Genomic instability at the locus of sterol C24-methyltransferase promotes amphotericin B resistance in Leishmania parasites
- PMID: 30716073
- PMCID: PMC6375703
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0007052
Genomic instability at the locus of sterol C24-methyltransferase promotes amphotericin B resistance in Leishmania parasites
Abstract
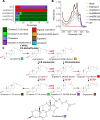
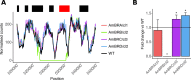
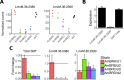
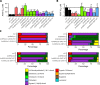
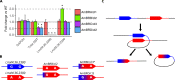
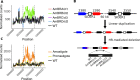
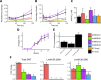
Amphotericin B is an increasingly important tool in efforts to reduce the global disease burden posed by Leishmania parasites. With few other chemotherapeutic options available for the treatment of leishmaniasis, the potential for emergent resistance to this drug is a considerable threat. Here we characterised four novel amphotericin B-resistant Leishmania mexicana lines. All lines exhibited altered sterol biosynthesis, and hypersensitivity to pentamidine. Whole genome sequencing demonstrated resistance-associated mutation of the sterol biosynthesis gene sterol C5-desaturase in one line. However, in three out of four lines, RNA-seq revealed loss of expression of sterol C24-methyltransferase (SMT) responsible for drug resistance and altered sterol biosynthesis. Additional loss of the miltefosine transporter was associated with one of those lines. SMT is encoded by two tandem gene copies, which we found to have very different expression levels. In all cases, reduced overall expression was associated with loss of the 3' untranslated region of the dominant gene copy, resulting from structural variations at this locus. Local regions of sequence homology, between the gene copies themselves, and also due to the presence of SIDER1 retrotransposon elements that promote multi-gene amplification, correlate to these structural variations. Moreover, in at least one case loss of SMT expression was not associated with loss of virulence in primary macrophages or in vivo. Whilst such repeat sequence-mediated instability is known in Leishmania genomes, its presence associated with resistance to a major antileishmanial drug, with no evidence of associated fitness costs, is a significant concern.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sterol 14α-demethylase mutation leads to amphotericin B resistance in Leishmania mexicana.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2017 Jun 16;11(6):e0005649. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0005649. eCollection 2017 Jun. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2017. PMID: 28622334 Free PMC article.
-
Amphotericin B resistance in Leishmania mexicana: Alterations to sterol metabolism and oxidative stress response.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2022 Sep 28;16(9):e0010779. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0010779. eCollection 2022 Sep. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2022. PMID: 36170238 Free PMC article.
-
Lathosterol Oxidase (Sterol C-5 Desaturase) Deletion Confers Resistance to Amphotericin B and Sensitivity to Acidic Stress in Leishmania major.mSphere. 2020 Jul 1;5(4):e00380-20. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00380-20. mSphere. 2020. PMID: 32611698 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Genetic Diversity and Genome Plasticity of Leishmania spp. in Treatment and the Search for Novel Chemotherapeutic Targets.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Jan 24;12:826287. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.826287. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35141175 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Limitations of Current Therapeutic Options, Possible Drug Targets and Scope of Natural Products in Control of Leishmaniasis.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2018;18(1):26-41. doi: 10.2174/1389557517666170425105129. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 28443518 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular Mechanisms of Drug Resistance in Leishmania spp.Pathogens. 2024 Sep 27;13(10):835. doi: 10.3390/pathogens13100835. Pathogens. 2024. PMID: 39452707 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sterol 14-alpha demethylase (CYP51) activity in Leishmania donovani is likely dependent upon cytochrome P450 reductase 1.PLoS Pathog. 2024 Jul 11;20(7):e1012382. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1012382. eCollection 2024 Jul. PLoS Pathog. 2024. PMID: 38991025 Free PMC article.
-
Amphotericin B resistance in Leishmania amazonensis: In vitro and in vivo characterization of a Brazilian clinical isolate.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2024 May 20;18(5):e0012175. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0012175. eCollection 2024 May. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2024. PMID: 38768213 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic Insight of Leishmania Parasite: In-Depth Review of Drug Resistance Mechanisms and Genetic Mutations.ACS Omega. 2024 Mar 8;9(11):12500-12514. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c09400. eCollection 2024 Mar 19. ACS Omega. 2024. PMID: 38524425 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In vitro susceptibility to miltefosine of amphotericin B-resistant Leishmania (Mundinia) martiniquensis.Parasitol Res. 2023 Dec;122(12):3027-3035. doi: 10.1007/s00436-023-07992-3. Epub 2023 Oct 5. Parasitol Res. 2023. PMID: 37796293
References
-
- Sundar S, More DK, Singh MK, Singh VP, Sharma S, Makharia A, et al. Failure of pentavalent antimony in visceral leishmaniasis in India: report from the center. 2000;31(2):1104–1107. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

