Inhibition of LOXL2 Enhances the Radiosensitivity of Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer Cells Associated with the Reversal of the EMT Process
- PMID: 30809541
- PMCID: PMC6369494
- DOI: 10.1155/2019/4012590
Inhibition of LOXL2 Enhances the Radiosensitivity of Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer Cells Associated with the Reversal of the EMT Process
Abstract
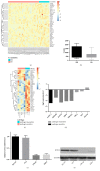
Introduction: Radiotherapy is the mainstay in the treatment of prostate cancer. However, significant radioresistance of castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC) cells constitutes a main obstacle in the treatment of this disease. By using bioinformatic data mining methods, LOXL2 was found to be upregulated in both androgen-independent prostate cancer cell lines and radioresistant tumor samples collected from patients with prostate cancer. We speculate that LOXL2 may play an important role in the radioresistance of CRPC cells.
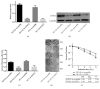
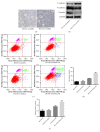
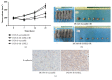
Methods: The effect of LOXL2 knockdown on the radiosensitivity of androgen-independent prostate cancer cells lines was measured by the clonogenic assay and xenograft tumor experiments under in vitro and in vivo conditions, respectively. In studies on the mechanism, we focused on the EMT phenotype changes and cell apoptosis changes induced by LOXL2 knockdown in DU145 cells. The protein levels of three EMT biomarkers, namely, E-cadherin, vimentin, and N-cadherin, were measured by western blotting and immunohistochemical staining. Cell apoptosis after irradiation was measured by flow cytometry and caspase-3 activity assay. Salvage experiment was also conducted to confirm the possible role of EMT in the radiosensitization effect of LOXL2 knockdown in CRPC cells.
Results: LOXL2 knockdown in CRPC cells enhanced cellular radiosensitivity under both in vitro and in vivo conditions. A significant reversal of EMT was observed in LOXL2-silenced DU145 cells. Cell apoptosis after irradiation was significantly enhanced by LOXL2 knockdown in DU145 cells. Results from the salvage experiment confirmed the key role of EMT process reversal in the radiosensitization effect of LOXL2 knockdown in DU145 cells.
Conclusions: LOXL2 plays an important role in the development of cellular radioresistance in CRPC cells. Targeting LOXL2 may be a rational avenue to overcome radioresistance in CRPC cells. A LOXL2-targeting strategy for CRPC treatment warrants detailed investigation in the future.
Figures
Similar articles
-
m6A Modification Promotes EMT and Metastasis of Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer by Upregulating NFIB.Cancer Res. 2024 Jun 14;84(12):1947-1962. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-23-1954. Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 38536119
-
Inhibition of LSD1 by Pargyline inhibited process of EMT and delayed progression of prostate cancer in vivo.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015 Nov 13;467(2):310-5. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.09.164. Epub 2015 Oct 3. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015. PMID: 26435505
-
PDLIM2 suppression efficiently reduces tumor growth and invasiveness of human castration-resistant prostate cancer-like cells.Prostate. 2016 Feb 15;76(3):273-85. doi: 10.1002/pros.23118. Epub 2015 Oct 26. Prostate. 2016. PMID: 26499308
-
Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition Signaling and Prostate Cancer Stem Cells: Emerging Biomarkers and Opportunities for Precision Therapeutics.Genes (Basel). 2021 Nov 27;12(12):1900. doi: 10.3390/genes12121900. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34946849 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epithelial-mesenchymal-transition regulators in prostate cancer: Androgens and beyond.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2017 Feb;166:84-90. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2016.05.007. Epub 2016 May 14. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 27189666 Review.
Cited by
-
Low Numbers of Vascular Vessels Correlate to Progression in Hormone-Naïve Prostate Carcinomas Undergoing Radical Prostatectomy.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Sep 12;11(9):1356. doi: 10.3390/cancers11091356. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31547460 Free PMC article.
-
The extracellular matrix component perlecan/HSPG2 regulates radioresistance in prostate cancer cells.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Aug 1;12:1452463. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1452463. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 39149513 Free PMC article.
-
Association between breast cancer cell migration and radiosensitivity in vitro.Oncol Lett. 2019 Dec;18(6):6877-6884. doi: 10.3892/ol.2019.11027. Epub 2019 Oct 31. Oncol Lett. 2019. PMID: 31807191 Free PMC article.
-
Define cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) in the tumor microenvironment: new opportunities in cancer immunotherapy and advances in clinical trials.Mol Cancer. 2023 Oct 2;22(1):159. doi: 10.1186/s12943-023-01860-5. Mol Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37784082 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular Matrix in the Tumor Microenvironment and Its Impact on Cancer Therapy.Front Mol Biosci. 2020 Jan 31;6:160. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2019.00160. eCollection 2019. Front Mol Biosci. 2020. PMID: 32118030 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Nakfoor B., Zietman A., Gerweck L., Shipley W. An assessment of the in vitro radiosensitivity of a human prostate cancer cell line: The influence of the hormonal millieu. International Journal of Radiation Oncology Biology Physics. 1994;30:p. 321. doi: 10.1016/0360-3016(94)90910-5. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

