Machine Learning Analyses on Data including Essential Oil Chemical Composition and In Vitro Experimental Antibiofilm Activities against Staphylococcus Species
- PMID: 30832446
- PMCID: PMC6429525
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules24050890
Machine Learning Analyses on Data including Essential Oil Chemical Composition and In Vitro Experimental Antibiofilm Activities against Staphylococcus Species
Abstract
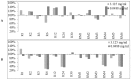
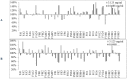
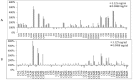
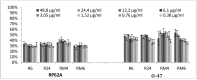
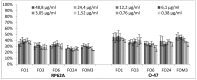
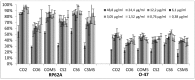
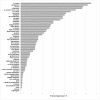
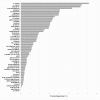
Biofilm resistance to antimicrobials is a complex phenomenon, driven not only by genetic mutation induced resistance, but also by means of increased microbial cell density that supports horizontal gene transfer across cells. The prevention of biofilm formation and the treatment of existing biofilms is currently a difficult challenge; therefore, the discovery of new multi-targeted or combinatorial therapies is growing. The development of anti-biofilm agents is considered of major interest and represents a key strategy as non-biocidal molecules are highly valuable to avoid the rapid appearance of escape mutants. Among bacteria, staphylococci are predominant causes of biofilm-associated infections. Staphylococci, especially Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) is an extraordinarily versatile pathogen that can survive in hostile environmental conditions, colonize mucous membranes and skin, and can cause severe, non-purulent, toxin-mediated diseases or invasive pyogenic infections in humans. Staphylococcus epidermidis (S. epidermidis) has also emerged as an important opportunistic pathogen in infections associated with medical devices (such as urinary and intravascular catheters, orthopaedic implants, etc.), causing approximately from 30% to 43% of joint prosthesis infections. The scientific community is continuously looking for new agents endowed of anti-biofilm capabilities to fight S. aureus and S epidermidis infections. Interestingly, several reports indicated in vitro efficacy of non-biocidal essential oils (EOs) as promising treatment to reduce bacterial biofilm production and prevent the inducing of drug resistance. In this report were analyzed 89 EOs with the objective of investigating their ability to modulate bacterial biofilm production of different S. aureus and S. epidermidis strains. Results showed the assayed EOs to modulated the biofilm production with unpredictable results for each strain. In particular, many EOs acted mainly as biofilm inhibitors in the case of S. epidermidis strains, while for S. aureus strains, EOs induced either no effect or stimulate biofilm production. In order to elucidate the obtained experimental results, machine learning (ML) algorithms were applied to the EOs' chemical compositions and the determined associated anti-biofilm potencies. Statistically robust ML models were developed, and their analysis in term of feature importance and partial dependence plots led to indicating those chemical components mainly responsible for biofilm production, inhibition or stimulation for each studied strain, respectively.
Keywords: Staphylococcus species; antimicrobial; biofilm; essential oil; machine learning.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest
Figures



Similar articles
-
Essential Oils Biofilm Modulation Activity, Chemical and Machine Learning Analysis. Application on Staphylococcus aureus Isolates from Cystic Fibrosis Patients.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Dec 4;21(23):9258. doi: 10.3390/ijms21239258. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33291608 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial and Antibiofilm Activity and Machine Learning Classification Analysis of Essential Oils from Different Mediterranean Plants against Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Molecules. 2018 Feb 23;23(2):482. doi: 10.3390/molecules23020482. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 29473844 Free PMC article.
-
Antibacterial, antibiofilm and antiquorum sensing effects of Thymus daenensis and Satureja hortensis essential oils against Staphylococcus aureus isolates.J Appl Microbiol. 2018 Feb;124(2):379-388. doi: 10.1111/jam.13639. Epub 2018 Jan 11. J Appl Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29144601
-
Antibiofilm activity of three Actinomycete strains against Staphylococcus epidermidis.Lett Appl Microbiol. 2019 Jan;68(1):73-80. doi: 10.1111/lam.13087. Epub 2018 Nov 22. Lett Appl Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 30338533 Review.
-
Biofilm formation by staphylococci in health-related environments and recent reports on their control using natural compounds.Crit Rev Microbiol. 2019 Mar;45(2):201-222. doi: 10.1080/1040841X.2019.1573802. Epub 2019 Feb 20. Crit Rev Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 30786799 Review.
Cited by
-
Feijoa Fruit Peel: Micro-morphological Features, Evaluation of Phytochemical Profile, and Biological Properties of Its Essential Oil.Antioxidants (Basel). 2019 Aug 19;8(8):320. doi: 10.3390/antiox8080320. Antioxidants (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31430937 Free PMC article.
-
In-Vitro Inhibition of Staphylococcal Pathogenesis by Witch-Hazel and Green Tea Extracts.Antibiotics (Basel). 2019 Nov 29;8(4):244. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics8040244. Antibiotics (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31795423 Free PMC article.
-
Advancing understanding of microbial biofilms through machine learning-powered studies.Food Sci Biotechnol. 2023 Aug 28;32(12):1653-1664. doi: 10.1007/s10068-023-01415-w. eCollection 2023 Oct. Food Sci Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37780593 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polymeric Carriers Designed for Encapsulation of Essential Oils with Biological Activity.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Apr 28;13(5):631. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13050631. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 33925127 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In Vitro Antioxidant and In Vivo Antigenotoxic Features of a Series of 61 Essential Oils and Quantitative Composition-Activity Relationships Modeled through Machine Learning Algorithms.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Sep 29;12(10):1815. doi: 10.3390/antiox12101815. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37891894 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Da Costa Krewer C., Santos Amanso E., Veneroni Gouveia G., de Lima Souza R., da Costa M.M., Aparecido Mota R. Resistance to antimicrobials and biofilm formation in Staphylococcus spp. isolated from bovine mastitis in the Northeast of Brazil. Trop Anim. Health Prod. 2015;47:511–518. doi: 10.1007/s11250-014-0752-9. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Satpathy S., Sen S.K., Pattanaik S., Raut S. Review on bacterial biofilm: An universal cause of contamination. Biocatal. Agric. Biotech. 2016;7:56–66. doi: 10.1016/j.bcab.2016.05.002. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

