COPII vesicles contribute to autophagosomal membranes
- PMID: 30787039
- PMCID: PMC6504894
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.201809032
COPII vesicles contribute to autophagosomal membranes
Abstract
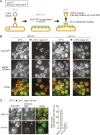
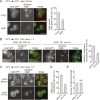
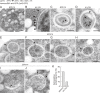
A hallmark of autophagy is the de novo formation of double-membrane vesicles called autophagosomes, which sequester various cellular constituents for degradation in lysosomes or vacuoles. The membrane dynamics underlying the biogenesis of autophagosomes, including the origin of the autophagosomal membrane, are still elusive. Although previous studies suggested that COPII vesicles are closely associated with autophagosome biogenesis, it remains unclear whether these vesicles serve as a source of the autophagosomal membrane. Using a recently developed COPII vesicle-labeling system in fluorescence and immunoelectron microscopy in the budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae, we show that the transmembrane cargo Axl2 is loaded into COPII vesicles in the ER. Axl2 is then transferred to autophagosome intermediates, ultimately becoming part of autophagosomal membranes. This study provides a definitive answer to a long-standing, fundamental question regarding the mechanisms of autophagosome formation by implicating COPII vesicles as a membrane source for autophagosomes.
© 2019 Shima et al.
Figures
Similar articles
-
An ER-Localized SNARE Protein Is Exported in Specific COPII Vesicles for Autophagosome Biogenesis.Cell Rep. 2016 Feb 23;14(7):1710-1722. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2016.01.047. Epub 2016 Feb 11. Cell Rep. 2016. PMID: 26876173
-
ER exit sites are physical and functional core autophagosome biogenesis components.Mol Biol Cell. 2013 Sep;24(18):2918-31. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E13-07-0381. Epub 2013 Jul 31. Mol Biol Cell. 2013. PMID: 23904270 Free PMC article.
-
A SNARE and specific COPII requirements define ER-derived vesicles for the biogenesis of autophagosomes.Autophagy. 2016 Jun 2;12(6):1049-50. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2016.1164368. Epub 2016 Apr 28. Autophagy. 2016. PMID: 27124469 Free PMC article.
-
Autophagic degradation of the endoplasmic reticulum.Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci. 2020;96(1):1-9. doi: 10.2183/pjab.96.001. Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci. 2020. PMID: 31932525 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms of COPII vesicle formation and protein sorting.FEBS Lett. 2007 May 22;581(11):2076-82. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2007.01.091. Epub 2007 Feb 14. FEBS Lett. 2007. PMID: 17316621 Review.
Cited by
-
Autophagy in Its (Proper) Context: Molecular Basis, Biological Relevance, Pharmacological Modulation, and Lifestyle Medicine.Int J Biol Sci. 2024 Apr 22;20(7):2532-2554. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.95122. eCollection 2024. Int J Biol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38725847 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Parallel phospholipid transfer by Vps13 and Atg2 determines autophagosome biogenesis dynamics.J Cell Biol. 2023 Jul 3;222(7):e202211039. doi: 10.1083/jcb.202211039. Epub 2023 Apr 28. J Cell Biol. 2023. PMID: 37115156 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprogenitor Cells From Patients With TBCK Encephalopathy Suggest Deregulation of Early Secretory Vesicle Transport.Front Cell Neurosci. 2022 Jan 13;15:803302. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2021.803302. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35095425 Free PMC article.
-
Autophagosome biogenesis: From membrane growth to closure.J Cell Biol. 2020 Jun 1;219(6):e202002085. doi: 10.1083/jcb.202002085. J Cell Biol. 2020. PMID: 32357219 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms governing autophagosome biogenesis.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2020 Aug;21(8):439-458. doi: 10.1038/s41580-020-0241-0. Epub 2020 May 5. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2020. PMID: 32372019 Review.
References
-
- Axe E.L., Walker S.A., Manifava M., Chandra P., Roderick H.L., Habermann A., Griffiths G., and Ktistakis N.T.. 2008. Autophagosome formation from membrane compartments enriched in phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate and dynamically connected to the endoplasmic reticulum. J. Cell Biol. 182:685–701. 10.1083/jcb.200803137 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

