PRMT5 is essential for B cell development and germinal center dynamics
- PMID: 30604754
- PMCID: PMC6318318
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-018-07884-6
PRMT5 is essential for B cell development and germinal center dynamics
Abstract
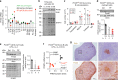
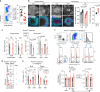
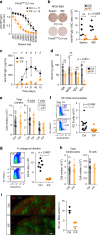
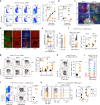
Mechanisms regulating B cell development, activation, education in the germinal center (GC) and differentiation, underpin the humoral immune response. Protein arginine methyltransferase 5 (Prmt5), which catalyzes most symmetric dimethyl arginine protein modifications, is overexpressed in B cell lymphomas but its function in normal B cells is poorly defined. Here we show that Prmt5 is necessary for antibody responses and has essential but distinct functions in all proliferative B cell stages in mice. Prmt5 is necessary for B cell development by preventing p53-dependent and p53-independent blocks in Pro-B and Pre-B cells, respectively. By contrast, Prmt5 protects, via p53-independent pathways, mature B cells from apoptosis during activation, promotes GC expansion, and counters plasma cell differentiation. Phenotypic and RNA-seq data indicate that Prmt5 regulates GC light zone B cell fate by regulating transcriptional programs, achieved in part by ensuring RNA splicing fidelity. Our results establish Prmt5 as an essential regulator of B cell biology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
PRMT5 interacts with the BCL6 oncoprotein and is required for germinal center formation and lymphoma cell survival.Blood. 2018 Nov 8;132(19):2026-2039. doi: 10.1182/blood-2018-02-831438. Epub 2018 Aug 6. Blood. 2018. PMID: 30082494 Free PMC article.
-
The protein arginine methyltransferase PRMT5 regulates Aβ-induced toxicity in human cells and Caenorhabditis elegans models of Alzheimer's disease.J Neurochem. 2015 Sep;134(5):969-77. doi: 10.1111/jnc.13191. Epub 2015 Jul 15. J Neurochem. 2015. PMID: 26086249
-
Protective Humoral Immunity in the Central Nervous System Requires Peripheral CD19-Dependent Germinal Center Formation following Coronavirus Encephalomyelitis.J Virol. 2017 Nov 14;91(23):e01352-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01352-17. Print 2017 Dec 1. J Virol. 2017. PMID: 28931676 Free PMC article.
-
Compartments and Connections Within the Germinal Center.Front Immunol. 2021 Mar 31;12:659151. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.659151. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33868306 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The germinal center response.Crit Rev Immunol. 2004;24(1):39-65. doi: 10.1615/critrevimmunol.v24.i1.20. Crit Rev Immunol. 2004. PMID: 14995913 Review.
Cited by
-
Dysregulation of epigenetic modifications in inborn errors of immunity.Epigenomics. 2024;16(19-20):1301-1313. doi: 10.1080/17501911.2024.2410695. Epub 2024 Oct 15. Epigenomics. 2024. PMID: 39404224 Review.
-
Protein Arginine Methyltransferase 5 in T Lymphocyte Biology.Trends Immunol. 2020 Oct;41(10):918-931. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2020.08.007. Epub 2020 Sep 2. Trends Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32888819 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Structure and Functions of PRMT5 in Human Diseases.Life (Basel). 2021 Oct 12;11(10):1074. doi: 10.3390/life11101074. Life (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34685445 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PRMT5-dependent transcriptional repression of c-Myc target genes promotes gastric cancer progression.Theranostics. 2020 Mar 15;10(10):4437-4452. doi: 10.7150/thno.42047. eCollection 2020. Theranostics. 2020. PMID: 32292506 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Protein Methyltransferases in Immunity.Molecules. 2024 Jan 11;29(2):360. doi: 10.3390/molecules29020360. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38257273 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

