Cell lineage-specific genome-wide DNA methylation analysis of patients with paediatric-onset systemic lupus erythematosus
- PMID: 30806140
- PMCID: PMC6557544
- DOI: 10.1080/15592294.2019.1585176
Cell lineage-specific genome-wide DNA methylation analysis of patients with paediatric-onset systemic lupus erythematosus
Abstract
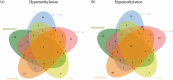
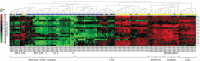
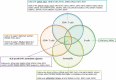
Patients with paediatric-onset systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) often present with more severe clinical courses than adult-onset patients. Although genome-wide DNA methylation (DNAm) profiling has been performed in adult-onset SLE patients, parallel data on paediatric-onset SLE are not available. Therefore, we undertook a genome-wide DNAm study in paediatric-onset SLE patients across multiple blood cell lineages. The DNAm profiles of four purified immune cell lineages (CD4 + T cells, CD8 + T cells, B cells and neutrophils) and whole blood were compared in 16 Chinese patients with paediatric-onset SLE and 13 healthy controls using the Illumina HumanMethylationEPIC BeadChip. Comparison of DNAm in whole blood and within each independent cell lineage identified a consistent pattern of loss of DNAm at 21 CpG sites overlapping 15 genes, which represented a robust, disease-specific DNAm signature for paediatric-onset SLE in our cohort. In addition, cell lineage-specific changes, involving both loss and gain of DNAm, were observed in both novel genes and genes with well-described roles in SLE pathogenesis. This study also highlights the importance of studying DNAm changes in different immune cell lineages rather than only whole blood, since cell type-specific DNAm changes facilitated the elucidation of the cell type-specific molecular pathophysiology of SLE.
Keywords: DNA methylation; MethylationEPIC; SLE; blood; cell composition; cell lineage-specific; lupus; paediatric-onset.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Genome-wide DNA methylation analysis of systemic lupus erythematosus reveals persistent hypomethylation of interferon genes and compositional changes to CD4+ T-cell populations.PLoS Genet. 2013;9(8):e1003678. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003678. Epub 2013 Aug 8. PLoS Genet. 2013. PMID: 23950730 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide DNA methylation analysis implicates enrichment of interferon pathway in African American patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and European Americans with lupus nephritis.J Autoimmun. 2023 Sep;139:103089. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2023.103089. Epub 2023 Jul 26. J Autoimmun. 2023. PMID: 37506491 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide DNA Methylation Analysis of Chinese Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Identified Hypomethylation in Genes Related to the Type I Interferon Pathway.PLoS One. 2017 Jan 13;12(1):e0169553. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0169553. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28085900 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic Variability in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: What We Learned from Genome-Wide DNA Methylation Studies.Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2017 Jun;19(6):32. doi: 10.1007/s11926-017-0657-5. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2017. PMID: 28470479 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impaired DNA methylation and its mechanisms in CD4(+)T cells of systemic lupus erythematosus.J Autoimmun. 2013 Mar;41:92-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2013.01.005. Epub 2013 Jan 20. J Autoimmun. 2013. PMID: 23340289 Review.
Cited by
-
The role of epigenetics in childhood autoimmune diseases with hematological manifestations.Pediatr Investig. 2022 Feb 21;6(1):36-46. doi: 10.1002/ped4.12309. eCollection 2022 Mar. Pediatr Investig. 2022. PMID: 35382418 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CeDAR: incorporating cell type hierarchy improves cell type-specific differential analyses in bulk omics data.Genome Biol. 2023 Feb 28;24(1):37. doi: 10.1186/s13059-023-02857-5. Genome Biol. 2023. PMID: 36855165 Free PMC article.
-
Disease Activity-Associated Alteration of mRNA m5 C Methylation in CD4+ T Cells of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Jun 5;8:430. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.00430. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 32582707 Free PMC article.
-
Exploration of Potential Integrated Models of N6-Methyladenosine Immunity in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus by Bioinformatic Analyses.Front Immunol. 2022 Feb 7;12:752736. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.752736. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35197962 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Epigenetics in Autoimmune/Inflammatory Disease.Front Immunol. 2019 Jul 4;10:1525. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01525. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31333659 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wakeland EK, Liu K, Graham RR, et al. Delineating the genetic basis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Immunity. 2001. September;15(3):397–408. - PubMed
-
- Ward MM, Polisson RP.. A meta-analysis of the clinical manifestations of older-onset systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1989. October;32(10):1226–1232. - PubMed
-
- Stichweh D, Arce E, Pascual V.. Update on pediatric systemic lupus erythematosus. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2004. September;16(5):577–587. - PubMed
-
- Kamphuis S, Silverman ED. Prevalence and burden of pediatric-onset systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2010. September;6(9):538–546. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
