RNA m6 A modification enzymes shape innate responses to DNA by regulating interferon β
- PMID: 30463905
- PMCID: PMC6295168
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.319475.118
RNA m6 A modification enzymes shape innate responses to DNA by regulating interferon β
Abstract
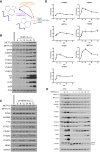
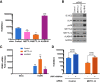
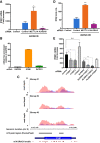
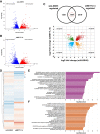
Modification of mRNA by N6-adenosine methylation (m6A) on internal bases influences gene expression in eukaryotes. How the dynamic genome-wide landscape of m6A-modified mRNAs impacts virus infection and host immune responses remains poorly understood. Here, we show that type I interferon (IFN) production triggered by dsDNA or human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) is controlled by the cellular m6A methyltrasferase subunit METTL14 and ALKBH5 demethylase. While METTL14 depletion reduced virus reproduction and stimulated dsDNA- or HCMV-induced IFNB1 mRNA accumulation, ALKBH5 depletion had the opposite effect. Depleting METTL14 increased both nascent IFNB1 mRNA production and stability in response to dsDNA. In contrast, ALKBH5 depletion reduced nascent IFNB1 mRNA production without detectably influencing IFN1B mRNA decay. Genome-wide transcriptome profiling following ALKBH5 depletion identified differentially expressed genes regulating antiviral immune responses, while METTL14 depletion altered pathways impacting metabolic reprogramming, stress responses, and aging. Finally, we determined that IFNB1 mRNA was m6A-modified within both the coding sequence and the 3' untranslated region (UTR). This establishes that the host m6A modification machinery controls IFNβ production triggered by HCMV or dsDNA. Moreover, it demonstrates that responses to nonmicrobial dsDNA in uninfected cells, which shape host immunity and contribute to autoimmune disease, are regulated by enzymes controlling m6A epitranscriptomic changes.
Keywords: RNA m6A modification; dsDNA signaling; human cytomegalovirus; innate immunity; virus infection.
© 2018 Rubio et al.; Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Restriction of Human Cytomegalovirus Replication by ISG15, a Host Effector Regulated by cGAS-STING Double-Stranded-DNA Sensing.J Virol. 2017 Apr 13;91(9):e02483-16. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02483-16. Print 2017 May 1. J Virol. 2017. PMID: 28202760 Free PMC article.
-
Ribosome biogenesis restricts innate immune responses to virus infection and DNA.Elife. 2019 Dec 16;8:e49551. doi: 10.7554/eLife.49551. Elife. 2019. PMID: 31841110 Free PMC article.
-
m6A modification impacts hepatic drug and lipid metabolism properties by regulating carboxylesterase 2.Biochem Pharmacol. 2021 Nov;193:114766. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2021.114766. Epub 2021 Sep 16. Biochem Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34536357
-
N (6)-Methyladenosine (m(6)A) Methylation in mRNA with A Dynamic and Reversible Epigenetic Modification.Mol Biotechnol. 2016 Jul;58(7):450-9. doi: 10.1007/s12033-016-9947-9. Mol Biotechnol. 2016. PMID: 27179969 Review.
-
The role of RNA adenosine demethylases in the control of gene expression.Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2019 Mar;1862(3):343-355. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2018.12.001. Epub 2018 Dec 11. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2019. PMID: 30550773 Review.
Cited by
-
The N6-methyladenosine RNA-binding protein YTHDF1 modulates the translation of TRAF6 to mediate the intestinal immune response.Nucleic Acids Res. 2021 Jun 4;49(10):5537-5552. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkab343. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021. PMID: 33999206 Free PMC article.
-
A multiomics dataset for the study of RNA modifications in human macrophage differentiation and polarisation.Sci Data. 2024 Feb 28;11(1):252. doi: 10.1038/s41597-024-03076-8. Sci Data. 2024. PMID: 38418823 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modification on immunity.Cell Commun Signal. 2022 Sep 9;20(1):140. doi: 10.1186/s12964-022-00939-8. Cell Commun Signal. 2022. PMID: 36085064 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNAs and RNA-Binding Proteins in Immuno-Metabolic Homeostasis and Diseases.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2019 Aug 20;6:106. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2019.00106. eCollection 2019. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2019. PMID: 31482095 Free PMC article. Review.
-
YTHDF2 Is Downregulated in Response to Host Shutoff Induced by DNA Virus Infection and Regulates Interferon-Stimulated Gene Expression.J Virol. 2023 Mar 30;97(3):e0175822. doi: 10.1128/jvi.01758-22. Epub 2023 Mar 14. J Virol. 2023. PMID: 36916936 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aguilo F, Zhang F, Sancho A, Fidalgo M, Di Cecilia S, Vashisht A, Lee DF, Chen CH, Rengasamy M, Andino B, et al. 2015. Coordination of m6A mRNA methylation and gene transcription by ZFP217 regulates pluripotency and reprogramming. Cell Stem Cell 17: 689–704. 10.1016/j.stem.2015.09.005 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Benboudjema L, Mulvey M, Gao Y, Pimplikar SW, Mohr I. 2003. Association of the herpes simplex virus type 1 Us11 gene product with the cellular kinesin light-chain related protein PAT1 results in the redistribution of both polypeptides. J Virol 77: 9192–9203. 10.1128/JVI.77.17.9192-9203.2003 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
