Multiple Variables at the Leukocyte Cell Surface Impact Fc γ Receptor-Dependent Mechanisms
- PMID: 30837990
- PMCID: PMC6382684
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00223
Multiple Variables at the Leukocyte Cell Surface Impact Fc γ Receptor-Dependent Mechanisms
Abstract
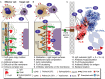
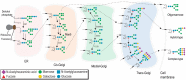
Fc γ receptors (FcγR) expressed on the surface of human leukocytes bind clusters of immunoglobulin G (IgG) to induce a variety of responses. Many therapeutic antibodies and vaccine-elicited antibodies prevent or treat infectious diseases, cancers and autoimmune disorders by binding FcγRs, thus there is a need to fully define the variables that impact antibody-induced mechanisms to properly evaluate candidate therapies and design new intervention strategies. A multitude of factors influence the IgG-FcγR interaction; one well-described factor is the differential affinity of the six distinct FcγRs for the four human IgG subclasses. However, there are several other recently described factors that may prove more relevant for disease treatment. This review covers recent reports of several aspects found at the leukocyte membrane or outside the cell that contribute to the cell-based response to antibody-coated targets. One major focus is recent reports covering post-translational modification of the FcγRs, including asparagine-linked glycosylation. This review also covers the organization of FcγRs at the cell surface, and properties of the immune complex. Recent technical advances provide high-resolution measurements of these often-overlooked variables in leukocyte function and immune system activation.
Keywords: ADCC—antibody dependent cellular cytotoxicity; ADCP—antibody dependent cellular phagocytosis; IgG; N-glycosylation; antibody; immune complex; post-translation modification.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Multi-Angle Effector Function Analysis of Human Monoclonal IgG Glycovariants.PLoS One. 2015 Dec 11;10(12):e0143520. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0143520. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26657484 Free PMC article.
-
CD16a with oligomannose-type N-glycans is the only "low-affinity" Fc γ receptor that binds the IgG crystallizable fragment with high affinity in vitro.J Biol Chem. 2018 Oct 26;293(43):16842-16850. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.004998. Epub 2018 Sep 13. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 30213862 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of immune complex size and glycosylation on IgG binding to human FcγRs.J Immunol. 2013 Apr 15;190(8):4315-23. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1200501. Epub 2013 Mar 18. J Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23509345
-
Functional diversification of IgGs through Fc glycosylation.J Clin Invest. 2019 Sep 3;129(9):3492-3498. doi: 10.1172/JCI130029. J Clin Invest. 2019. PMID: 31478910 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural analysis of Fc/FcγR complexes: a blueprint for antibody design.Immunol Rev. 2015 Nov;268(1):201-21. doi: 10.1111/imr.12365. Immunol Rev. 2015. PMID: 26497522 Review.
Cited by
-
Inflammatory activation of the FcγR and IFNγR pathways co-influences the differentiation and activity of osteoclasts.Front Immunol. 2022 Sep 6;13:958974. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.958974. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36148242 Free PMC article.
-
The Chicken Embryo Model: A Novel and Relevant Model for Immune-Based Studies.Front Immunol. 2021 Nov 19;12:791081. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.791081. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34868080 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Negative Effect of Preexisting Immunity on Influenza Vaccine Responses Transcends the Impact of Vaccine Formulation Type and Vaccination History.J Infect Dis. 2023 Feb 1;227(3):381-390. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiac068. J Infect Dis. 2023. PMID: 35199825 Free PMC article.
-
FcγR-Mediated Trogocytosis 2.0: Revisiting History Gives Rise to a Unifying Hypothesis.Antibodies (Basel). 2022 Jul 5;11(3):45. doi: 10.3390/antib11030045. Antibodies (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35892705 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A self-binding immune complex vaccine elicits strong neutralizing responses against herpes simplex virus in mice.Front Immunol. 2023 May 2;14:1085911. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1085911. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37205110 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

