TAZ couples Hippo/Wnt signalling and insulin sensitivity through Irs1 expression
- PMID: 30679431
- PMCID: PMC6345998
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-019-08287-x
TAZ couples Hippo/Wnt signalling and insulin sensitivity through Irs1 expression
Abstract
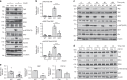
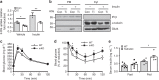
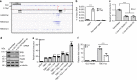
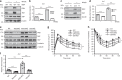
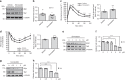
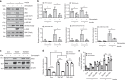
Insulin regulates blood glucose levels by binding its receptor and stimulating downstream proteins through the insulin receptor substrate (IRS). Impaired insulin signalling leads to metabolic syndrome, but the regulation of this process is not well understood. Here, we describe a novel insulin signalling regulatory pathway involving TAZ. TAZ upregulates IRS1 and stimulates Akt- and Glut4-mediated glucose uptake in muscle cells. Muscle-specific TAZ-knockout mice shows significantly decreased Irs1 expression and insulin sensitivity. Furthermore, TAZ is required for Wnt signalling-induced Irs1 expression, as observed by decreased Irs1 expression and insulin sensitivity in muscle-specific APC- and TAZ-double-knockout mice. TAZ physically interacts with c-Jun and Tead4 to induce Irs1 transcription. Finally, statin administration decreases TAZ, IRS1 level and insulin sensitivity. However, in myoblasts, the statin-mediated decrease in insulin sensitivity is counteracted by the expression of a constitutively active TAZ mutant. These results suggest that TAZ is a novel insulin signalling activator that increases insulin sensitivity and couples Hippo/Wnt signalling and insulin sensitivity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Nexilin, a cardiomyopathy-associated F-actin binding protein, binds and regulates IRS1 signaling in skeletal muscle cells.PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e55634. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0055634. Epub 2013 Jan 30. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23383252 Free PMC article.
-
Over-expression of NYGGF4 (PID1) inhibits glucose transport in skeletal myotubes by blocking the IRS1/PI3K/AKT insulin pathway.Mol Genet Metab. 2011 Mar;102(3):374-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2010.11.165. Epub 2010 Dec 13. Mol Genet Metab. 2011. PMID: 21185755
-
TAZ enhances mammary cell proliferation in 3D culture through transcriptional regulation of IRS1.Cell Signal. 2018 Dec;52:12-22. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2018.08.012. Epub 2018 Aug 20. Cell Signal. 2018. PMID: 30138697
-
Divergent Roles of IRS (Insulin Receptor Substrate) 1 and 2 in Liver and Skeletal Muscle.Curr Med Chem. 2017;24(17):1827-1852. doi: 10.2174/0929867324666170426142826. Curr Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 28462703 Review.
-
Regulation of insulin sensitivity by serine/threonine phosphorylation of insulin receptor substrate proteins IRS1 and IRS2.Diabetologia. 2012 Oct;55(10):2565-2582. doi: 10.1007/s00125-012-2644-8. Epub 2012 Aug 8. Diabetologia. 2012. PMID: 22869320 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Danggui Shaoyao San Alleviates Early Cognitive Impairment in Alzheimer's Disease Mice Through IRS1/GSK3β/Wnt3a-β-Catenin Pathway.Brain Behav. 2024 Oct;14(10):e70056. doi: 10.1002/brb3.70056. Brain Behav. 2024. PMID: 39344343 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelial TAZ inhibits capillarization of liver sinusoidal endothelium and damage-induced liver fibrosis via nitric oxide production.Theranostics. 2023 Jul 16;13(12):4182-4196. doi: 10.7150/thno.83714. eCollection 2023. Theranostics. 2023. PMID: 37554269 Free PMC article.
-
CTGF-D4 Amplifies LRP6 Signaling to Promote Grafts of Adult Epicardial-derived Cells That Improve Cardiac Function After Myocardial Infarction.Stem Cells. 2022 Mar 16;40(2):204-214. doi: 10.1093/stmcls/sxab016. Stem Cells. 2022. PMID: 35257185 Free PMC article.
-
TAZ deficiency exacerbates psoriatic pathogenesis by increasing the histamine-releasing factor.Cell Biosci. 2024 May 11;14(1):60. doi: 10.1186/s13578-024-01246-0. Cell Biosci. 2024. PMID: 38734624 Free PMC article.
-
Dysfunctional Mechanotransduction through the YAP/TAZ/Hippo Pathway as a Feature of Chronic Disease.Cells. 2020 Jan 8;9(1):151. doi: 10.3390/cells9010151. Cells. 2020. PMID: 31936297 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

