Transcriptional profiling at the DLK1/MEG3 domain explains clinical overlap between imprinting disorders
- PMID: 30801013
- PMCID: PMC6382400
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.aau9425
Transcriptional profiling at the DLK1/MEG3 domain explains clinical overlap between imprinting disorders
Abstract
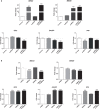
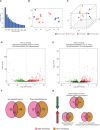
Imprinting disorders (IDs) often affect growth in humans, leading to diseases with overlapping features, regardless of the genomic region affected. IDs related to hypomethylation of the human 14q32.2 region and its DLK1/MEG3 domain are associated with Temple syndrome (TS14). TS14 is a rare type of growth retardation, the clinical signs of which overlap considerably with those of Silver-Russell syndrome (SRS), another ID related to IGF2 down-regulation at 11p15.5 region. We show that 14q32.2 hypomethylation affects expression, not only for genes at this locus but also for other imprinted genes, and especially lowers IGF2 levels at 11p15.5. Furthermore, expression of nonimprinted genes is also affected, some of which are also deregulated in SRS patients. These findings highlight the epigenetic regulation of gene expression at the DLK1/MEG3 domain. Expression profiling of TS14 and SRS patients highlights common signatures, which may account for the clinical overlap observed between TS14 and SRS.
Figures


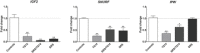
Similar articles
-
Epimutations of the IG-DMR and the MEG3-DMR at the 14q32.2 imprinted region in two patients with Silver-Russell Syndrome-compatible phenotype.Eur J Hum Genet. 2015 Aug;23(8):1062-7. doi: 10.1038/ejhg.2014.234. Epub 2014 Nov 5. Eur J Hum Genet. 2015. PMID: 25351781 Free PMC article.
-
Chromosome 14q32.2 Imprinted Region Disruption as an Alternative Molecular Diagnosis of Silver-Russell Syndrome.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2018 Jul 1;103(7):2436-2446. doi: 10.1210/jc.2017-02152. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2018. PMID: 29659920
-
Novel 14q32.2 paternal deletion encompassing the whole DLK1 gene associated with Temple syndrome.Clin Epigenetics. 2024 May 7;16(1):62. doi: 10.1186/s13148-024-01652-8. Clin Epigenetics. 2024. PMID: 38715103 Free PMC article.
-
New developments in Silver-Russell syndrome and implications for clinical practice.Epigenomics. 2016 Apr;8(4):563-80. doi: 10.2217/epi-2015-0010. Epub 2016 Apr 12. Epigenomics. 2016. PMID: 27066913 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Silver-Russell syndrome: genetic basis and molecular genetic testing.Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2010 Jun 23;5:19. doi: 10.1186/1750-1172-5-19. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2010. PMID: 20573229 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pregnancy Serum DLK1 Concentrations Are Associated With Indices of Insulin Resistance and Secretion.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2021 May 13;106(6):e2413-e2422. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgab123. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2021. PMID: 33640968 Free PMC article.
-
Familial central precocious puberty due to DLK1 deficiency: novel genetic findings and relevance of serum DLK1 levels.Eur J Endocrinol. 2023 Sep 1;189(3):422-428. doi: 10.1093/ejendo/lvad129. Eur J Endocrinol. 2023. PMID: 37703313 Free PMC article.
-
Pioneering studies on monogenic central precocious puberty.Arch Endocrinol Metab. 2019 Aug 22;63(4):438-444. doi: 10.20945/2359-3997000000164. Arch Endocrinol Metab. 2019. PMID: 31460623 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functional characterization of DLK1/MEG3 locus on chromosome 14q32.2 reveals the differentiation of pituitary neuroendocrine tumors.Aging (Albany NY). 2020 Dec 29;13(1):1422-1439. doi: 10.18632/aging.202376. Epub 2020 Dec 29. Aging (Albany NY). 2020. PMID: 33472171 Free PMC article.
-
Imprinted Long Non-Coding RNAs in Mammalian Development and Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Sep 4;24(17):13647. doi: 10.3390/ijms241713647. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37686455 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Eggermann T., Perez de Nanclares G., Maher E. R., Temple I. K., Tümer Z., Monk D., Mackay D. J. G., Grønskov K., Riccio A., Linglart A., Netchine I., Imprinting disorders: A group of congenital disorders with overlapping patterns of molecular changes affecting imprinted loci. Clin. Epigenetics 7, 123 (2015). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gabory A., Ripoche M.-A., Le Digarcher A., Watrin F., Ziyyat A., Forné T., Jammes H., Ainscough J. F. X., Surani M. A., Journot L., Dandolo L., H19 acts as a trans regulator of the imprinted gene network controlling growth in mice. Development 136, 3413–3421 (2009). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

