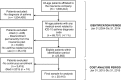
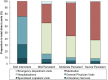
Health care costs and resource utilization for different asthma severity stages in Colombia: a claims data analysis
- PMID: 30459927
- PMCID: PMC6231276
- DOI: 10.1186/s40413-018-0205-4
Health care costs and resource utilization for different asthma severity stages in Colombia: a claims data analysis
Abstract
Background: Asthma is one of the most common chronic respiratory conditions worldwide. Asthma-related economic burden has been reported in Latin America, but knowledge about its economic impact to the Colombian health care system and the influence of disease severity is lacking. This study estimated direct medical costs and health care resource utilization (HCRU) in patients with asthma according to severity in Colombia.
Methods: This study identified all-age patients who had at least one medical event linked to an asthma diagnosis (CIE-10: J45-J46) between 2004 and 2014. Patients were selected if they had a continuous enrollment and uninterrupted insurance coverage between January 1-2015 and December 31-2015 and were categorized into 4 different severity levels using a modified algorithm based on Leidy criteria. Healthcare utilization and costs were estimated in a 1-year period after the identification period. A Generalized Linear Model (GLM) with gamma distribution and log link was used to analyze costs adjusting for patient demographics.
Results: A total of 20,410 patients were included: 69.5% had mild intermittent, 18.0% mild persistent, 6.9% moderate persistent and 5.5% severe persistent asthma; with mean costs (SD) of $67 (134), $482 (1506), $1061 (1983), $2235 (3426) respectively (p < 0.001). The mean total direct cost was estimated at $331 (1278) per patient. Medication and hospitalization had the higher proportion in total costs (46% and 31% respectively). General physician visits was the most used service (57.2%) and short-acting β-2 agonists the most used medication (24%).
Conclusions: Health services utilization and direct costs of asthma were highly related to disease severity. Nationwide health policies aimed at the effective control of asthma are necessary and would play an important role in reducing the associated economic impact.
Keywords: Asthma; Cost of illness; Health care costs; Health care utilization.
Conflict of interest statement
This study was approved by the Ethical Committee of the University of Cartagena (Minute 36, October 11th 2011).Not applicable.The authors declare that they have no competing interests.Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Economic Burden of Illness Among Patients with Severe Asthma in a Managed Care Setting.J Manag Care Spec Pharm. 2016 Jul;22(7):848-61. doi: 10.18553/jmcp.2016.22.7.848. J Manag Care Spec Pharm. 2016. PMID: 27348285 Free PMC article.
-
Economic burden in direct costs of concomitant chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and asthma in a Medicare Advantage population.J Manag Care Pharm. 2008 Mar;14(2):176-85. doi: 10.18553/jmcp.2008.14.2.176. J Manag Care Pharm. 2008. PMID: 18331119 Free PMC article.
-
Healthcare costs and resource utilization of asthma in Germany: a claims data analysis.Eur J Health Econ. 2016 Mar;17(2):195-201. doi: 10.1007/s10198-015-0671-3. Epub 2015 Feb 26. Eur J Health Econ. 2016. PMID: 25716136 Free PMC article.
-
The Economic Burden of Pediatric Asthma in the United States: Literature Review of Current Evidence.Pharmacoeconomics. 2019 Feb;37(2):155-167. doi: 10.1007/s40273-018-0726-2. Pharmacoeconomics. 2019. PMID: 30315512 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Asthma costs and social impact.Asthma Res Pract. 2017 Jan 6;3:1. doi: 10.1186/s40733-016-0029-3. eCollection 2017. Asthma Res Pract. 2017. PMID: 28078100 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cost-utility of tiotropium in patients with severe asthma.Cost Eff Resour Alloc. 2024 Jan 18;22(1):4. doi: 10.1186/s12962-023-00508-x. Cost Eff Resour Alloc. 2024. PMID: 38238836 Free PMC article.
-
Availability of secondary healthcare data for conducting pharmacoepidemiology studies in Colombia: A systematic review.Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2020 Oct;8(5):e00661. doi: 10.1002/prp2.661. Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2020. PMID: 32965783 Free PMC article.
-
Zero tolerance for asthma deaths in children.J Pediatr (Rio J). 2020 Jul-Aug;96(4):403-405. doi: 10.1016/j.jped.2019.07.002. Epub 2019 Jul 26. J Pediatr (Rio J). 2020. PMID: 31356764 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Cost-utility of triple versus dual inhaler therapy in moderate to severe asthma.BMC Pulm Med. 2021 Dec 5;21(1):398. doi: 10.1186/s12890-021-01777-z. BMC Pulm Med. 2021. PMID: 34865635 Free PMC article.
-
Asthma and cognitive dysfunction in older adults: the mediating role of systemic immune-inflammation index.Sci Rep. 2024 Nov 8;14(1):27194. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-76393-y. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39516478 Free PMC article.
References
-
- The Global Asthma Report 2014. Auckland, New Zealand: 2014.
-
- Hay S, Abajobir AA, Abate KH, et al. Global, regional, and national disability-adjusted life-years (DALYs) for 333 diseases and injuries and healthy life expectancy (HALE) for 195 countries and territories, 1990–2016: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2016. Lancet. 2017;390:1260–1344. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32130-X. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Soriano JB, Abajobir AA, Abate KH, et al. Global, regional, and national deaths, prevalence, disability-adjusted life years, and years lived with disability for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and asthma, 1990–2015: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2015. Lancet Respir Med. 2017;5:691–706. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(17)30293-X. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources