The Yin and Yang of Myeloid Derived Suppressor Cells
- PMID: 30555467
- PMCID: PMC6280921
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02776
The Yin and Yang of Myeloid Derived Suppressor Cells
Abstract
In recent years, most of our knowledge about myeloid derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) has come from cancer studies, which depicts Yin side of MDSCs. In cancer, inherent immunosuppressive action of MDSCs favors tumor progression by inhibiting antitumor immune response. However, recently Yang side of MDSCs has also been worked out and suggests the role in maintenance of homeostasis during non-cancer situations like pregnancy, obesity, diabetes, and autoimmune disorders. Continued work in this area has armored the biological importance of these cells as master regulators of immune system and prompted scientists all over the world to look from a different perspective. Therefore, explicating Yin and Yang arms of MDSCs is obligatory to use it as a double edged sword in a much smarter way. This review is an attempt toward presenting a synergistic coalition of all the facts and controversies that exist in understanding MDSCs, bring them on the same platform and approach their "Yin and Yang" nature in a more comprehensive and coherent manner.
Keywords: epigenetics; homeostasis; immune regulation; immunosuppression; myeloid derived suppressor cells.
Figures
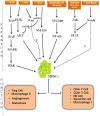
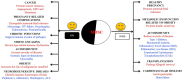
Similar articles
-
Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells: Not Only in Tumor Immunity.Front Immunol. 2019 May 15;10:1099. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01099. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31156644 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dual roles of myeloid-derived suppressor cells in various diseases: a review.Arch Pharm Res. 2024 Jul;47(7):597-616. doi: 10.1007/s12272-024-01504-2. Epub 2024 Jul 15. Arch Pharm Res. 2024. PMID: 39008186 Review.
-
Roles of the Exosomes Derived From Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells in Tumor Immunity and Cancer Progression.Front Immunol. 2022 Jan 27;13:817942. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.817942. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35154134 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phenotypic and Functional Diversities of Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells in Autoimmune Diseases.Mediators Inflamm. 2018 Dec 23;2018:4316584. doi: 10.1155/2018/4316584. eCollection 2018. Mediators Inflamm. 2018. PMID: 30670926 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expansion and functions of myeloid-derived suppressor cells in the tumor microenvironment.Cancer Lett. 2016 Sep 28;380(1):253-6. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2015.10.022. Epub 2015 Oct 28. Cancer Lett. 2016. PMID: 26519756 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Myeloid Cells in Circulation and Tumor Microenvironment of Colorectal Cancer Patients with Early and Advanced Disease Stages.J Immunol Res. 2020 Jun 12;2020:9678168. doi: 10.1155/2020/9678168. eCollection 2020. J Immunol Res. 2020. PMID: 32626789 Free PMC article.
-
Myeloid-derived suppressor cells alleviate adverse ventricular remodeling after acute myocardial infarction.Mol Cell Biochem. 2024 Sep 12. doi: 10.1007/s11010-024-05112-y. Online ahead of print. Mol Cell Biochem. 2024. PMID: 39264395
-
Immunomodulatory actions of myeloid-derived suppressor cells in the context of innate immunity.Innate Immun. 2024 Jan;30(1):2-10. doi: 10.1177/17534259231215581. Epub 2023 Nov 28. Innate Immun. 2024. PMID: 38018014 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gefitinib Results in Robust Host-Directed Immunity Against Salmonella Infection Through Proteo-Metabolomic Reprogramming.Front Immunol. 2021 Mar 31;12:648710. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.648710. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33868285 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells in Cancer Immunotherapy.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Sep 15;12(9):2626. doi: 10.3390/cancers12092626. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32942545 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Han S, Yang Y. Phenotypic and functional dissection of myeloid-derived suppressor cells. Appl Biol Chem. (2016) 59:367–71. 10.1007/s13765-016-0172-9 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

