Cancer-associated fibroblasts induce epithelial-mesenchymal transition of bladder cancer cells through paracrine IL-6 signalling
- PMID: 30744595
- PMCID: PMC6371428
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-019-5353-6
Cancer-associated fibroblasts induce epithelial-mesenchymal transition of bladder cancer cells through paracrine IL-6 signalling
Abstract
Background: Cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs), activated by tumour cells, are the predominant type of stromal cells in cancer tissue and play an important role in interacting with neoplastic cells to promote cancer progression. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) is a key feature of metastatic cells. However, the mechanism by which CAFs induce EMT program in bladder cancer cells remains unclear.
Methods: To investigate the role of CAFs in bladder cancer progression, healthy primary bladder fibroblasts (HFs) were induced into CAFs (iCAFs) by bladder cancer-derived exosomes. Effect of conditioned medium from iCAFs (CM iCAF) on EMT markers expression of non-invasive RT4 bladder cancer cell line was determined by qPCR and Western blot. IL6 expression in iCAFs was evaluated by ELISA and Western blot. RT4 cell proliferation, migration and invasion were assessed in CM iCAF +/- anti-IL6 neutralizing antibody using cyQUANT assay, scratch test and transwell chamber respectively. We investigated IL6 expression relevance for bladder cancer progression by querying gene expression datasets of human bladder cancer specimens from TCGA and GEO genomic data platforms.
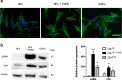
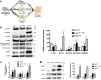
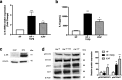
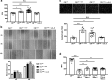
Results: Cancer exosome-treated HFs showed CAFs characteristics with high expression levels of αSMA and FAP. We showed that the CM iCAF induces the upregulation of mesenchymal markers, such as N-cadherin and vimentin, while repressing epithelial markers E-cadherin and p-ß-catenin expression in non-invasive RT4 cells. Moreover, EMT transcription factors SNAIL1, TWIST1 and ZEB1 were upregulated in CM iCAF-cultured RT4 cells compared to control. We also showed that the IL-6 cytokine was highly expressed by CAFs, and its receptor IL-6R was found on RT4 bladder cancer cells. The culture of RT4 bladder cancer cells with CM iCAF resulted in markedly promoted cell growth, migration and invasion. Importantly, inhibition of CAFs-secreted IL-6 by neutralizing antibody significantly reversed the IL-6-induced EMT phenotype, suggesting that this cytokine is necessary for CAF-induced EMT in the progression of human bladder cancer. Finally, we observed that IL6 expression is up-regulated in aggressive bladder cancer and correlate with CAF marker ACTA2.
Conclusions: We conclude that CAFs promote aggressive phenotypes of non-invasive bladder cancer cells through an EMT induced by the secretion of IL-6.
Keywords: Bladder cancer; CAFs; EMT; IL-6.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Bladder biopsies from paediatric patients undergoing non-oncologic urologic surgery were obtained at the CHU de Québec-Université Laval Research Center in accordance with the institutional review board. All legal guardians of donors provided their formal, informed and written consent, each agreeing to supply a biopsy for this study.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
Frédéric Pouliot has received speaker’s bureau honoraria from Sanofi, Genzyme, Amgen, Astellas, and Janssen; he is a consultant/advisory board member of Sanofi, Abbvie, Astellas, Janssen, Genzyme and Roche. No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed by the other authors.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[SP13786 Inhibits the Migration and Invasion of Lung Adenocarcinoma Cell A549 by Supressing Stat3-EMT via CAFs Exosomes].Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2021 Jun 20;24(6):384-393. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2021.104.07. Epub 2021 May 24. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2021. PMID: 34024061 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Snail1-dependent cancer-associated fibroblasts induce epithelial-mesenchymal transition in lung cancer cells via exosomes.QJM. 2019 Aug 1;112(8):581-590. doi: 10.1093/qjmed/hcz093. QJM. 2019. PMID: 31106370
-
TGF-β1 dominates stromal fibroblast-mediated EMT via the FAP/VCAN axis in bladder cancer cells.J Transl Med. 2023 Jul 17;21(1):475. doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-04303-3. J Transl Med. 2023. PMID: 37461061 Free PMC article.
-
The role of CAF derived exosomal microRNAs in the tumour microenvironment of melanoma.Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2021 Jan;1875(1):188456. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2020.188456. Epub 2020 Oct 22. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33153973 Review.
-
Cancer-associated fibroblasts: a versatile mediator in tumor progression, metastasis, and targeted therapy.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2024 Sep;43(3):1095-1116. doi: 10.1007/s10555-024-10186-7. Epub 2024 Apr 11. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2024. PMID: 38602594 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Immuno-Surgical Management of Pancreatic Cancer with Analysis of Cancer Exosomes.Cells. 2020 Jul 9;9(7):1645. doi: 10.3390/cells9071645. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32659892 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tumor microenvironment and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in bladder cancer: Cytokines in the game?Front Mol Biosci. 2023 Jan 9;9:1070383. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.1070383. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Biosci. 2023. PMID: 36699696 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exosomes Regulate the Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Cancer.Front Oncol. 2022 Mar 14;12:864980. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.864980. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35359397 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comprehensive bioinformatic analysis reveals a cancer-associated fibroblast gene signature as a poor prognostic factor and potential therapeutic target in gastric cancer.BMC Cancer. 2022 Jun 23;22(1):692. doi: 10.1186/s12885-022-09736-5. BMC Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35739492 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of Cisplatin Resistance in HPV Negative Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinomas.Cells. 2022 Feb 5;11(3):561. doi: 10.3390/cells11030561. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35159370 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Pugashetti N, Alibhai SMH, Yap SA. Non-muscle-invasive bladder Cancer: review of diagnosis and management. J Curr Clin Care. 2015;5:40–50.
-
- Kamat AM, M Hahn N, A Efstathiou J, P Lerner S, Malmstrom P-U, Choi W, et al. Bladder cancer. The lancet. Elsevier Ltd. 2016;388:2796–2810. - PubMed
-
- Sanli O, Dobruch J, Knowles MA, Burger M, Alemozaffar M, Nielsen ME, et al. Bladder cancer. Nature Publishing Group Macmillan Publishers Limited. 2017;3:1–19. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

