Exosomes: composition, biogenesis, and mechanisms in cancer metastasis and drug resistance
- PMID: 30940145
- PMCID: PMC6444571
- DOI: 10.1186/s12943-019-0991-5
Exosomes: composition, biogenesis, and mechanisms in cancer metastasis and drug resistance
Abstract
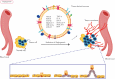
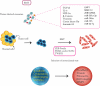
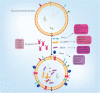
Tumor-derived exosomes (TDEs) participate in formation and progression of different cancer processes, including tumor microenvironment (TME) remodeling, angiogenesis, invasion, metastasis and drug-resistance. Exosomes initiate or suppress various signaling pathways in the recipient cells via transmitting heterogeneous cargoes. In this review we discuss exosome biogenesis, exosome mediated metastasis and chemoresistance. Furthermore, tumor derived exosomes role in tumor microenvironment remodeling, and angiogenesis is reviewed. Also, exosome induction of epithelial mesenchymal transition (EMT) is highlighted. More importantly, we discuss extensively how exosomes regulate drug resistance in several cancers. Thus, understanding exosome biogenesis, their contents and the molecular mechanisms and signaling pathways that are responsible for metastasis and drug-resistance mediated by TDEs may help to devise novel therapeutic approaches for cancer progression particularly to overcome therapy-resistance and preventing metastasis as major factors of cancer mortality.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Emerging role of tumor microenvironment derived exosomes in therapeutic resistance and metastasis through epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition.Life Sci. 2021 Sep 1;280:119750. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119750. Epub 2021 Jun 23. Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 34171378 Review.
-
The Role of Exosomes in Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition and Cell Functional Properties in Head and Neck Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Apr 5;15(7):2156. doi: 10.3390/cancers15072156. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37046817 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of tumour-derived exosomes in metastasis.Biomed Pharmacother. 2022 Mar;147:112657. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112657. Epub 2022 Jan 22. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022. PMID: 35078096 Review.
-
The multifaceted role of exosomes in cancer progression: diagnostic and therapeutic implications [corrected].Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2018 Jun;41(3):223-252. doi: 10.1007/s13402-018-0378-4. Epub 2018 Apr 17. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2018. PMID: 29667069 Review.
-
Exosome-mediated metabolic reprogramming: the emerging role in tumor microenvironment remodeling and its influence on cancer progression.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020 Oct 19;5(1):242. doi: 10.1038/s41392-020-00359-5. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020. PMID: 33077737 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Role of Exosomal miRNAs and the Tumor Microenvironment in Drug Resistance.Cells. 2020 Jun 11;9(6):1450. doi: 10.3390/cells9061450. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32545155 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exosomes: Methods for Isolation and Characterization in Biological Samples.Methods Mol Biol. 2024;2835:181-213. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-3995-5_17. Methods Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 39105917 Review.
-
Extracellular signals regulate the biogenesis of extracellular vesicles.Biol Res. 2022 Nov 26;55(1):35. doi: 10.1186/s40659-022-00405-2. Biol Res. 2022. PMID: 36435789 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulated secretion of mutant p53 negatively affects T lymphocytes in the tumor microenvironment.Oncogene. 2024 Jan;43(2):92-105. doi: 10.1038/s41388-023-02886-1. Epub 2023 Nov 11. Oncogene. 2024. PMID: 37952080 Free PMC article.
-
Platelets Extracellular Vesicles as Regulators of Cancer Progression-An Updated Perspective.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jul 22;21(15):5195. doi: 10.3390/ijms21155195. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32707975 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

