420-432. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M073734. Epub 2016 Dec 10. J Lipid Res. 2017. PMID: 27941027 Free PMC article.
-
Pathophysiology of lipid droplet proteins in liver diseases.Exp Cell Res. 2016 Jan 15;340(2):187-92. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2015.10.021. Epub 2015 Oct 26. Exp Cell Res. 2016. PMID: 26515554 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of lipid droplet proteins in liver steatosis.J Physiol Biochem. 2011 Dec;67(4):629-36. doi: 10.1007/s13105-011-0110-6. Epub 2011 Aug 17. J Physiol Biochem. 2011. PMID: 21847662 Review.
Cited by
-
Yam Gruel alone and in combination with metformin regulates hepatic lipid metabolism disorders in a diabetic rat model by activating the AMPK/ACC/CPT-1 pathway.Lipids Health Dis. 2024 Jan 25;23(1):28. doi: 10.1186/s12944-024-02014-2. Lipids Health Dis. 2024. PMID: 38273354 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid droplets in pathogen infection and host immunity.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2024 Mar;45(3):449-464. doi: 10.1038/s41401-023-01189-1. Epub 2023 Nov 22. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2024. PMID: 37993536 Review.
-
Hepatitis C virus nonstructural protein 5A perturbs lipid metabolism by modulating AMPK/SREBP-1c signaling.Lipids Health Dis. 2019 Nov 4;18(1):191. doi: 10.1186/s12944-019-1136-y. Lipids Health Dis. 2019. PMID: 31684957 Free PMC article.
-
Isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 mutation enhances 24(S)-hydroxycholesterol production and alters cholesterol homeostasis in glioma.Oncogene. 2020 Oct;39(40):6340-6353. doi: 10.1038/s41388-020-01439-0. Epub 2020 Aug 27. Oncogene. 2020. PMID: 32855525
-
Lipid Droplet-Associated Proteins Perilipin 1 and 2: Molecular Markers of Steatosis and Microvesicular Steatotic Foci in Chronic Hepatitis C.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 7;23(24):15456. doi: 10.3390/ijms232415456. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36555099 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

