A multi-task convolutional deep neural network for variant calling in single molecule sequencing
- PMID: 30824707
- PMCID: PMC6397153
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-019-09025-z
A multi-task convolutional deep neural network for variant calling in single molecule sequencing
Abstract
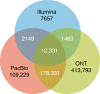
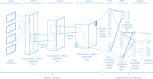
The accurate identification of DNA sequence variants is an important, but challenging task in genomics. It is particularly difficult for single molecule sequencing, which has a per-nucleotide error rate of ~5-15%. Meeting this demand, we developed Clairvoyante, a multi-task five-layer convolutional neural network model for predicting variant type (SNP or indel), zygosity, alternative allele and indel length from aligned reads. For the well-characterized NA12878 human sample, Clairvoyante achieves 99.67, 95.78, 90.53% F1-score on 1KP common variants, and 98.65, 92.57, 87.26% F1-score for whole-genome analysis, using Illumina, PacBio, and Oxford Nanopore data, respectively. Training on a second human sample shows Clairvoyante is sample agnostic and finds variants in less than 2 h on a standard server. Furthermore, we present 3,135 variants that are missed using Illumina but supported independently by both PacBio and Oxford Nanopore reads. Clairvoyante is available open-source ( https://github.com/aquaskyline/Clairvoyante ), with modules to train, utilize and visualize the model.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A universal SNP and small-indel variant caller using deep neural networks.Nat Biotechnol. 2018 Nov;36(10):983-987. doi: 10.1038/nbt.4235. Epub 2018 Sep 24. Nat Biotechnol. 2018. PMID: 30247488
-
Clair3-trio: high-performance Nanopore long-read variant calling in family trios with trio-to-trio deep neural networks.Brief Bioinform. 2022 Sep 20;23(5):bbac301. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbac301. Brief Bioinform. 2022. PMID: 35849103 Free PMC article.
-
Deepbinner: Demultiplexing barcoded Oxford Nanopore reads with deep convolutional neural networks.PLoS Comput Biol. 2018 Nov 20;14(11):e1006583. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1006583. eCollection 2018 Nov. PLoS Comput Biol. 2018. PMID: 30458005 Free PMC article.
-
HELLO: improved neural network architectures and methodologies for small variant calling.BMC Bioinformatics. 2021 Aug 14;22(1):404. doi: 10.1186/s12859-021-04311-4. BMC Bioinformatics. 2021. PMID: 34391391 Free PMC article.
-
The Future of Livestock Management: A Review of Real-Time Portable Sequencing Applied to Livestock.Genes (Basel). 2020 Dec 9;11(12):1478. doi: 10.3390/genes11121478. Genes (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33317066 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Somatic and Germline Variant Calling from Next-Generation Sequencing Data.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2022;1361:37-54. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-91836-1_3. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2022. PMID: 35230682
-
A primer on deep learning in genomics.Nat Genet. 2019 Jan;51(1):12-18. doi: 10.1038/s41588-018-0295-5. Epub 2018 Nov 26. Nat Genet. 2019. PMID: 30478442 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Using synthetic chromosome controls to evaluate the sequencing of difficult regions within the human genome.Genome Biol. 2022 Jan 12;23(1):19. doi: 10.1186/s13059-021-02579-6. Genome Biol. 2022. PMID: 35022065 Free PMC article.
-
Validation of genetic variants from NGS data using deep convolutional neural networks.BMC Bioinformatics. 2023 Apr 20;24(1):158. doi: 10.1186/s12859-023-05255-7. BMC Bioinformatics. 2023. PMID: 37081386 Free PMC article.
-
Nanopore sequencing: a rapid solution for infectious disease epidemics.Sci China Life Sci. 2019 Aug;62(8):1101-1103. doi: 10.1007/s11427-019-9596-x. Epub 2019 Jul 31. Sci China Life Sci. 2019. PMID: 31372817 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

