Subsets of exhausted CD8+ T cells differentially mediate tumor control and respond to checkpoint blockade
- PMID: 30778252
- PMCID: PMC6673650
- DOI: 10.1038/s41590-019-0312-6
Subsets of exhausted CD8+ T cells differentially mediate tumor control and respond to checkpoint blockade
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Subsets of exhausted CD8+ T cells differentially mediate tumor control and respond to checkpoint blockade.Nat Immunol. 2019 Nov;20(11):1556. doi: 10.1038/s41590-019-0528-5. Nat Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31582823 Free PMC article.
Abstract
T cell dysfunction is a hallmark of many cancers, but the basis for T cell dysfunction and the mechanisms by which antibody blockade of the inhibitory receptor PD-1 (anti-PD-1) reinvigorates T cells are not fully understood. Here we show that such therapy acts on a specific subpopulation of exhausted CD8+ tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs). Dysfunctional CD8+ TILs possess canonical epigenetic and transcriptional features of exhaustion that mirror those seen in chronic viral infection. Exhausted CD8+ TILs include a subpopulation of 'progenitor exhausted' cells that retain polyfunctionality, persist long term and differentiate into 'terminally exhausted' TILs. Consequently, progenitor exhausted CD8+ TILs are better able to control tumor growth than are terminally exhausted T cells. Progenitor exhausted TILs can respond to anti-PD-1 therapy, but terminally exhausted TILs cannot. Patients with melanoma who have a higher percentage of progenitor exhausted cells experience a longer duration of response to checkpoint-blockade therapy. Thus, approaches to expand the population of progenitor exhausted CD8+ T cells might be an important component of improving the response to checkpoint blockade.
Figures

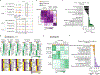
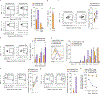


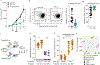
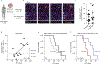
Comment in
-
States of exhaustion.Nat Rev Cancer. 2019 Apr;19(4):185. doi: 10.1038/s41568-019-0129-5. Nat Rev Cancer. 2019. PMID: 30846872 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Intratumoral Tcf1+PD-1+CD8+ T Cells with Stem-like Properties Promote Tumor Control in Response to Vaccination and Checkpoint Blockade Immunotherapy.Immunity. 2019 Jan 15;50(1):195-211.e10. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2018.12.021. Epub 2019 Jan 8. Immunity. 2019. PMID: 30635237
-
PD-L1 Checkpoint Inhibition Narrows the Antigen-Specific T Cell Receptor Repertoire in Chronic Lymphocytic Choriomeningitis Virus Infection.J Virol. 2020 Aug 31;94(18):e00795-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00795-20. Print 2020 Aug 31. J Virol. 2020. PMID: 32641478 Free PMC article.
-
TOX-expressing terminally exhausted tumor-infiltrating CD8+ T cells are reinvigorated by co-blockade of PD-1 and TIGIT in bladder cancer.Cancer Lett. 2021 Feb 28;499:137-147. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2020.11.035. Epub 2020 Nov 27. Cancer Lett. 2021. PMID: 33249194
-
CD8 T Cell Exhaustion in Chronic Infection and Cancer: Opportunities for Interventions.Annu Rev Med. 2018 Jan 29;69:301-318. doi: 10.1146/annurev-med-012017-043208. Annu Rev Med. 2018. PMID: 29414259 Review.
-
Significance of evaluating tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) and programmed cell death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression in breast cancer.Med Mol Morphol. 2017 Dec;50(4):185-194. doi: 10.1007/s00795-017-0170-y. Epub 2017 Sep 21. Med Mol Morphol. 2017. PMID: 28936553 Review.
Cited by
-
Taurine enhances the antitumor efficacy of PD-1 antibody by boosting CD8+ T cell function.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2023 Apr;72(4):1015-1027. doi: 10.1007/s00262-022-03308-z. Epub 2022 Oct 20. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2023. PMID: 36261540 Free PMC article.
-
Clonal lineage tracing reveals mechanisms skewing CD8+ T cell fate decisions in chronic infection.J Exp Med. 2023 Jan 2;220(1):e20220679. doi: 10.1084/jem.20220679. Epub 2022 Oct 31. J Exp Med. 2023. PMID: 36315049 Free PMC article.
-
Unraveling temporal and spatial biomarkers of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in colorectal cancer: insights into the crucial role of immunosuppressive cells.J Transl Med. 2023 Nov 8;21(1):794. doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-04600-x. J Transl Med. 2023. PMID: 37940972 Free PMC article.
-
Reprogramming the anti-tumor immune response via CRISPR genetic and epigenetic editing.Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2021 Apr 24;21:592-606. doi: 10.1016/j.omtm.2021.04.009. eCollection 2021 Jun 11. Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2021. PMID: 34095343 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immune Regulation in Time and Space: The Role of Local- and Long-Range Genomic Interactions in Regulating Immune Responses.Front Immunol. 2021 May 11;12:662565. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.662565. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34046034 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

