Nuclear condensates of the Polycomb protein chromobox 2 (CBX2) assemble through phase separation
- PMID: 30514760
- PMCID: PMC6364756
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.006620
Nuclear condensates of the Polycomb protein chromobox 2 (CBX2) assemble through phase separation
Abstract
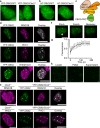
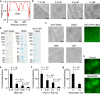
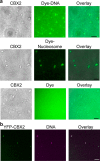
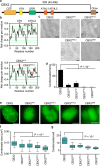
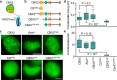
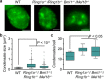
Polycomb group (PcG) proteins repress master regulators of development and differentiation through organization of chromatin structure. Mutation and dysregulation of PcG genes cause developmental defects and cancer. PcG proteins form condensates in the cell nucleus, and these condensates are the physical sites of PcG-targeted gene silencing via formation of facultative heterochromatin. However, the physiochemical principles underlying the formation of PcG condensates remain unknown, and their determination could shed light on how these condensates compact chromatin. Using fluorescence live-cell imaging, we observed that the Polycomb repressive complex 1 (PRC1) protein chromobox 2 (CBX2), a member of the CBX protein family, undergoes phase separation to form condensates and that the CBX2 condensates exhibit liquid-like properties. Using site-directed mutagenesis, we demonstrated that the conserved residues of CBX2 within the intrinsically disordered region (IDR), which is the region for compaction of chromatin in vitro, promote the condensate formation both in vitro and in vivo We showed that the CBX2 condensates concentrate DNA and nucleosomes. Using genetic engineering, we report that trimethylation of Lys-27 at histone H3 (H3K27me3), a marker of heterochromatin formation produced by PRC2, had minimal effects on the CBX2 condensate formation. We further demonstrated that the CBX2 condensate formation does not require CBX2-PRC1 subunits; however, the condensate formation of CBX2-PRC1 subunits depends on CBX2, suggesting a mechanism underlying the assembly of CBX2-PRC1 condensates. In summary, our results reveal that PcG condensates assemble through liquid-liquid phase separation (LLPS) and suggest that phase-separated condensates can organize PcG-bound chromatin.
Keywords: CBX2; PRC1; PcG; Polycomb; chromatin; chromatin modification; chromatin regulation; chromatin structure; epigenetics; gene regulation; heterochromatin; histone; histone methylation; liquid-liquid phase separation; phase separation.
© 2019 Tatavosian et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article
Figures
Similar articles
-
Phase-Separated Transcriptional Condensates Accelerate Target-Search Process Revealed by Live-Cell Single-Molecule Imaging.Cell Rep. 2020 Oct 13;33(2):108248. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2020.108248. Cell Rep. 2020. PMID: 33053359 Free PMC article.
-
Principles of assembly and regulation of condensates of Polycomb repressive complex 1 through phase separation.Cell Rep. 2023 Oct 31;42(10):113136. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2023.113136. Epub 2023 Sep 26. Cell Rep. 2023. PMID: 37756159 Free PMC article.
-
Sparse CBX2 nucleates many Polycomb proteins to promote facultative heterochromatinization of Polycomb target genes.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Feb 5:2024.02.05.578969. doi: 10.1101/2024.02.05.578969. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 38370615 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Biological functions of chromobox (CBX) proteins in stem cell self-renewal, lineage-commitment, cancer and development.Bone. 2021 Feb;143:115659. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2020.115659. Epub 2020 Sep 24. Bone. 2021. PMID: 32979540 Review.
-
Molecular architecture of polycomb repressive complexes.Biochem Soc Trans. 2017 Feb 8;45(1):193-205. doi: 10.1042/BST20160173. Biochem Soc Trans. 2017. PMID: 28202673 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Phase-Separated Transcriptional Condensates Accelerate Target-Search Process Revealed by Live-Cell Single-Molecule Imaging.Cell Rep. 2020 Oct 13;33(2):108248. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2020.108248. Cell Rep. 2020. PMID: 33053359 Free PMC article.
-
LLPSDB: a database of proteins undergoing liquid-liquid phase separation in vitro.Nucleic Acids Res. 2020 Jan 8;48(D1):D320-D327. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz778. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020. PMID: 31906602 Free PMC article.
-
The disordered C terminus of ALKBH5 promotes phase separation and paraspeckles assembly.J Biol Chem. 2023 Aug;299(8):105071. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2023.105071. Epub 2023 Jul 18. J Biol Chem. 2023. PMID: 37474102 Free PMC article.
-
Liquid-liquid phase separation of H3K27me3 reader BP1 regulates transcriptional repression.Genome Biol. 2024 Mar 11;25(1):67. doi: 10.1186/s13059-024-03209-7. Genome Biol. 2024. PMID: 38468348 Free PMC article.
-
Principles of 3D compartmentalization of the human genome.Cell Rep. 2021 Jun 29;35(13):109330. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109330. Cell Rep. 2021. PMID: 34192544 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brown S. W. (1966) Heterochromatin. Science 151, 417–425 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

